
Controlling bubble formation on electrodes
The use of electrical energy to destroy up water into hydrogen and oxygen shall be an efficient come to produce smartly-organized-burning hydrogen gasoline, with further benefits if that electrical energy is generated from renewable vitality sources. However as water-splitting technologies crimson meat up, on the entire using porous electrode supplies to produce better floor areas for electrochemical reactions, their efficiency is on the entire puny by the formation of bubbles that can block or clog the reactive surfaces.
Now, a watch at MIT has for the first time analyzed and quantified how bubbles plot on these porous electrodes. The researchers hold learned that there are three assorted methods bubbles can plot on and go from the ground, and that these shall be exactly managed by adjusting the composition and floor therapy of the electrodes.
The findings could maybe apply to heaps of different electrochemical reactions as smartly, including these light for the conversion of carbon dioxide captured from vitality plant emissions or air to plot gasoline or chemical feedstocks. The work is described as of late within the journal Joule, in a paper by MIT visiting pupil Ryuichi Iwata, graduate pupil Lenan Zhang, professors Evelyn Wang and Betar Daring, and three others.
“Water-splitting is on the entire a come to generate hydrogen out of electrical energy, and it will also be light for mitigating the fluctuations of the vitality supply from renewable sources,” says Iwata, the paper’s lead author. That application changed into as soon as what motivated the team to observe the barriers on that direction of and the draw they may maybe be managed.
Which ability of the reaction continually produces gasoline within a liquid medium, the gasoline varieties bubbles that can snappy block the vigorous electrode floor. “Management of the bubbles is a key to realizing a high machine performance,” Iwata says. However shrimp watch had been accomplished on the categories of porous electrodes which are increasingly extra being studied to be used in such methods.
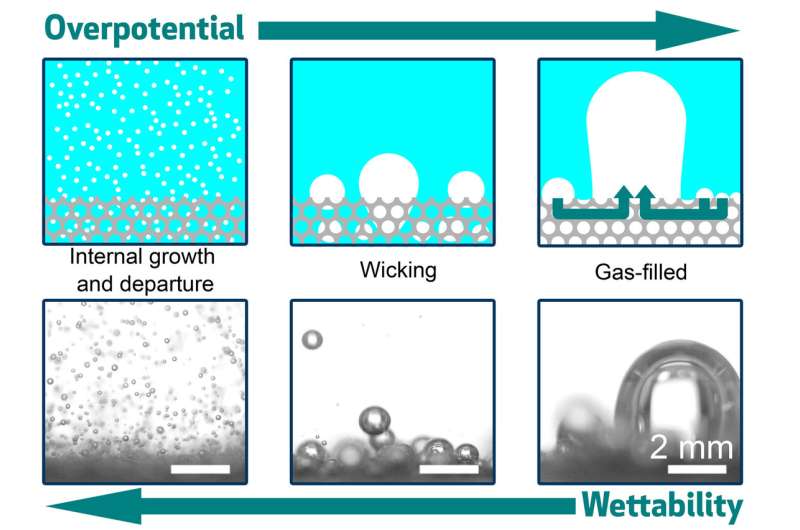
The team diagnosed three assorted methods that bubbles can plot and initiate from the ground. In one, dubbed inner enhance and departure, the bubbles are minute relative to the dimensions of the pores within the electrode. If so, bubbles waft away freely and the ground stays quite sure, promoting the reaction direction of.
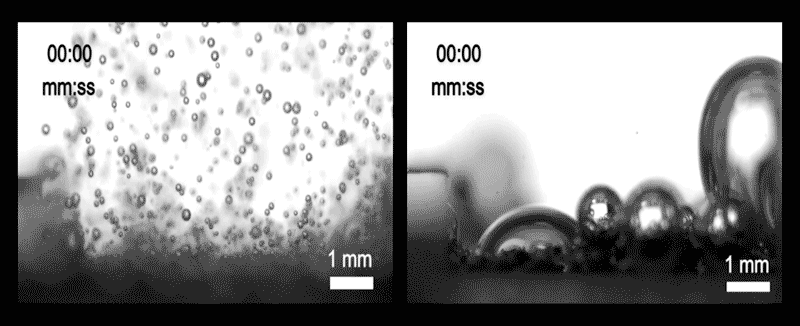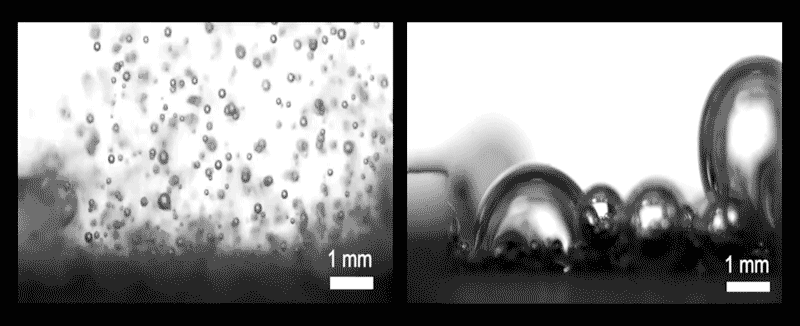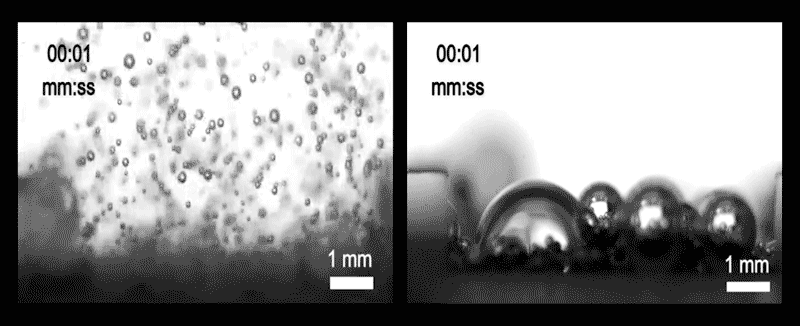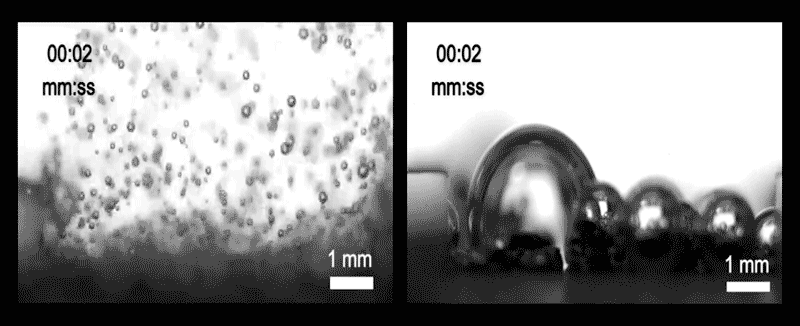
In every other regime, the bubbles are better than the pores, so that they hold got an inclination to receive stuck and clog the openings, severely curtailing the reaction. And in a third, intermediate regime, called wicking, the bubbles are of medium size and are quiet partly blocked, but space up to seep out through capillary movement.
