
Scientists spy the molecular mechanism of unlit-streaked dwarf virus in rice
Rice viruses are prevalent in diverse rice-growing international locations and in general problem off serious damages to rice production. Among them, the rice unlit-streaked dwarf virus (RBSDV), transmitted by the little brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus, causes large losses in China’s grain yields yearly. Therefore, discovering the transmission mechanism of RBSDV is of good significance for its effective control.
The examine group led by Prof. Wu Jianxiang and Prof. Zhou Xueping from the Zhejiang College Faculty of Agriculture and Biotechnology published an originate-come by admission to article entitled “Rice unlit-streaked dwarf virus P10 promotes phosphorylation of GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) to induce autophagy in L. striatellus” within the journal Autophagy.
The examine group discovered that the early share of RBSDV an infection in L. striatellus can induce autophagy, leading to the suppression of RBSDV invasion and accumulation whereas inhibiting autophagy can promote RBSDV invasion and accumulation and thus toughen the mortality rate of RBSDV-infected L. striatellus. This skill that autophagy, as an innate immune response, plays a crucial role within the fight against RBSDV invasion.
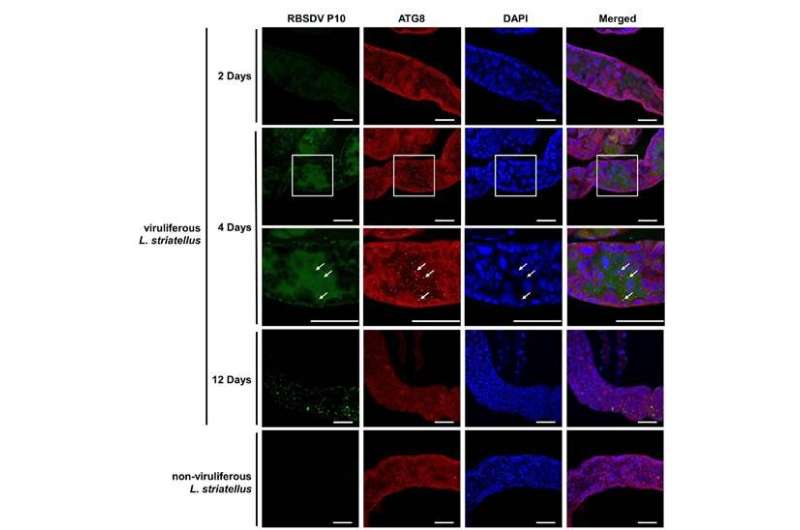
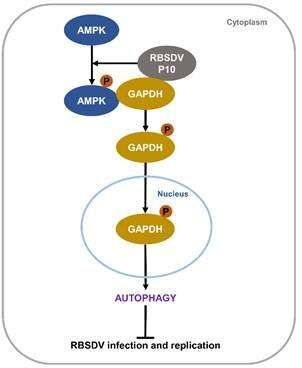
Furthermore, the major capsid protein (also identified as P10) of RBSDV on my own can induce autophagy in both Sf9 and L. striatellus cells. Yeast two-hybrid (Y2H), pull down, Co-IP assays confirmed that RBSDV P10 can work along side GAPDH in vivo and in vitro. Extra experiments indicated that Sf9 cells expressing RBSDV P10 can promote the phosphorylation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), ensuing in GAPDH phosphorylation and relocation of GAPDH from the cytoplasm to the nucleus.
Meanwhile, RBSDV invasion or feeding recombinant expressed RBSDV P10 can also also promote LsAMPK phosphorylation, leading to LsGAPDH phosphorylation and the translocation of the phosphorylated LsGAPDH from the cytoplasm to the nucleus to spark off the autophagy pathway in L. striatellus. Co-IP and in vitro phosphorylation assays confirmed that AMPK interacts with GAPDH, phosphorylated AMPK can phosphorylate GAPDH, and silencing AMPK genes can inhibit the incidence of GAPDH phosphorylation, translocation of GAPDH into the nucleus and autophagy.
This glimpse exhibits that RBSDV invasion or RBSDV P10 can induce AMPK phosphorylation, that will consequence in GAPDH phosphorylation and the translocation of phosphorylated GAPDH into the nucleus. Once internal the nucleus, phosphorylated GAPDH can spark off autophagy to suppress virus an infection. “Our examine illuminates the mechanism wherein RBSDV induces autophagy in L. striatellus, and indicates that the autophagy pathway in an insect vector participates within the anti-RBSDV innate immune response,” acknowledged Prof. Wu. “This will doubtless provide novel insights into RBSDV control.”
More records:
Qi Wang et al, Rice unlit-streaked dwarf virus P10 promotes phosphorylation of GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) to induce autophagy in Laodelphax striatellus, Autophagy (2021). DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1954773
Offered by
Zhejiang College
Citation:
Scientists spy the molecular mechanism of unlit-streaked dwarf virus in rice (2021, September 6)
retrieved 6 September 2021
from https://phys.org/records/2021-09-scientists-molecular-mechanism-unlit-streaked-dwarf.html
This yarn is arena to copyright. Along with any lovely dealing for the unbiased of personal glimpse or examine, no
allotment can be reproduced with out the written permission. The inform is supplied for records purposes only.