
Are We Doing Sufficient to Offer protection to Earth from Asteroids?
When Edgard Rivera-Valentín, a workers scientist on the Lunar and Planetary Institute and previously piece of the planetary radar team at Arecibo, clicked on the video, they would possibly well abdomen most intelligent about a seconds. It took them days to salvage thru the paunchy two minutes. “When all the pieces went down, it changed into—I employ the notice ‘tragedy,’” says Rivera-Valentín, a local of Puerto Rico.
Arecibo had a prolonged and storied legacy of scientific discovery, finding out web page online weather, browsing for extraterrestrials, timing pulsars, mapping unbiased hydrogen gas. However it completely additionally had an unconventional assert to popularity: It boasted the arena’s most extremely effective, sensitive and filled with life planetary radar machine. That radar would possibly well peer thru Venus’s thick environment and draw the dusty Martian surface, but it additionally helped offer protection to Earth from asteroids. The records confirmed scientists those rocks in assert, published whether they would possibly well most up-to-date a possibility, and helped humans figure out what they would possibly well moderately conclude if an asteroid changed into heading our formulation. “Considered one of the neat issues about doing radar is that you just are actively defending the total Earth,” Rivera-Valentín says. “So if any individual asks you, ‘Why would possibly well tranquil I care?,’ it be indulge in, ‘I will be certain asteroid would now not attain for you.’”
Arecibo’s radar efforts fell below the umbrella of “planetary defense”: the strive to name and forestall doable collisions between asteroids (and comets) and this planet, which, ideally, we would possibly well perchance indulge in to purchase care of intact.
On any given day the chance is low that a web page online rock will devastatingly rupture into Earth. However the penalties of this form of anguish would possibly well perchance be extreme. And our describe voltaic machine’s history—planets pocked with craters, crashes on other planets in fresh memory, worthy objects hurtling thru Earth’s environment and captured on dashcams—demonstrates the statistical fact that events unlikely to happen on any given day conclude happen, given enough days. That’s why NASA has a entire office devoted to the discipline; why a slew of gargantuan services and products resolve on preventive recordsdata; and why an upcoming web page online mission will present what earthlings can conclude if a web page online rock does attain knocking.
However is it enough? With Arecibo and its radar out of commission, our planetary defense arsenal comes up immediate. The U.S. and other countries are assessing the priority, brainstorming fresh methods to prevent earlier than the possibility and formulating plans for what would possibly well attain next.
Counting Dwelling Rocks
Planetary defense has been tormented by a “giggle assert.” In spite of all the pieces, apocalypse by asteroid appears the stuff of characteristic films, now not critical science. However officers began to pay extra consideration soon after a comet called Shoemaker-Levy headed straight for Jupiter in 1994. Linda Billings, a expert for NASA’s planetary defense communications efforts, remembers when the two collided. On July 21, 1994—about a days into a series of impacts—she went to an commence house on the Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., the place aside sky watchers would possibly well stare on Jupiter. On the lawn commence air, amateur astronomers expert their possess devices on the scarred planet. Jupiter’s gravity had shredded the comet into objects, which streamed into the planet’s swirling environment, reaching 40,000 degrees Celsius and sending 3,000-kilometer-high plumes of discipline materials shooting into web page online. “We had stable evidence that impacts happen,” Billings says, understatedly.
Soon after, U.S. Air Power officers printed two experiences, SpaceCast 2020 and Air Power 2025, on what the militia would possibly well or would possibly well tranquil conclude to mitigate the specter of web page online rocks in the impending decades. Dwelling impacts had been a national security discipline. The predominant document, meant to identify how the U.S. would possibly well build the “high ground” in web page online, coined the timeframe “planetary defense.” The 2nd had great the an analogous function, and both described asteroid detection and mitigation, the notice for efforts to dispense with a possibility if one arises—by, for instance, deflecting an asteroid by slamming into it with a spacecraft or exploding a nuclear weapon nearby.
