
Chip-basically basically based optical tweezers levitate nanoparticles in a vacuum
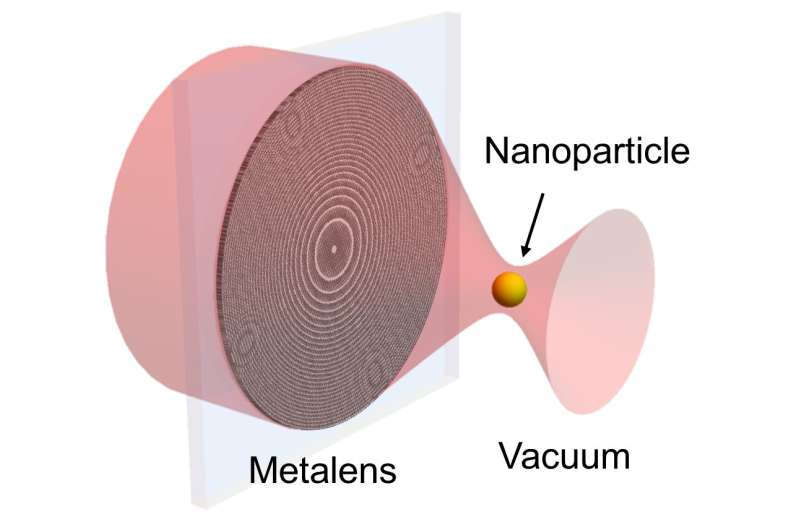
Researchers maintain created cramped chip-basically basically based optical tweezers which would maybe even be extinct to optically levitate nanoparticles in a vacuum. Optical tweezers—which make spend of a tightly centered laser beam to abet living cells, nanoparticles and various objects—would possibly maybe additionally be extinct for a good deal of precision measurements and sensing applications. However, these optical traps are repeatedly produced with beefy optical substances.
“By the spend of an ultrathin metalens, we reduced the diameter of the focusing lens from about 25 mm to about 0.4 mm,” said study team chief Tongcang Li from Purdue University. “The chip-basically basically based construct would possibly maybe additionally be extinct to win an integrated and versatile optical way for studying near-ground forces by trapping an object not as a lot as 1 micrometer a ways from a ground. It’ll even be helpful for trapping frosty atoms in a vacuum to appear quantum processes.”
In Optica journal, researchers at Purdue University and Pennsylvania Teach University file the first realization of on-chip optical levitation in a vacuum with an ultrathin metalens. Conducting this feat in a vacuum helps enhance the sensitivity of how.
“Optically levitated particles would possibly maybe additionally be extinct to win accelerometers and gyroscopes that will potentially be extinct in navigation,” said Li. “Scientists are also the spend of optically levitated particles to understand for darkish matter and darkish energy and to appear gravity at brief distances, which will deepen our working out of nature.”
Toward a portable entice
This contemporary study grows out of outdated work wherein the researchers extinct optical levitation in a vacuum to win the quickest human-made rotor and the most sensitive torque detector ever reported.
“As a next step, we wished to make optical levitation abilities extra useful by minimizing the way ample to make it portable,” said Li. “We started by cutting back the scale of the focusing lens by the spend of a metalens, a win of flat lens that uses nanostructures to focal level light.”
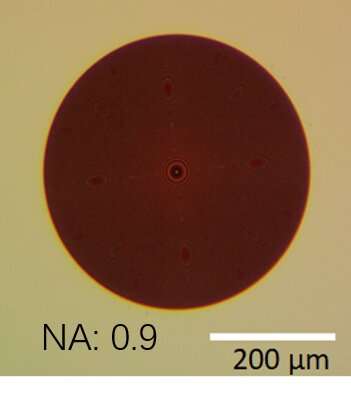
Within the contemporary work, the researchers designed a metalens consisting of hundreds of silicon nanopillars. The diameter of the metalens modified into about 50 instances smaller than that of the veteran honest lens that they extinct sooner than.
“Other study groups maintain lately demonstrated metalens-basically basically based optical trapping in liquids,” said Kunhong Shen, the first author of this work. “Even supposing performing optical trapping in a vacuum helps cut noise from liquid or air, it is miles regularly powerful extra refined to attain.”
Levitating with a flat lens
To confirm their contemporary optical construct, the researchers guided an intense laser beam onto the metalens to generate trapping forces. They then sprayed a diluted nanoparticle resolution into the trapping space. When a nanoparticle becomes trapped, it would seem as a colorful space which would maybe even be seen with a camera. Photon detectors measured the nanoparticle’s circulation in valid time.
They confirmed that the metalens would possibly maybe levitate a nanoparticle in a vacuum at a tension of 2×10-4 Torr—about 1/4,000,000 atmospheric tension—without requiring any feedback stabilization. They had been also in a role to switch a levitating nanoparticle between two separate optical traps.
“Our metalens is a nanostructure layer with a thickness of merely 500 nm and a grand numerical aperture of about 0.9. It offers identical performance as a veteran beefy lens,” said study team chief Xingjie Ni from the Pennsylvania Teach University. “The metalens is fully vacuum-appropriate. And extra apparently, we can flexibly construct it to construct extra features, shall we embrace, filtering out low-spatial-frequency substances from the focusing light, which we maintain proven to be valuable for optical levitation of nanoparticles.”
The researchers are really working to enhance the cramped levitation devices by boosting the transmission and focusing effectivity of the metalens. Additionally they must make the diameter of the metalens even smaller to make optical levitation extra useful for valid-world applications.
More files:
Kunhong Shen et al, On-chip optical levitation with a metalens in vacuum, Optica (2021). DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.438410
Citation:
Chip-basically basically based optical tweezers levitate nanoparticles in a vacuum (2021, October 21)
retrieved 21 October 2021
from https://phys.org/files/2021-10-chip-basically basically based-optical-tweezers-levitate-nanoparticles.html
This doc is field to copyright. Other than any gorgeous dealing for the cause of private look or study, no
share would possibly maybe very properly be reproduced without the written permission. The remark is offered for files features fully.