
Astronomers derive cloud atlas for first price, Jupiter-like exoplanets
Big planets in our solar system and circling diversified stars receive outlandish clouds now not just like the rest on Earth, and the gasoline giants orbiting shut to their stars—so-known as sizzling Jupiters—boast essentially the most monstrous.
A crew of astronomers from the united states, Canada and the UK receive now come up with a mannequin that predicts which of the many forms of proposed clouds, from sapphire to smoggy methane haze, to query on sizzling Jupiters of diversified temperatures, as much as thousands of levels Kelvin.
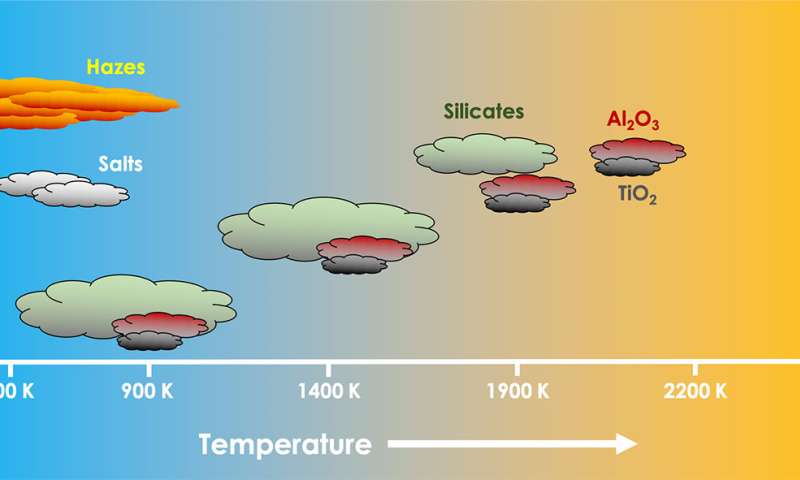
Surprisingly, essentially the most usual invent of cloud, anticipated over a astronomical vary of temperatures, might possibly possibly simply accrued consist of liquid or strong droplets of silicon and oxygen, like melted quartz or molten sand. On cooler sizzling Jupiters, below about 950 Kelvin (1,250 levels Fahrenheit), skies are dominated by a hydrocarbon haze, no doubt smog.
The mannequin can support astronomers studying the gases within the atmospheres of these weird and wonderful and distant worlds, since clouds interfere with measurements of the atmospheric composition. It is some distance going to also moreover support planetary scientists realize the atmospheres of cooler broad planets and their moons, much like Jupiter and Saturn’s moon Titan in our possess solar system.
“The forms of clouds that might possibly possibly exist in these sizzling atmospheres are issues that we don’t in actual fact accept as true with as clouds within the solar system,” talked about Peter Gao, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of California, Berkeley, who is first author of a paper describing the mannequin that appeared Would possibly possibly possibly 25 within the journal Nature Astronomy. “There had been objects that predict diversified compositions, but the purpose of this explore change into once to assess which of these compositions in actual fact topic and compare the mannequin to the available info that we receive.”
The explore takes good thing about a verbalize over the past decade within the explore of exoplanet atmospheres. Even supposing exoplanets are too distant and unlit to be visible, many telescopes—namely, the Hubble Dwelling Telescope—are ready to apartment stars and buy starlight passing by the atmospheres of planets as they cross in entrance of their stars. The wavelengths of light that are absorbed, printed by spectroscopic measurements, speak astronomers which parts assemble up the ambiance. Thus some distance, this variety and others receive learned or inferred the presence of water, methane, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, potassium and sodium gases and, in essentially the most updated of the planets, vaporized aluminum oxide, iron and titanium.
Nonetheless whereas some planets appear to receive clear atmospheres and clear spectroscopic aspects, many receive clouds that entirely block the starlight filtering by, preventing the explore of gases below the upper cloud layers. The compositions of the gases can speak astronomers how exoplanets invent and whether or now now not the constructing blocks of life are insist spherical diversified stars.
“Now we receive learned diverse clouds: some forms of particles—now now not molecules, but tiny droplets—that are placing out in these atmospheres,” Gao talked about. “We do now not in actual fact know what they’re made from, but they’re contaminating our observations, no doubt making it more advanced for us to assess the composition and abundances of worthy molecules, like water and methane.”
Ruby clouds
To speak these observations, astronomers receive proposed many weird and wonderful forms of clouds, composed of aluminum oxides, much like corundum, the stuff of rubies and sapphires; molten salt, much like potassium chloride; silicon oxides, or silicates, like quartz, the principle factor of sand; sulfides of manganese or zinc that exist as rocks on Earth; and organic hydrocarbon compounds. The clouds can even be liquid or strong aerosols, Gao talked about.