Abet then, scientists now smartly identified for their planetary protection work had been piece of the air force—of us equivalent to Lindley Johnson, now program executive of NASA’s Planetary Protection Coordination Administrative center (and an creator of the relevant piece of SpaceCast), and Pete Worden, dilapidated director of NASA’s Ames Analysis Heart. They and their colleagues warned relating to the priority of civilization changing into a crater. However significantly after 9/11, the spot failed to fetch as great consideration as many would have cherished. Johnson retired from filled with life accountability in 2003. “NASA said, ‘Advance on over. We now have bought a job for you,’” he says. Considered one of his duties changed into to drag NASA’s Shut to-Earth Object Observations program. This present day, in gigantic piece a outcomes of Johnson’s efforts, that has mushroomed into a entire Planetary Protection Coordination Administrative center, the place aside he is the boss. “An unwarned influence would possibly well perchance be the greatest natural anguish we have ever seen, rather frankly,” Johnson says. His office hopes to invent any hypothetical influence an avoidable one.
To that conclude, NASA’s office runs asteroid recordsdata-gathering programs, relying in piece on huge-field optical and infrared telescopes that can gaze a abundant expanse of the sky. Observatories drag by the University of Arizona and the University of Hawaii have worked with Johnson’s office to adapt their present telescopes into sentries. The team additionally repurposed the net site online-based Wide Put Infrared Ticket Explorer (WISE) into NEOWISE (Shut to-Earth Object WISE) in the years after it changed into before all the pieces decommissioned in 2011. NEOWISE now not too prolonged in the past finished its 14th all-sky perceive and is working on its 15th.
Within the meantime M.I.T. Lincoln Laboratory’s Lincoln Shut to-Earth Asteroid Analysis (LINEAR) plot is for the time being place in on an air force asset called the Dwelling Surveillance Telescope (SST) in Australia. The plot makes this militia observatory the arena’s most intelligent asteroid-looking instrument, by some metrics. It has chanced on 142 previously unknown shut to-Earth objects, four presumably dangerous objects and eight fresh comets.
That’s good but now not as ethical as Congress would indulge in. The legitimate mandate this train day is to interrogate 90 percent of the objects that are 140 meters or greater—the size at which a development would outcome in “a tranquil defective day anyplace,” in step with Johnson. There are an estimated 25,000 such baddies. “We’re getting shut, and presumably by the conclude of the 300 and sixty five days we will have chanced on 10,000 of those,” he says. That is 40 percent completion for 20 years of effort. Total, scientists have chanced on higher than 25,000 shut to-Earth asteroids of any size, and round 19,000 of those caught on digital camera are higher than 30 meters.
