
‘Blue’ and ‘Gold’ satellites headed to Mars in 2024
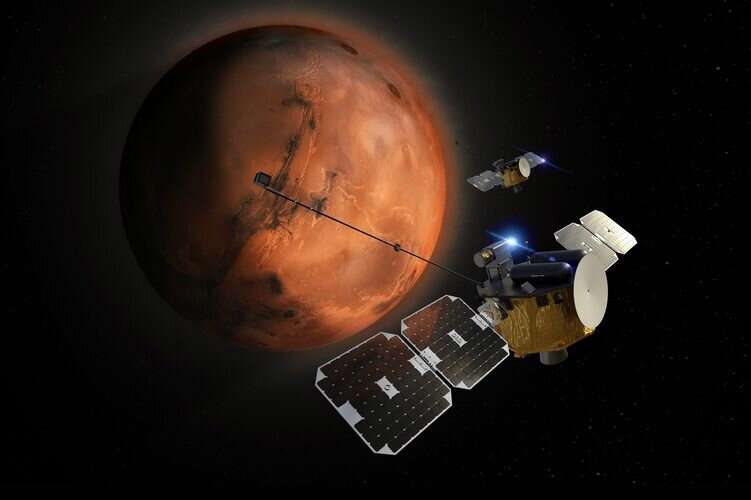

An interplanetary mission led by the University of California, Berkeley, to position two satellites—dubbed “Blue” and “Gold”—into orbit around Mars has been officially approved to prepare for launch in October 2024.
The announcement remaining week by NASA skill that by 2026 the spacecraft is ceaselessly exploring the crimson planet‘s environment and its interaction with the photograph voltaic wind.
Called the Flee and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers (ESCAPADE) mission, it’s miles the fruits of two years of intense work by scientists at UC Berkeley’s Articulate Sciences Laboratory (SSL) to order that relatively less pricey spacecraft—the procure, develop, check, integration and launch will designate less than $80 million—can also be assembled in a transient time-frame to explore moderately a couple of planets. Unprecedented NASA planetary missions continuously require bigger than a decade of preparation and might perhaps perhaps exceed $1 billion in costs.
“ESCAPADE and two moderately a couple of NASA missions now not too long up to now approved are experiments to peek whether advances in the gap industry over the remaining five to 10 years can translate to a substantial better bang for the buck in the case of science per greenback,” acknowledged mission chief Robert Lillis, SSL’s companion director for planetary science and astrobiology. “Sending two spacecraft to Mars for the final designate of beneath $80 million is upright unprecedented, however fresh NASA management is taking the likelihood.”
The UC Berkeley team will work with Rocket Lab, an enviornment contractor based in Long Seaside, California, which can provide two Photon spacecraft to accommodate and give a seize to the instruments. The academic/industry collaboration is an instance of what NASA hopes to again with its Tiny Modern Missions for Planetary Exploration (SIMPLEx) program, designed to fund compelling planetary space science with small satellites and provide more opportunities for flight ride to the science community.
These missions signify “a brand fresh industrial, elevated risk, high reward system of doing things,” Lillis acknowledged. “In catch 22 situation of spending $800 million for a 95% likelihood of success, will we use $80 million for an 80% likelihood? That is what NASA is making an are trying and search out out with these missions.”
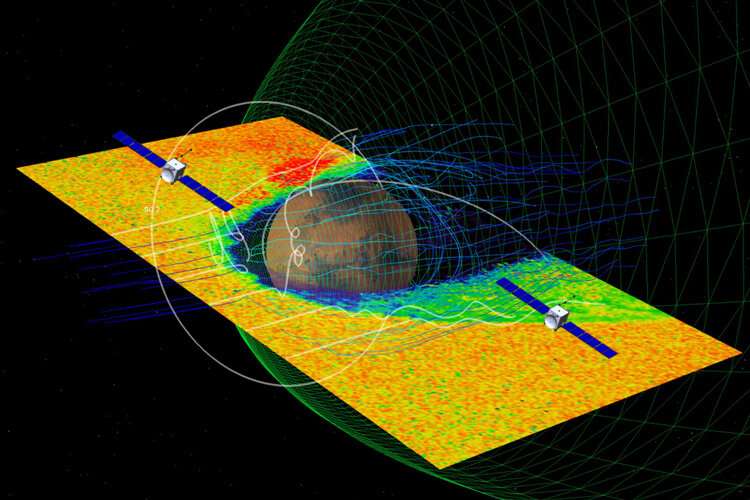
The mission’s plot is to rep recordsdata that might perhaps perhaps presumably assist reconstruct the climate history of Mars and judge how and when it misplaced its environment, which changed into as soon as dense ample to permit for running water, in conjunction with rivers, lakes and presumably oceans. ESCAPADE moreover will study the ionosphere of Mars, which can interfere with radio communications on the bottom and between Earth and Mars colonists.
