
A nanoparticle’s size is dazzling-tuned to provide excessive-resolution photos sooner than and for the duration of surgical procedures
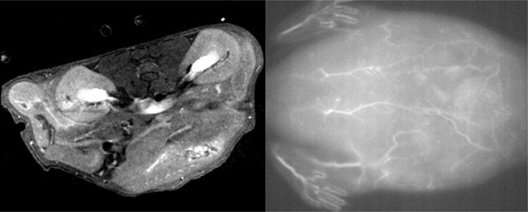
Scientists possess found a draw to control the scale of special nanoparticles to optimize their exercise for both magnetic resonance and strategy-infrared imaging. Their blueprint could abet surgeons exercise the identical nanoparticles to visualise tumors factual sooner than after which for the duration of surgical map utilizing the 2 reasonably a few imaging ways. Their findings were published within the journal Science and Technology of Developed Materials.
“Magnetic resonance imaging is automatically utilized in pre-operative diagnosis, whereas surgeons possess started utilizing strategy-infrared fluorescence imaging for the duration of surgical procedures,” says nanobiotechnologist Kyohei Okubo of Tokyo College of Science. “Our nanoparticle probes could provide a bimodality that will be clinically attention-grabbing to medical system researchers and medical doctors.”
Ceramic nanoparticles made with the rare earth metals ytterbium (Yb) and erbium (Er) possess demonstrated low toxicity and prolonged strategy-infrared luminescence, displaying promise as a distinction agent in MRI scans and a fluorescing agent for strategy-infrared fluorescence imaging. Photos of blood vessels and organs in stay our bodies is also bought with the 2 imaging ways by additional modifying the nanoparticle surfaces with polyethylene glycol (PEG)-basically based fully mostly polymers. However to toughen listing resolution, scientists must possess more defend a watch on over nanoparticle size for the duration of the fabrication route of.
Okubo and his colleagues used a step-by-step fabrication route of that begins with mixing rare earth oxides in water and trifluoracetic acid. The aggregate is heated to create a solid. Then it’s dissolved in resolution, oleic acid is added and gasoline is eliminated. So-called rare-earth-doped ceramic nanoparticles create when this resolution is cooled.
A few more steps result within the coating of the nanoparticle surfaces with PEG. The scientists found they could tiresome the expansion charge of the nanoparticles by increasing their concentration sooner than the coating route of. This allowed them to create nanoparticles 15 and 45 nanometres in diameter.
The crew conducted a bunch of tests to survey the properties of their nanoparticles. They found that they’ll be used for acquiring excessive-quality photos of blood vessels in stay mice utilizing MRI and strategy-infrared fluorescence imaging ways. Further tests confirmed the nanoparticles exhibited minimal toxicity on mouse fibroblast cells when utilized in low concentrations. They moreover possess a transient half of-life, which manner they’d be cleared reasonably fleet from the physique, making them safe for scientific exercise.
The crew subsequent aims to research how reasonably a few distributions of paramagnetic ions on the nanoparticles possess an affect on their magnetic properties. They moreover goal to be aware whether modifications made to the nanoparticles could make them acceptable for exercise in light-basically based fully mostly ‘photodynamic’ therapies for treating skin cancers and acne, for example.
More records:
Kyohei Okubo et al. Dimension-managed bimodal in vivo nanoprobes as strategy-infrared phosphors and optimistic distinction agents for magnetic resonance imaging, Science and Technology of Developed Materials (2021). DOI: 10.1080/14686996.2021.1887712
Citation:
A nanoparticle’s size is dazzling-tuned to provide excessive-resolution photos sooner than and for the duration of surgical procedures (2021, March 10)
retrieved 10 March 2021
from https://phys.org/records/2021-03-nanoparticle-size-dazzling-tuned-excessive-resolution-photos.html
This doc is enviornment to copyright. Other than any handsome dealing for the goal of non-public watch or evaluation, no
portion is inclined to be reproduced with out the written permission. The converse material is equipped for records functions easiest.