
A 5-sigma frequent model anomaly is probably going
Probably the most greatest chances for proving beyond-the-frequent-model physics relies on something called the Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix. The frequent model insists that the CKM matrix, which describes the mixing of quarks, must mild be unitary. But rising proof suggests that all through definite kinds of radioactive decay, the unitarity of the CKM matrix would possibly well well damage.
On the 2021 Tumble Assembly of the APS Division of Nuclear Physics, researchers focus on how a NASA lunar mission and most well-known theoretical progress would possibly well well back snap the frequent model.
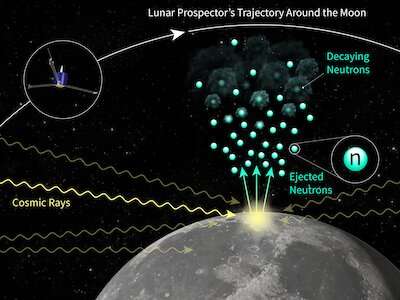
The free neutron lifetime performs the biggest role in sorting out CKM matrix unitarity. Nonetheless, two prevailing programs for measuring it war severely. So Jack Wilson and a team at The Johns Hopkins Utilized Physics Laboratory and Durham University made up our minds to deem exterior the box—by going to outer home.
Piggybacking on recordsdata from NASA’s Lunar Prospector Mission, which sent a spacecraft to orbit the moon, the scientists made the second-ever free neutron lifetime size from home. They diminished uncertainty by an philosophize of magnitude.
“Our consequence opens up a third strategy of measuring the neutron lifetime. Utilizing this device in an actual mission would possibly well well direct to an terminate a a protracted time-lengthy puzzle in basic physics,” acknowledged Wilson, who will share the consequences at the assembly on October 13.
A newsletter is drawing near near the same day from Physical Assessment C.
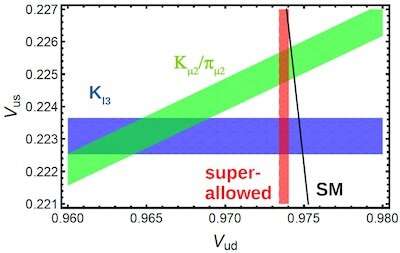
Eventually, breaking the CKM matrix unitarity—and finding physics beyond the frequent model—would quiz a stronger discrepancy between thought and experiment. Essentially the most most sleek overview of the discipline measured the disagreement at about three sigma.
“The current critical stage of the seen anomalies isn’t any longer yet sufficient to uncover a discovery. The most well-known limiting element is the precision stage of the frequent model thought inputs,” acknowledged Chien Yeah Seng, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Bonn.
On the assembly, Seng will share the fable at the back of the theoretical research that revealed this hint of recent physics and would possibly well even focus on progress in making the conclusion facet extra ethical.
His collaborator Luchang Jin, a professor at the University of Connecticut and regarded one of the theoretical pioneers at the back of the most sleek muon g–2 calculations, items most sleek research refining a key theoretical element. The stare dramatically reduces uncertainties in the low energy constants feeble for theoretical calculations.
Seng will lay out the path to finding a five-sigma discrepancy, at the side of Jin’s work on radiative corrections, isospin-breaking corrections, and nuclear building corrections. He predicts lets peep a step forward even in the subsequent few years.
More recordsdata:
Jack T. Wilson et al, Measurement of the free neutron lifetime the exercise of the neutron spectrometer on NASA’s Lunar Prospector mission, Physical Assessment C (2021). journals.aps.org/prc/authorized/ … bb86f2391418e62c559e
Citation:
A 5-sigma frequent model anomaly is probably going (2021, October 12)
retrieved 12 October 2021
from https://phys.org/recordsdata/2021-10-sigma-frequent-anomaly.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Besides any horny dealing for the rationale of personal stare or research, no
fragment shall be reproduced without the written permission. The divulge is equipped for recordsdata functions greatest.