Gao adapted pc objects first and foremost created for Earth’s water clouds and subsequently extended to the cloudy atmospheres of planets like Jupiter, which has ammonia and methane clouds. He expanded the mannequin even extra to the worthy increased temperatures considered on sizzling gasoline broad planets—as much as 2,800 Kelvin, or 4,600 levels Fahrenheit (2,500 levels Celsius)—and the parts prone to condense into clouds at these temperatures.
The mannequin takes into yarn how gases of a massive different of atoms or molecules condense into droplets, how these droplets develop or evaporate and whether or now now not they’re inclined to be transported within the ambiance by winds or updrafts, or sink due to gravity.
“The premise is that the identical bodily principles e book the formation of all forms of clouds,” talked about Gao, who has moreover modeled sulfuric acid clouds on Venus. “What I receive done is to prefer this mannequin and elevate it out to the remainder of the galaxy, making it ready to simulate silicate clouds and iron clouds and salt clouds.”
He then compared his predictions to available info on 30 exoplanets out of a entire of about 70 transiting exoplanets with recorded transmission spectra to this point.
The mannequin printed that just a few the outlandish clouds proposed over time are advanced to invent since the power required to condense the gases is too excessive. Silicate clouds condense with out inconvenience, on the opposite hand, and dominate over a 1,200-stage Kelvin vary of temperatures: from about 900 to 2,000 Kelvin. That’s a unfold of about 2,000 levels Fahrenheit.
Per the mannequin, in essentially the most updated atmospheres, aluminum oxides and titanium oxides condense into excessive-level clouds. In exoplanets with cooler atmospheres, these clouds invent deeper within the planet and are obscured by increased silicate clouds. On even cooler exoplanets, these silicate clouds moreover invent deeper within the ambiance, leaving clear greater atmospheres. At even cooler temperatures, ultraviolet light from the exoplanet’s star converts organic molecules like methane into extremely long hydrocarbon chains that invent a excessive-level haze identical to smog. This smog can obscure decrease-lying salt clouds of potassium or sodium chloride.
For these astronomers looking for a cloudless planet to more with out inconvenience explore the gases within the ambiance, Gao suggested focusing on planets between about 900 and 1,400 Kelvin, or these hotter than about 2,200 Kelvin.
“The presence of clouds has been measured in a different of exoplanet atmospheres sooner than, but it is miles once we glance collectively at a astronomical sample that we are capable of receive aside the physics and chemistry within the atmospheres of these worlds,” talked about co-author Hannah Wakeford, an astrophysicist at the University of Bristol within the U.Okay. “The dominant cloud species is as traditional as sand—it is miles now not any doubt sand—and this will be in actual fact thrilling to be capable to measure the spectral signatures of the clouds themselves for the first time with the upcoming James Webb Dwelling Telescope (JWST).”
Future observations, much like these by NASA’s JWST, scheduled for launch within a couple of years, might possibly possibly simply accrued be ready to substantiate these predictions and more than likely shed light on the hidden cloud layers of planets nearer to house. Gao talked about that identical outlandish clouds might possibly possibly simply exist at depths within Jupiter or Saturn where the temperatures are shut to those learned on sizzling Jupiters.
“On yarn of there are millions of exoplanets versus correct one Jupiter, we are capable of explore a bunch of them and seek what the everyday is and how that compares to Jupiter,” Gao talked about.
He and his colleagues idea to take a look at the mannequin towards observational info from diversified exoplanets and moreover from brown dwarfs, which are typically gasoline broad planets so huge they’re nearly stars. They, too, receive clouds.
“In studying planetary atmospheres within the solar system, we typically receive the context of images. We would now now not receive such a good fortune with exoplanets. They are correct dots or shadows,” talked about Jonathan Fortney of UC Santa Cruz. “That’s a massive loss in info. Nonetheless what we enact must assemble up for that might possibly possibly even be a worthy increased sample dimension. And that lets in us to explore developments—right here, a kind in cloudiness—with planetary temperature, one thing that we correct would now now not receive the lush of in our solar system.”
Extra info:
Peter Gao et al. Aerosol composition of sizzling broad exoplanets dominated by silicates and hydrocarbon hazes, Nature Astronomy (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-020-1114-3
Citation:
Astronomers derive cloud atlas for first price, Jupiter-like exoplanets (2020, Would possibly possibly possibly 26)
retrieved 26 Would possibly possibly possibly 2020
from https://phys.org/info/2020-05-astronomers-cloud-atlas-sizzling-jupiter-like.html
This file is topic to copyright. Rather then any lovely dealing for the explanation of personal explore or be taught, no
portion shall be reproduced with out the written permission. The inform is geared up for info capabilities very finest.