
Community assembly trajectory of invertebrates in deadwood: Convergence after divergence
Natural forests have a elephantine quantity of deadwood, which is a key contributor to biodiversity. Deadwood affords habitats and sources for a elephantine diversity of organisms including invertebrates. The habitats and sources alternate at some stage in decomposition by microbial and invertebrate decomposers, and this in turn can have an effect on the associated organisms. Though there are many invertebrates in deadwood, puny is famous about their community dynamics, despite their elephantine importance for the woodland machine.
Researchers from the Life like Ecology Employees on the Wuhan Botanical Backyard, collaborating with researchers from Netherlands, investigated invertebrate communities in decomposing logs of 10 tree species over four years in two contrasting forests in Netherlands. Six faunal groups, Annelida (earthworms), Chilopoda (centipedes), Coleoptera (beetles), Diplopoda (millipedes), Diptera (flies, midges) and Isopoda (woodlice) had been studied.
In step with the researchers, invertebrate communities had been stricken by tree species, decay phases and incubation forests.
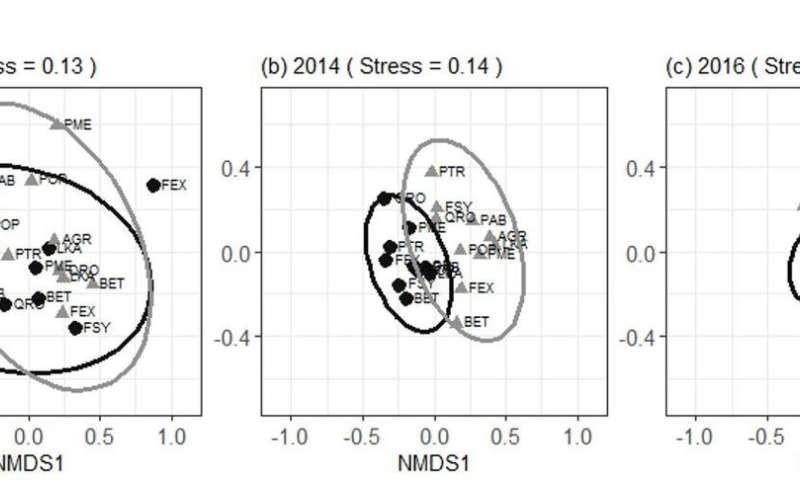
The fauna community composition in the logs on the foundation differed across tree species in the major year, which can presumably well very nicely be triggered by interspecific distinction in the unusual log aspects and traits. The initial decay affords a diversity of various microhabitats, microclimates in and underneath bark forms, and sources, including nutrients and sugars in unusual or degrading phloem and cambium. However the composition converged as bark and wooden decomposition progressed over four years of decay.
A similar patterns of divergence adopted by convergence had been noticed at three ranges of taxonomic resolution (major clades stage, household stage and species stage of macroinvertebrates) and at various hierarchical spatial scales (amongst tree species within residing and between contrasting forests).
This scrutinize has shown most indispensable trajectories of invertebrate community assembly in deadwood, with a key feature for results of deadwood properties on invertebrate community composition. It adds classic insights into the unusual ideas of succession, and emphasizes that more functionally various tree species and logs in various decay phases increase rich invertebrate fauna in woodland. These patterns may perhaps presumably well picture administration choices to promote woodland invertebrate diversity.
The scrutinize, published in the journal Ecosystems, is titled “Fauna community convergence at some stage in decomposition of deadwood across tree species and forests.”
Extra files:
Juan Zuo et al. Fauna Community Convergence At some level of Decomposition of Deadwood All the device in which thru Tree Species and Forests, Ecosystems (2020). DOI: 10.1007/s10021-020-00558-9
Quotation:
Community assembly trajectory of invertebrates in deadwood: Convergence after divergence (2020, December 10)
retrieved 10 December 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-12-trajectory-invertebrates-deadwood-convergence-divergence.html
This document is field to copyright. Besides any honest dealing for the reason of personal scrutinize or overview, no
share may perhaps presumably well very nicely be reproduced with out the written permission. The divulge material is out there for files functions handiest.