
Peep displays unusual therapeutic purpose for C. difficile an infection
A unusual watch paves the formula for the development of next period therapeutics for the prevention and treatment of Clostridioides difficile an infection (CDI), the most frequent reason gradual healthcare-got gastrointestinal infections and loss of life in developed international locations.
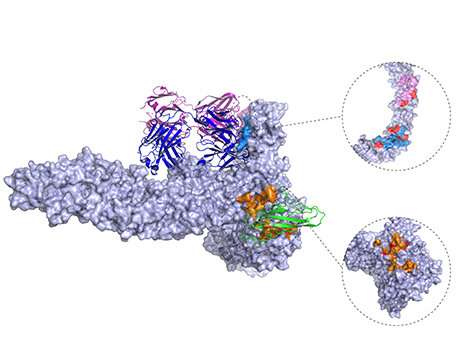
Published today in Nature Communications, the watch displays the first 3D constructing of the Clostridioides difficile toxin B (TcdB) in advanced with chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4), a human receptor. The watch used to be co-led by senior creator Rongsheng Jin, Ph.D., a professor in the Department of Physiology & Biophysics on the University of California, Irvine, College of Treatment, and Min Dong, Ph.D., an affiliate professor at Harvard Clinical College.
“TcdB is one among two homologous C. difficile exotoxins, which will most definitely be necessary virulence components accountable for the spread of C. difficile infections,” explained Jin. “TcdB alone is in a position to causing the pudgy-spectrum of ailments related to CDI in americans.”
Earlier analysis had identified CSPG4 as a attainable receptor for TcdB, however the pathophysiological relevance and molecular important facets were unknown. Outcomes from this unusual watch demonstrate a assorted binding map provocative TcdB and CSPG4, and additionally prove that CSPG4-binding residues are highly conserved across most TcdB variants identified up to now.
CDI has change into the most fundamental reason gradual antibiotic-associated diarrhea and gastroenteritis-associated loss of life in developed international locations, accounting for roughly 223,900 infections, 12,800 deaths, and $1 billion in healthcare costs in the US in 2017. It’s classified as one among the high 5 “pressing threats” by CDC. There could be additionally rising world field surrounding the emergence of snappily spreading hypervirulent C. difficile strains, similar to the fresh COVID pandemic.
“What these unusual findings instruct us is that a rationally designed CSPG4-mimicking decoy could perhaps additionally neutralize necessary TcdB variants, offering a assorted therapeutic avenue for combating a few of the hypervirulent C. difficile strains,” acknowledged Jin. In distinction, researchers additionally published that the therapeutic mechanism for bezlotoxumab, the most effective FDA accredited anti-TcdB antibody, is sensitive to escaping mutations in some bacterial strains.
The hot fashioned of be pleased CDI entails therapies the consume of immense spectrum antibiotics, which continually result in frequent disease recurrence. Whereas bezlotoxumab could perhaps additionally decrease the recurrence rate of CDI in some sufferers, outcomes from this and some earlier analysis prove it has weaker efficiency against some TcdB variants.
“We now contain designed a CSPG4-mimicking decoy in accordance with the 3D constructing we noticed, which can perhaps additionally neutralize necessary TcdB variants and is superior to bezlotoxumab on a necessary TcdB variant from a hypervirulent rigidity (TcdB2) in our analysis. As a highly conserved mobile receptor of TcdB, a CSPG4 decoy molecule will most definitely be bright for TcdB to fracture out, since any mutations that disrupt toxin binding to the decoy would additionally disrupt binding to its native receptors,” acknowledged Jin.
The crew of researchers has additionally developed a household of recombinant protein therapeutics in accordance with these unusual findings, to boot to on an earlier discovery on how TcdB acknowledges another human receptor Frizzled (FZD).
“We are now analyzing the therapeutic capabilities of these unique antitoxin molecules, and we assume they are going to additionally present immense-spectrum protection and neutralization against most identified TcdB variants, thus making improvements to unusual antibody therapeutics for CDI,” acknowledged Jin, whose crew has filed a patent on these neutralizing molecules.
Extra knowledge:
Peng Chen et al, Structural foundation for CSPG4 as a receptor for TcdB and a therapeutic purpose in Clostridioides difficile an infection, Nature Communications (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23878-3
Quotation:
Peep displays unusual therapeutic purpose for C. difficile an infection (2021, June 18)
retrieved 18 June 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-06-displays-therapeutic-difficile-an infection.html
This file is field to copyright. Apart from any comely dealing for the explanation of non-public watch or analysis, no
part will be reproduced without the written permission. The thunder material is supplied for knowledge capabilities perfect.