
Tunable ‘metasurface’ is resembling optical swiss army knife
MIT engineers and colleagues tale crucial unusual advances on a tunable metasurface, or flat optical design patterned with nanoscale structures, that they evaluate to a Swiss army knife whereas its passive predecessor will be regarded as proper one instrument, adore a flat-bladed screwdriver. Key to the work is a clear fabric found by the team that hastily and reversibly changes its atomic structure fixed with heat.
“The functions opened up by the skill to hastily reconfigure metasurfaces are broad,” says Yifei Zhang, first author of a paper reporting primarily the most modern advances in a recent danger of Nature Nanotechnology. Zhang is a graduate student within the Department of Gives Science and Engineering (DMSE). “We’re infected for the reason that contemporary work overcomes several boundaries to put into effect these metasurfaces into exact-world functions.”
Says Affiliate Professor Arka Majumdar of the University of Washington, Seattle, of those functions: “I envision [that] this know-how may maybe perchance perchance also revolutionize optical neural networks, depth sensing, and Lidar know-how for autonomous vehicles.” Majumdar was not concerned with the research.
Electrical switch
In the Nature Nanotechnology paper, the MIT researchers report the employ of electrical currents to reversibly swap the fabric structure—and ensuing from this reality optical properties—of the unusual metasurface. Previously, they earlier pudgy lasers or a furnace to provide the essential heat. “This is essential because we can now combine the total fascinating optical design, along with the electrical switch, on a silicon chip to originate a miniaturized optics platform,” says Juejun Hu, leader of the work and an Affiliate Professor of Gives Science and Engineering in DMSE.
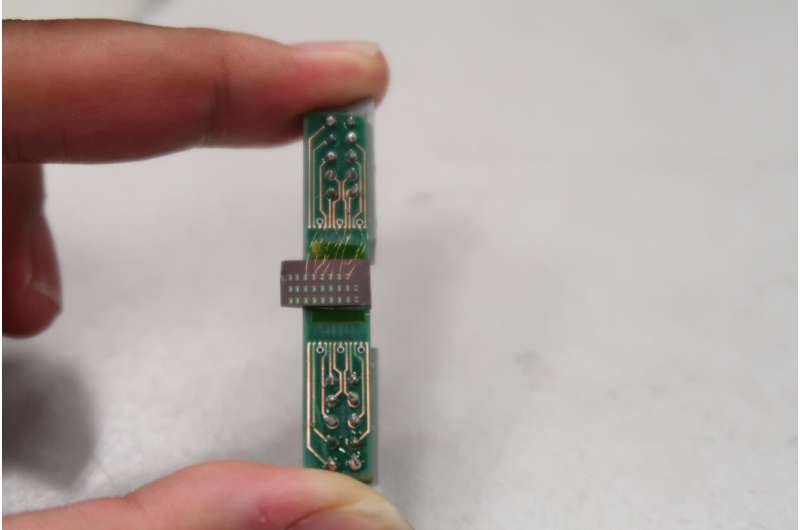

The team additionally experiences demonstrating “a chain of tunable optical functions the employ of the platform,” Hu says. These embody a beam steering design where “by switching the fabric to moderately a few [internal] structures, we can ship gentle in one direction versus some other, .” Beam steering is key to self-driving vehicles, though Hu emphasizes that the design he and colleagues demonstrated is silent moderately rudimentary. “It be extra a proof of precept.”
As well to Zhang and Hu, authors of the unusual paper are Junhao Liang, Bilal Azhar, Mikhail Y. Shalaginov, Skylar Deckoff-Jones, Carlos Rios, and Tian Gu, all of MIT DMSE; Clayton Fowler, Sensong An, and Hualiang Zhang of the University of Massachusetts, Lowell; Jeffrey B. Chou, Christopher M. Roberts, and Vladimir Liberman of MIT Lincoln Laboratory; Myungkoo Kang and Kathleen A. Richardson of the University of Central Florida, and Clara Rivero-Baleine of Lockheed Martin Corporation. Hu and Gu are additionally affiliated with MIT’s Gives Review Laboratory.
A brand unusual fabric
Section-swap offers (PCMs) swap their structure fixed with heat. They are earlier commercially in rewritable CDs and DVDs. Explains Hu, “a laser beam changes the structure of the fabric within the neighborhood, from amorphous to crystalline, and that swap will be earlier to encode ones and zeros—digital files.”
Nonetheless, historical PCMs safe barriers in phrases of optical functions. For one, they are opaque. They couldn’t let gentle traipse by. “That motivated us to take into myth correct into a brand unusual portion-swap fabric for optical gadgets that is evident,” Hu says. Earlier this year his team reported that including some other ingredient, selenium, to a historical PCM did the trick.
The unusual fabric, easy of germanium, selenium, antimony, and tellurium (GSST), is key to the unusual metasurface. The metasurface, in turn, just isn’t proper a thin film of GSST, or not it is a film of GSST handiest about half of a millimeter square patterned with some 100,000 nanoscale structures. And these, in turn, “will enable you to manipulate the propagation of sunshine. So you may maybe perchance perchance presumably also remodel a series of those nanostructures into, for instance, a lens,” Hu says.
Harish Bhaskaran is a Professor on the University of Oxford who was not concerned with the research. He commented on the work as a complete and on the advances reported within the unusual paper:
“It is some distance a very crucial space of work as such tunable metasurfaces, i.e., surfaces that can modulate the reflection of sunshine despite the indisputable reality that they are nominally ‘flat’ or very skinny, are extremely bright. They are able to dramatically lower the bulk of lenses, which unnecessary to affirm are earlier in every little thing that manipulates gentle. [MIT’s] employ of portion swap offers which could perchance perchance be low loss (i.e., they derive small or no gentle) offers a exact pathway in direction of making this a reality. The authors are additionally among the many first to illustrate the dynamic tuning the employ of heaters that are controlled electrically.” (In the equivalent danger of Nature Nanotechnology a team from Stanford additionally experiences controlling metasurfaces with electrical heating the employ of a clear attain.)
Per a News & Views article within the equivalent danger of Nature Nanotechnology about the MIT and Stanford advances, “these works derive a leap forward within the tunable PCM-primarily based metasurfaces.” Nonetheless, the News & Views authors emphasize that both approaches safe drawbacks.
The Hu team is addressing some of those drawbacks. As an example, the heater earlier of their miniaturized optics platform is currently fabricated from steel. But “metals are problematic for optics, because they derive gentle,” Hu says. “We’re engaged on a brand unusual heater fabricated from silicon that is evident.”
Hu describes the work overall as especially thrilling since it started with the discovery of a brand unusual fabric that the team then engineered for a brand unusual application. “This cuts all the design in which by from offers innovation to design integration, which I non-public in all fairness uncommon.”
The work was supported by the US Defense Evolved Review Initiatives Agency and the US Air Force. The researchers additionally acknowledge the usage of companies and products offered by the MIT Gives Review Laboratory, the MIT Microsystems Expertise Laboratories, and the Harvard University Heart for Nanoscale Programs.
More files:
Yifei Zhang et al, Electrically reconfigurable non-unstable metasurface the employ of low-loss optical portion-swap fabric, Nature Nanotechnology (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-021-00881-9
Citation:
Tunable ‘metasurface’ is resembling optical swiss army knife (2021, August 11)
retrieved 11 August 2021
from https://phys.org/data/2021-08-tunable-metasurface-akin-optical-swiss.html
This file is arena to copyright. As a replace of any fine dealing for the reason of non-public survey or research, no
portion may maybe perchance perchance be reproduced without the written permission. The whisper material is offered for files applications handiest.