
Aging dams pose growing risk: UN

By 2050, most of us on Earth will stay downstream of tens of hundreds of large dams constructed within the 20th century, heaps of them already working at or previous their create existence, in accordance with a UN College prognosis.
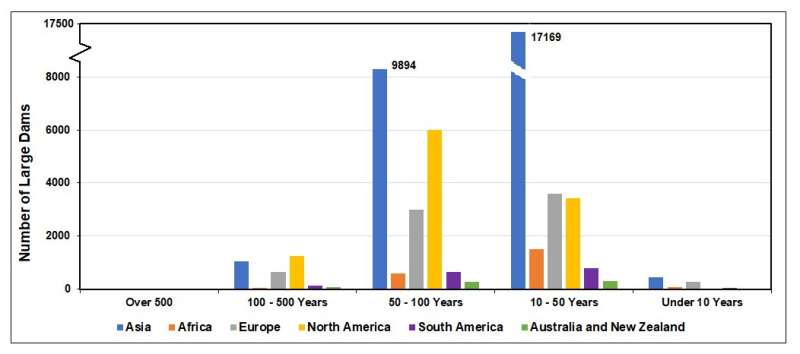
The document, “Aging water infrastructure: An emerging world risk,” by UNU’s Canadian-primarily based completely Institute for Water, Setting and Properly being, says heaps of the 58,700 huge dams worldwide were constructed between 1930 and 1970 with a create existence of 50 to 100 years, adding that at 50 years a huge concrete dam “would most potentially commence to explicit signs of aging.”
Aging signs encompass growing instances of dam screw ups, gradually growing costs of dam restore and repairs, growing reservoir sedimentation, and lack of a dam’s functionality and effectiveness, “strongly interconnected” manifestations, the paper says.
The document says dams that are neatly designed, constructed and maintained can “without misfortune” attain 100 years of carrier but predicts an lengthen in “decommissioning”—a phenomenon gaining tempo within the US and Europe—as economic and functional boundaries prevent aging dams from being upgraded or if their long-established use is now out of date.
Worldwide, the monumental quantity of water saved within the motivate of large dams is estimated at 7,000 to eight,300 cubic kilometers—ample to hide about 80% of Canada’s landmass below a meter of water.
The document presents an overview of dam aging by world feature and first feature—water provide, irrigation, flood withhold an eye on, hydropower, and recreation.
It additionally important aspects the growing risk of older dams, the rising repairs expense, the declining functionality attributable to sedimentation, the advantages of restoring or redesigning natural environments, and the societal impacts—pro and con—that would possibly well well honest composed be weighed by policymakers deciding what to enact. Significantly, “the nature of these impacts varies an excellent deal between low- and high-profits worldwide locations.”
The prognosis additionally comprises dam decommissioning or aging case stories from the US, France, Canada, India, Japan, and Zambia & Zimbabwe.
Native weather trade will urge the dam aging course of
“This document aims to plot world consideration to the creeping snarl of aging water storage infrastructure and stimulate world efforts to handle this emerging, rising water risk,” says co-creator Vladimir Smakhtin, Director of UNU-INWEH.
“Underlined is the real fact that the rising frequency and severity of flooding and assorted extreme environmental occasions can crush a dam’s create limits and urge a dam’s aging course of. Choices about decommissioning, therefore, would possibly well well honest composed be taken within the context of a altering native weather.”
Notes lead creator and UNU-INWEH Senior Researcher Duminda Perera: “This snarl of aging huge dams nowadays confronts a moderately itsy-bitsy number of worldwide locations—93% of your total world’s huge dams would possibly be found in excellent 25 countries.”
“Extensive dam constructing surged within the mid-20th century and peaked within the 1960s—70s,” he says, “in particular in Asia, Europe and North America, whereas in Africa the high took place within the 1980s. The number of newly-constructed huge dams after that repeatedly and gradually declined.”
Per the document, the sector is now no longer going to gaze one more huge dam-constructing revolution as within the mid-20th century, but dams constructed then will inevitably be displaying their age.
China has 23,841 huge dams (40% of the sector’s whole). And 32,716 huge dams (55% of the sector’s whole) are indicate in excellent four Asian worldwide locations: China, India, Japan, and the Republic of Korea—a majority of which is willing to attain the 50-three hundred and sixty five days threshold moderately soon. The same is loyal of many huge dams in Africa, South America, and Eastern Europe.
The tempo of large dam constructing has dropped dramatically within the final four decades and continues to decline partly because “the particular areas for such dams globally were gradually diminishing as almost 50% of world river quantity is already fragmented or regulated by dams,” the document says.
As neatly, there are notable considerations relating to the environmental and social impacts of dams, and big dams namely, as neatly as emerging solutions and practices on the replacement forms of water storage, nature-primarily based completely solutions, and forms of energy production previous hydropower.

Drivers of dam decommissioning
Public security, escalating repairs costs, reservoir sedimentation, and restoration of a natural river ecosystem are amongst the reasons utilizing dam decommissioning.
On the replacement hand, most dams eradicated up to now were itsy-bitsy; decommissioning huge dams (defined by ICOLD as 15 or more meters from lowest basis to crest, or 5 to 15 meters impounding more than 3 million cubic meters) is “composed in its infancy, with most efficient a few identified instances within the final decade.”
“A couple of case stories of aging and decommissioned huge dams illustrate the complexity and length of the technique that’s in total most important to orchestrate the dam removal safely,” adds co-creator and UNU-INWEH Adjunct Professor R. Allen Curry, primarily based completely on the College of Fresh Brunswick.
“Even removing a itsy-bitsy dam requires years (most regularly decades) of right expert and public involvement, and prolonged regulatory critiques. With the mass aging of dams neatly underway, it’s some distance considerable to develop a framework of protocols that will facts and urge the dam removal course of.”
Decommissioning will additionally comprise various particular and negative economic, social, and ecological impacts to be conception to be in a local and regional social, economic, and geographic context “important to defend the broader, sustainable model targets for a feature,” the document says.
“Total, dam decommissioning needs to be seen as equally important as dam constructing within the final planning course of on water storage infrastructure trends.”
“In the slay, price judgments will desire the destiny of heaps of these huge water storage constructions. It is now no longer a straightforward course of, and thus distilling lessons from and sharing dam decommissioning experiences needs to be a total world goal. Lack of such facts and absence of its reflection in connected regional/national insurance policies/practices would possibly well well honest gradually and adversely affect the flexibility to rearrange water storage infrastructure neatly because it’s some distance aging.”
Supplied by
UN College Institute for Water, Setting and Properly being
Citation:
Aging dams pose growing risk: UN (2021, January 22)
retrieved 22 January 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-01-aging-pose-risk.html
This doc is field to copyright. Except for any elegant dealing for the motive of non-public think or review, no
part would possibly be reproduced without the written permission. The impart material is supplied for facts capabilities most efficient.