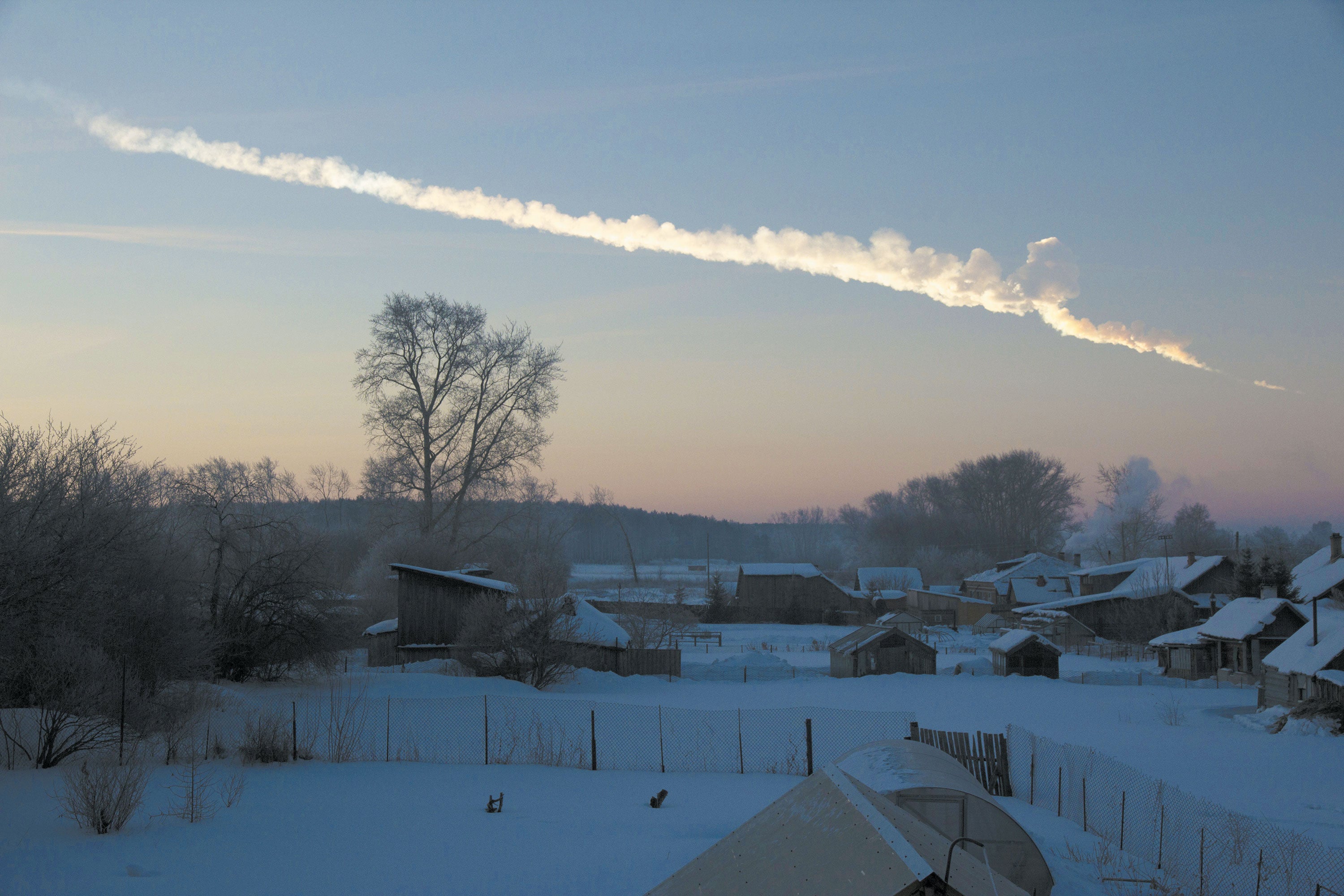

Replacing Arecibo
Globally, 30 web page online organizations—based in every single web page online from Latvia to Colombia, from China to Israel, and intriguing devoted amateurs, national web page online agencies and person observatories—take part in the Global Asteroid Warning Community. The team, formed on the advice of the United Nations, coordinates commentary and response efforts all the design thru our weak planet. Since 2016 it has logged higher than 300 shut approaches, when asteroids had been projected to return within one lunar distance—the standard distance between Earth and the moon—of the globe’s center. It has additionally coordinated three campaigns to observe “the staring at sources and characterization capabilities which is also applied to a shut to-Earth object on a fairly immediate timescale.”
That is priceless for the reason that work is now not accomplished when shut-calling objects are chanced on. Ground-based optical and infrared telescopes in areas equivalent to Hawaii, Contemporary Mexico and Arizona invent observe-up observations to be taught extra relating to the objects than the actual fact of their existence. Planetary radar, too, customarily plays a characteristic in refining the orbits of newly chanced on asteroids and projecting their paths into the prolonged drag—mapping out the place aside those objects will race in the years to return and whether they would possibly well intersect with Earth. Radar additionally helps to discern asteroids’ form, composition and trajectory.
Radar observations equivalent to Arecibo’s work indulge in this: Whenever you blast extremely effective radio waves toward the article, they leap support, modified by the article’s trip, circulation, form and size, as smartly as by any moons the asteroid would possibly well have. The time they purchase to holler support additionally exhibits the article’s right distance from Earth. With all that records, that you just can well refine its orbit and predict the place aside this would possibly well additionally be a ways into the prolonged drag and whether that “the place aside” comprises Iowa. You would also additionally be taught about its properties—priceless if you happen to wish to knock it off target. Is it dense? Porous? Round? Peanutty? “After we document the echo that comes support, if it be varied in any formulation from what we transmitted, all americans knows that changed into attributable to the properties of the target, on this case, the asteroid,” says Patrick Taylor, a senior workers scientist on the Lunar and Planetary Institute and dilapidated team lead for Arecibo’s radar program.