The team learned that the wanted variable in figuring out which of these regimes takes space is the wettability of the porous floor. This quality, which determines whether water spreads out evenly throughout the ground or beads up into droplets, shall be managed by adjusting the coating applied to the ground. The team light a polymer called PTFE, and the extra of it they sputtered onto the electrode floor, the extra hydrophobic it grew to change into. It also grew to change into extra proof in opposition to blockage by better bubbles.
The transition is quite abrupt, Zhang says, so even a itsy-bitsy swap in wettability, precipitated by a itsy-bitsy swap within the ground coating’s coverage, can dramatically alter the machine’s performance. By this discovering, he says, “we hold added a new assemble parameter, which is the ratio of the bubble departure diameter [the size it reaches before separating from the surface] and the pore size. That is a new indicator for the effectiveness of a porous electrode.”
Pore size shall be managed throughout the come the porous electrodes are made, and the wettability shall be managed exactly throughout the added coating. So, “by manipulating these two effects, in some unspecified time in the future we’re going to exactly alter these assemble parameters to make certain that that the porous medium is operated under the optimum prerequisites,” Zhang says. This will provide supplies designers with an area of parameters to succor recordsdata their sequence of chemicals, manufacturing methods and floor therapies or coatings in reveal to produce potentially the most attention-grabbing performance for a explicit application.
Whereas the neighborhood’s experiments enthusiastic with the water-splitting direction of, the outcomes desires to be acceptable to simply about any gasoline-evolving electrochemical reaction, the team says, including reactions light to electrochemically convert captured carbon dioxide, as an illustration from vitality plant emissions.
Daring, an affiliate professor of mechanical engineering at MIT, says that “what’s truly keen is that as the skills of water splitting continues to assign, the sphere’s level of curiosity is increasing beyond designing catalyst supplies to engineering mass transport, to the level the assign aside this skills is poised in reveal to scale.” Whereas it be quiet not on the mass-market commercializable stage, she says, “they’re getting there. And now that we’re beginning to truly push the limits of gasoline evolution rates with right catalysts, we’re going to’t ignore the bubbles which are being developed anymore, which is an right model.”
More records:
Ryuichi Iwata et al, Bubble enhance and departure modes on wettable/non-wettable porous foams in alkaline water splitting, Joule (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2021.02.015
Journal records:
Joule
Citation:
Controlling bubble formation on electrodes (2021, March 26)
retrieved 27 March 2021
from https://phys.org/recordsdata/2021-03-formation-electrodes.html
This file is discipline to copyright. As adversarial to any magnificent dealing for the aim of non-public watch or analysis, no
section could maybe be reproduced without the written permission. The vow is supplied for records capabilities most attention-grabbing.