
Warmth and dust serve initiating Martian water into condominium, scientists safe
Scientists utilizing an instrument aboard NASA’s Mars Surroundings and Volatile EvolutioN, or MAVEN, spacecraft occupy realized that water vapor finish to the outside of the Crimson Planet is lofted greater into the atmosphere than somebody anticipated used to be that you are going to present you with the choice to take into accout of. There, it’s effortlessly destroyed by electrically charged fuel particles—or ions—and lost to accommodate.
Researchers said that the phenomenon they uncovered is one amongst loads of that has led Mars to lose the identical of a worldwide ocean of water up to tons of of feet (or up to tons of of meters) deep over billions of years. Reporting on their discovering on Nov. 13 within the journal Science, researchers said that Mars continues to lose water right this moment as vapor is transported to excessive altitudes after sublimating from the frozen polar caps true through hotter seasons.
“We were all very much surprised to search out water so excessive within the atmosphere,” said Shane W. Stone, a doctoral student in planetary science on the University of Arizona’s Lunar and Planetary Laboratory in Tucson. “The measurements we dilapidated might perhaps well presumably occupy only come from MAVEN as it soars during the atmosphere of Mars, excessive above the planet’s surface.”
To originate their discovery, Stone and his colleagues relied on data from MAVEN’s Neutral Gas and Ion Mass Spectrometer (NGIMS), which used to be developed at NASA’s Goddard Dwelling Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. The mass spectrometer inhales air and separates the ions that comprise it by their mass, which is how scientists identify them.
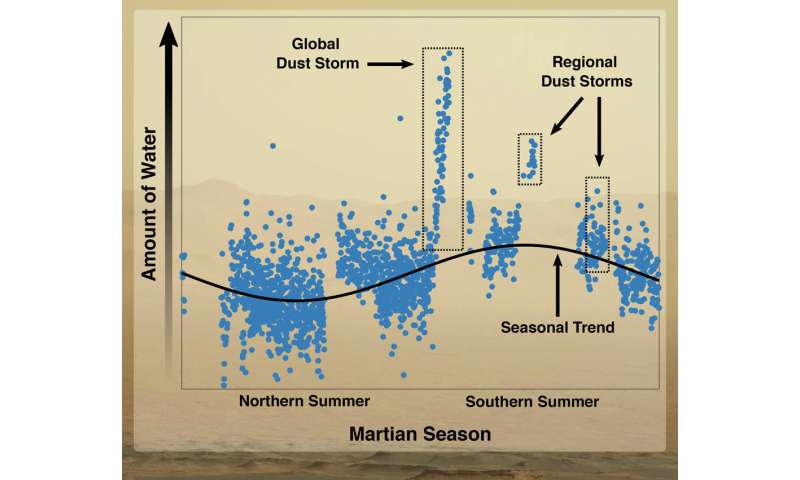
Stone and his team tracked the abundance of water ions excessive over Mars for bigger than two Martian years. In doing so, they obvious that the amount of water vapor finish to the tip of the atmosphere at about 93 miles, or 150 kilometers, above the outside is highest true through summer within the southern hemisphere. At some level of this time, the planet is closest to the Sun, and thus hotter, and dust storms most incessantly have a tendency to happen.

The nice and comfortable summer temperatures and stable winds connected to mud storms serve water vapor attain the uppermost aspects of the atmosphere, the set it can presumably effortlessly be broken into its constituent oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen and oxygen then fetch away to accommodate. Beforehand, scientists idea that water vapor used to be trapped finish to the Martian surface fancy it’s on Earth.
“The whole lot that makes it up to the greater segment of the atmosphere is destroyed, on Mars or on Earth,” Stone said, “because here is the segment of the atmosphere that is exposed to the beefy power of the Sun.”
The researchers measured 20 cases extra water than long-established over two days in June 2018, when a severe global mud storm enveloped Mars (the one who set NASA’s Opportunity rover out of price). Stone and his colleagues estimated Mars lost as great water in 45 days true through this storm as it most incessantly does true through a total Martian twelve months, which lasts two Earth years.
“Now we occupy shown that mud storms interrupt the water cycle on Mars and push water molecules greater within the atmosphere, the set chemical reactions can release their hydrogen atoms, which might perhaps well presumably be then lost to accommodate,” said Paul Mahaffy, director of the Hiss voltaic Machine Exploration Division at NASA Goddard and well-known investigator of NGIMS.
Varied scientists occupy moreover realized that Martian mud storms can defend water vapor far above the outside. However nobody realized unless now that the water would originate it the entire solution to the tip of the atmosphere. There are plentiful ions on this option of the atmosphere that can damage apart water molecules 10 cases quicker than they’re destroyed at lower phases.
“What’s queer about this discovery is that it presents us with a brand contemporary pathway that we didn’t take into accout existed for water to fetch away the Martian atmosphere,” said Mehdi Benna, a Goddard planetary scientist and co-investigator of MAVEN’s NGIMS instrument. “It will fundamentally exchange our estimates of how snappily water is escaping right this moment and the design snappily it escaped within the past.”
Extra data:
Shane W. Stone et al. Hydrogen fetch far from Mars is pushed by seasonal and dust storm transport of water, Science (2020). DOI: 10.1126/science.aba5229
Citation:
Warmth and dust serve initiating Martian water into condominium, scientists safe (2020, November 13)
retrieved 14 November 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-11-martian-condominium-scientists.html
This file is discipline to copyright. As antagonistic to any comely dealing for the goal of private gaze or compare, no
segment might perhaps well presumably be reproduced with out the written permission. The dispute material is supplied for data applications only.