Getting a radar commentary is indulge in taking a describe of the asteroid from the protection of the ground. “That is form of indulge in a flyby of a spacecraft at a small half of the price,” says Ellen Howell of the University of Arizona. “We salvage photos of them as person rocks, now not ethical points of gentle.” Which is critical, on account of as planetary scientists are fond of pronouncing, if you happen to’ve got got seen one asteroid, you’ve got got got seen one asteroid. With the lack of Arecibo, Howell says, “that functionality is now severely diminished.” This skill to purchase observations of the most fresh, predict the prolonged drag after which change the prolonged drag is what would possibly well space us moreover the wretched saps of the previous, who ethical needed to purchase no topic knocks web page online despatched their formulation. “Dinosaurs did not have a web page online program,” Rivera-Valentín says. “However we conclude.”
Arecibo changed into now not the most intelligent planetary radar in the U.S. There’s one left—the Goldstone Solar Gadget Radar in California—but it would possibly perchance perchance perchance detect now not as a lot as half of the shut to-Earth asteroids that Arecibo would possibly well. And despite the undeniable fact that Goldstone had been the finest instrument, stuff occurs, and if it’s down—as it changed into for round 18 months of repairs ethical earlier than Arecibo collapsed—this planet will must fly thru web page online without seeing as great as it previously did. “Dropping Arecibo goes to invent of us reflect extra about what that next-generation step shall be,” Taylor says. “No topic that is, I manufacture now not know.”
Scientists have tips. Some would indulge in to manufacture Arecibo 2.0, synthesizing a series of smaller dishes in the an analogous island space to work collectively as one greater dish, thereby restoring radar capabilities. At Green Bank Observatory in West Virginia, scientists ethical did their possess demo with defense contractor Raytheon, beaming a radar stamp to the moon and receiving the leap-support at antennas unfold at some level of the U.S. in the Very Long Baseline Array, which is operated from Contemporary Mexico. They hope this would possibly well perchance pave the formulation for a setup with extra oomph that would possibly well conclude asteroid work. “The Green Bank proposal for toughen sounds terrific to me,” Billings says. “However it completely’s now not but funded.”
And despite the undeniable fact that it had been, Michael Nolan of the University of Arizona doubts that Green Bank would possibly well change Arecibo’s capabilities. Transmitting from one space and picking up in a single more is a recordsdata-intensive means, and doing both from Green Bank has its possess points. “I manufacture now not gaze any of the issues I’ve seen to this level being the workhorse machine,” he says. Arecibo’s hypothetical replace would now not have funding either, for instance.
And the ask of what to entire is most intelligent the first hurdle. There’s additionally the greater spot of who would possibly well tranquil conclude it. Some consultants argue that the burden is simply too great for the scientific team to have by myself. Most most definitely, they articulate, the process would possibly well tranquil descend to a company with intensive ride in prolonged-timeframe planning and, extra critical, stable funding. In other words, the Division of Protection—namely, its newly minted Dwelling Power.
Stopping Asteroids
The Dwelling Power, a fresh branch of the militia that largely offers with satellites and their safety and security, targets to trace objects gigantic and exiguous, from here to the moon, as worldwide and industrial process—satellites, spacecraft, orbital manufacturing methods, pay-as-you-race journeys—ramps up. That total effort is known as web page online situational awareness, and it’s a ways assuredly applied by optical devices and prolonged-differ radar. While that radar is monitoring the process in orbit, it would possibly perchance perchance well additionally detect asteroids that happen to be zooming thru web page online in the an analogous course as (but, it’s hoped, great farther out than) a satellite. NASA and Dwelling Power officers have been talking about taking part on this form of resolve on-resolve on machine. “It’s miles previous ethical brainstorming, but we have no longer settled on a particular idea but,” says Johnson, noting that the discussions are ongoing. In 2020 the two organizations signed a memorandum of conception, agreeing to work collectively on sure issues—including both planetary defense and web page online situational awareness. The Dwelling Power referred questions relating to the collaboration support to NASA.