“With simultaneous two-level observations of the photograph voltaic wind and Mars’s ionosphere and magnetosphere, ESCAPADE will lift us the first ‘stereo’ negate of this highly dynamic plasma environment,” Lillis acknowledged.
“This constellation of two satellites at Mars will resolution mountainous questions about the environment and the photograph voltaic wind in right time,” acknowledged Shannon Curry, mission scientist for the mission at UC Berkeley.
Rocket Lab, which teamed with UC Berkeley in June, has been constructing rockets and spacecraft platforms since 2006 for civil, defense and industrial prospects. NASA evaluated the mission’s preliminary procure and mission plan and determined remaining week that each UC Berkeley and Rocket Lab had met all milestones—known as key resolution functions—needed to prepare for launch. The following steps encompass the remaining procure of the mission and constructing the instruments.
“ESCAPADE is an innovative mission that demonstrates that superior interplanetary science is now within sight for a share of worn costs, and we’re proud to develop it that you just would also think about with Photon,” acknowledged Rocket Lab founder and CEO Peter Beck in a commentary. “Passing the most predominant resolution level is a principal milestone in ESCAPADE’s model and is testament to the enviornment-class science and engineering work of the UC Berkeley and Rocket Lab teams. We are pleased to procure the green gentle from NASA to proceed to flight.”
The mission builds on decades of ride at SSL in constructing satellite instruments and fleets of spacecraft to explore areas around Earth, the moon and Mars, specializing in magnetic field interactions with the wind of particles from the sun. Every of the two satellites, named after UC Berkeley’s college colours, will lift instruments built at SSL to measure the float of high vitality electrons and ionized oxygen and carbon dioxide molecules escaping from Mars, magnetic field detectors built at UCLA and a probe to measure slower or thermal ions built at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University in Daytona Seaside, Florida.
With twin satellites, it’s miles skill to measure stipulations simultaneously at two areas around the planet, Lillis acknowledged, permitting scientists to join plasma stipulations at one catch 22 situation to the escaping ion flux at one more. Over the course of the mission, the two satellites will alternate positions to device the upper environment and magnetosphere of close to the final planet from an altitude of between 150 and 10,000 kilometers.
When selected by NASA in 2019 to procure $8.3 million for a conceptual procure, ESCAPADE changed into scheduled to piggyback aboard a rocket that changed into launching one more mission, known as Psyche, in August 2022. Nonetheless that different evaporated when the launch automobile changed into changed, and NASA hunted for one more possibility. The agency at remaining deciding to launch ESCAPADE as a secondary payload aboard a queer, as-but-unselected industrial rocket
“For ESCAPADE, we’re evaluating a different of rideshare strategies to permit this critically principal science while moreover reducing costs,” acknowledged Alan Zide, program government for the mission at NASA headquarters, in a weblog publish on NASA’s site.
In consequence, while the instruments stay unchanged, they must composed be reconfigured to suit the Photon platform.
“The instruments have not changed, the science targets have not changed, however the entirety from the launch pad to the orbit in space is entirely moderately a couple of,” Lillis acknowledged. “We are going with a novel contractor, a queer propulsion system and a extraordinarily essential shorter mission plan in getting to Mars.”
The skedaddle to Mars will seize about 11 months, after which Blue and Gold will separate and launch their mission.
Lillis acknowledged that his reaction to NASA’s resolution changed into “upright unbridled pleasure and happiness,” however admitted that he might perhaps perhaps presumably now not relaxation easy except early in 2026, “after we procure our first recordsdata from orbit around Mars.”
Citation:
‘Blue’ and ‘Gold’ satellites headed to Mars in 2024 (2021, August 23)
retrieved 23 August 2021
from https://phys.org/recordsdata/2021-08-blue-gold-satellites-mars.html
This legend is field to copyright. Other than any heavenly dealing for the motive of deepest study or study, no
allotment will be reproduced with out the written permission. The mutter material is equipped for recordsdata capabilities only.