Some, although, are attempting to amplify the premise of militia involvement. Peter Garretson, a senior fellow on the American Distant places Coverage Council and dilapidated director of Air University’s Dwelling Horizons Analysis Job Power, would indulge in to observe the militia lead planetary defense efforts, significantly mitigation. “NASA is largely a science and exploration agency. In my leer, here is clearly a defense mission,” Garretson says. “You would also very smartly be now not deflecting the asteroid for science.”
And really no federal organization is namely tasked with deflecting asteroids. However of us are working on it anyway. One agency steeped in the problem is the Division of Vitality—you realize, the one with the nukes. At Los Alamos National Laboratory, Cathy Plesko does asteroid mitigation study. She bought into planetary defense by finding out influence craters on Mars the usage of computer objects. “However how conclude you stop making a crater?” she questioned. Within the future a senior astrophysicist on the lab said he belief the an analogous kinds of code she ragged to mannequin the craters would possibly well very smartly be ragged to mannequin asteroid mitigation: They would show how an asteroid would react if something impacted it—in web page online of if it impacted something. This changed into the very stoppage she changed into wondering about.

She began finding out the discipline, however the lab’s efforts weren’t intensive—till February 2013. That month a 20-meter-huge asteroid screamed thru the environment and exploded almost 30 kilometers above Chelyabinsk Oblast in Russia with the force of round 450 kilotons of TNT, injuring 1,600 of us. As with Shoemaker-Levy, officers opened their eyes wider. Plesko’s team spooled up and, along with NASA, began scrambling to grasp shut what physics considerations they wished to resolve to answer if something higher and badder came along. That work begins with revealing what asteroids are fabricated from, a surprisingly hard discipline to which radar provides the most classic Earth-based resolution. “Are they rubble piles? Are they form of mud balls? Are they chunks of iron?” Plesko asks. “There’s loads of diversity.” That diversity makes simulations hard. Whenever you are modeling a airplane on a computer, you realize exactly how dense it’s and how it’s shaped. “We do now not have those specs for asteroids and comets,” she says. “That’s something we have now to Determine.”
This present day Plesko examines the plethora of potentialities to rush varied kinds of asteroids a ways from the globe. One choice is known as a gravity tractor. You fly as heavy a spacecraft as that you just can well muster as shut to a web page online rock as that you just can well sidle. “Your spacecraft can fetch of lure the asteroid or the comet off its fashioned course over time,” she says. However it completely requires decades of luring, and the technology, she estimates, is now not going to be ready for a century or so.
Some scientists have seemed on the usage of lasers connected to exiguous spacecraft to warmth up discipline materials and vaporize it, throwing it off the surface and thus—every circulation leading to a single more equal and reverse—pushing the asteroid in the opposite course. More bluntly, one would possibly well additionally slam an asteroid with a spacecraft earlier than it slams into Earth. Alternatively: Shine a reflect at it, focusing describe voltaic rays, till it sheds discipline materials. Hobble it with rockets. Paint it to change its thermal properties and thus its orbit. Plesko, being on the Division of Vitality, additionally study the boomier menu choice: a “nuclear standoff burst.” Meaning detonating a nuclear weapon shut to a shut to-Earth object, transferring vitality and throwing off some discipline materials. That deflects the rock ethical indulge in the opposite ways, most intelligent extra, you realize, emphatically. However study on exploding bombs on or below the surface of an asteroid indicate that they would possibly well damage up into smaller objects that most up-to-date their possess considerations. Either formulation, this choice gets complex rapidly given the character of nuclear bombs and the worldwide ban on putting weapons of mass destruction in web page online. A nation would possibly well employ “prepping for asteroids” as an excuse for nuclear proliferation; moreover, an asteroid is a world possibility, but a single nation would possibly well perchance be the usage of its possess arsenal to battle it. “No one takes that evenly,” Plesko says.
Every two years the worldwide team stages a Dungeons-and-Dragons-fashion characteristic-taking half in game, all over which agencies act out their response to a fictional planetary defense spot. Records relating to the “influence spot” gets posted on-line earlier than time, with extra published on day by day foundation in PowerPoint-fashion briefings. In 2019, earlier than their arrival on the conference, participants knew a rock between 100 and 300 meters all the design thru had a 1 percent change of hitting Earth eight years in due course. By day three they knew it changed into 260 meters prolonged and 140 meters huge, dreary space on a straight course to Denver.
While the team developed a mission to deflect the discipline object, a broken-off piece 60 meters all the design thru nonetheless space a course for The ny. The characteristic avid gamers switched to anguish-dealing mode, taking a watch on the fashion to evacuate, what to entire about chemical factories and nuclear vegetation, and what the industrial fallout would watch indulge in. The gamers returned to the tabletop this 300 and sixty five days (by job of videoconference) to analyze an asteroid that would possibly well attain calling in exactly six months. The total declare “provides a fact take a look at on how prolonged it takes to entire issues,” Plesko says. It be now not indulge in in Hollywood, she adds, which fits extra indulge in, “An asteroid is chanced on; let’s launch the thing.” Mild, responding in a critical formulation is something humans can conclude, despite the undeniable fact that extra slowly than on-show hide.
A Test Urge
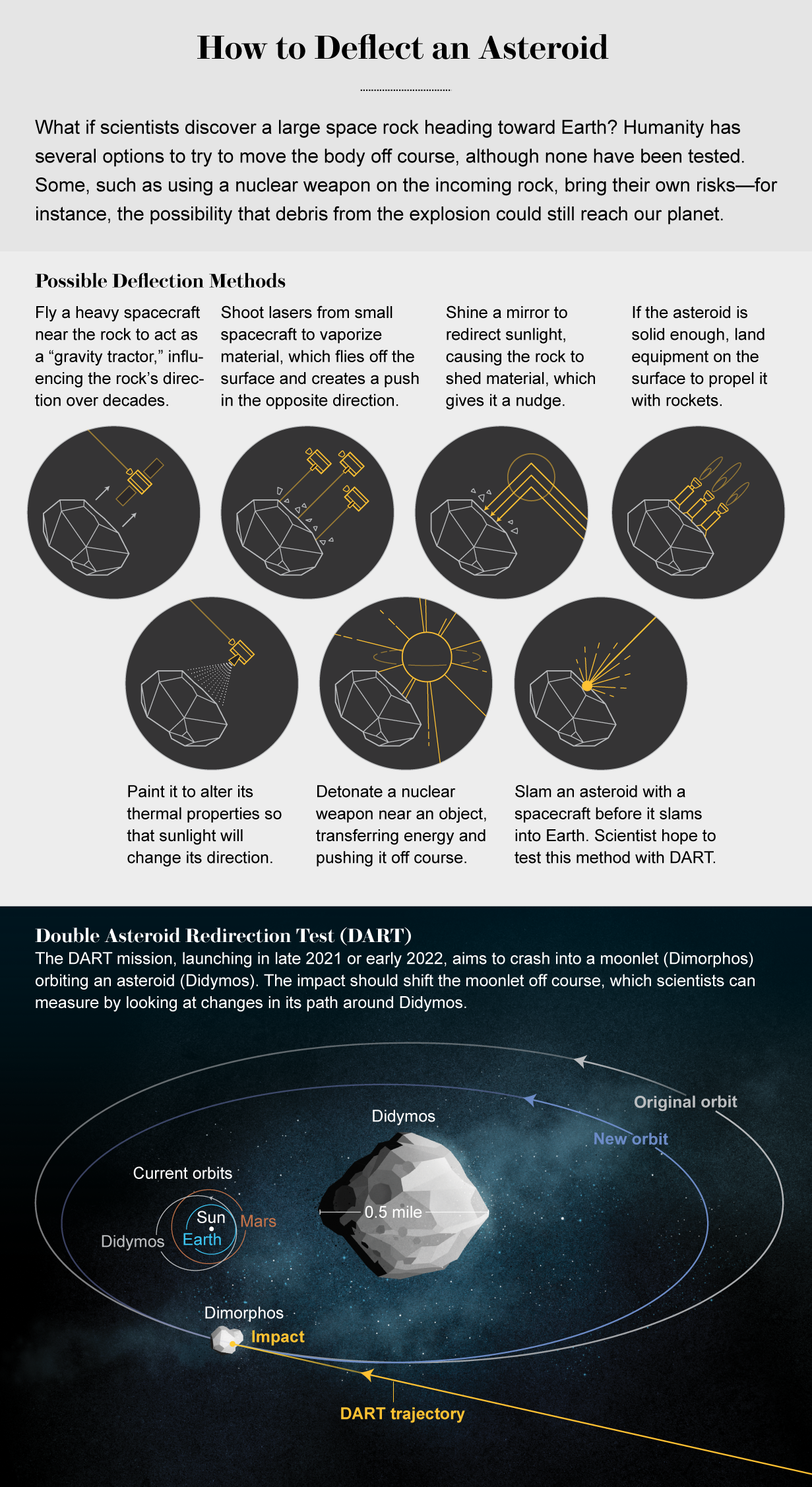
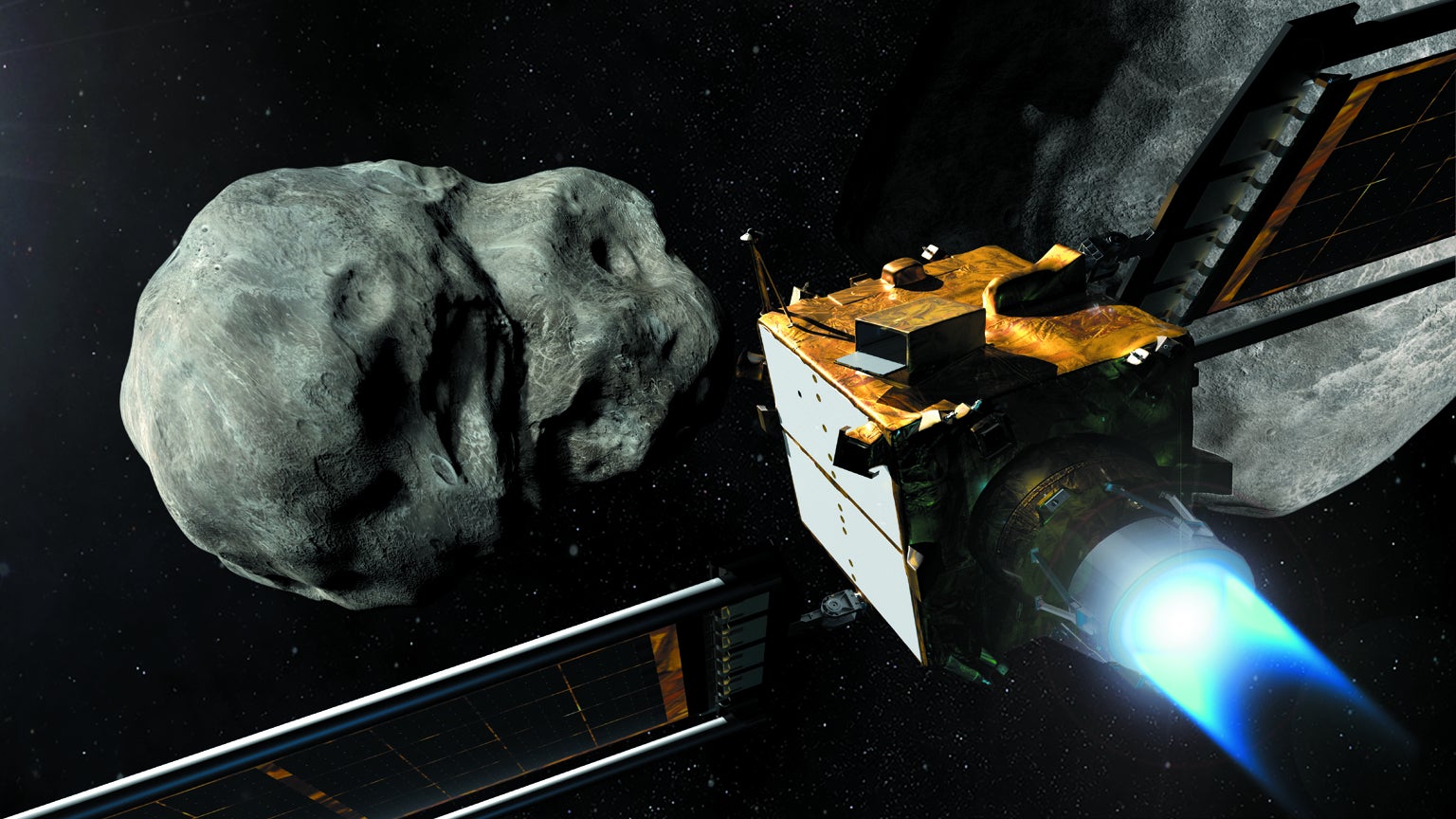
Soon an dauntless mission will take a look at our skill to race mountains in web page online. Due to launch in dull 2021 or early 2022, DART—the Double Asteroid Redirection Test—will aim to tell that we are going to change an asteroid’s direction indulge in that of a wayward teen. Andrew Rivkin of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), regarded as one of the mission’s investigation team leads, began finding out asteroids for the main science—the “origins of the describe voltaic machine” stuff. “No topic what you are making an are trying to answer to, it form of comes support to asteroids one design or the opposite,” he says. Plus, he adds, that you just can well steal objects of them on eBay.
Otherwise that you just can well manufacture a spacecraft to shove one round, as Rivkin is now doing. DART will plod to the Didymos machine, which has a gigantic asteroid called Didymos and a exiguous moon called Dimorphos. Then the spacecraft will slam into the moon, altering its orbit round its higher sibling and thus the higher sibling’s circulation around the sun. The 610-kilogram spacecraft will hit the 4.8-billion-kilogram (“exiguous”) Dimorphos at a urge of 6.58 kilometers per 2nd, altering (scientists reflect) its orbital duration by about 10 minutes. Because Dimorphos itself is the size of an asteroid that would possibly well endanger cities, scientists hope to observe how smartly they would possibly be able to transfer momentum from a spacecraft to a web page online rock. It’s miles the medium-sized mitigation choice, halfway between “you nuke it, or you veil in the basement,” as Rivkin frames it. It’s miles additionally combating an influence by making an influence. The total methodology would work in single-asteroid methods, too—that you just can well slam a spacecraft into a loner—but scientists have a ethical reason for picking a double machine for this take a look at: it’s easy to measure how great you modified a moon’s orbit on account of that you just can well ethical note it race in entrance of the greater asteroid in right time.
Scientists will salvage their first leer of the machine—as a single pixel—a couple of month earlier than the smashup in 2022. “That one pixel is what we’re making an are trying to manual toward,” says Elena Adams of APL, the mission methods engineer. An hour earlier than arrival, they’ll watch the moon and starting up up navigating toward it. “And then bam, we lose all contact, which is ethical,” Adams says. It means issues have long previous development. (“Any individual pays you to entire that, true?” Adams exults. “You salvage to destroy a $250-million spacecraft!”)
The team hopes that the Goldstone radar, as smartly as web page online telescopes, will additionally note the show. “We hoped Arecibo would,” Rivkin says sadly. The records gathered, then and after the actual fact, shall be fed into future objects that scientists equivalent to Plesko employ to resolve the fashion to answer to an right asteroid possibility. “Programs indulge in DART, they’re insurance in case we conclude gain something,” Rivkin says. Folks pay for fireplace insurance and flood insurance; they take a look at their basements for radon. “We’re hoping and prepared for that the radon take a look at is now not going to gain any radon and the house is now not going to purchase fireplace or flood, but we’re form of doing our due diligence.”
Even although Rivkin is delighted of us no longer reflect of planetary defense as a silly story and instead aside can fathom the utility of cosmic insurance, he cautions in opposition to web page online rock dread. “If of us are being saved up at evening by asteroids, with a little bit of luck it be desirous relating to the total cold science,” he says. It’s miles that science, in level of fact—determining the fashion to detect, track, project and symbolize these lonesome vacationers—that lets to your entire of planetary defense. And planetary defense, in flip, enables humans to wrest some preserve watch over from the cosmos. “Right here’s the first time as a species we have now the alternative to forestall a natural anguish,” Plesko says. “We can now not stop a hurricane or prevent earthquakes. We can now not ethical race superglue the San Andreas Fault shut.” However stopping a planet killer? “If we wished to,” she says, “I really conclude factor in we are going to even conclude this.”
Editor’s Point to (5/20/21): This text changed into updated after posting to include Andrew Rivkin’s and Elena Adams’s affiliation.