
Contemporary NIST mission to originate nano-thermometers might perchance perhaps perhaps revolutionize temperature imaging
Cheaper fridges? Stronger hip implants? A greater working out of human disease? All of these will likely be likely and more, someday, consequently of an formidable contemporary mission underway on the National Institute of Requirements and Technology (NIST).
NIST researchers are in the early stages of a massive enterprise to originate and originate a snappy of small extremely-sensitive thermometers. If they succeed, their system might perchance be the first to originate real-time measurements of temperature on the puny scale in an opaque three-D volume—which can perchance perhaps perhaps embody scientific implants, fridges, and even the human physique.
The mission is concept as Thermal Magnetic Imaging and Succor an eye on (Thermal MagIC), and the researchers hiss it might perchance perchance truly perchance perhaps perhaps revolutionize temperature measurements in many fields: biology, medication, chemical synthesis, refrigeration, the auto industry, plastic manufacturing—”quite necessary wherever temperature performs a necessary feature,” acknowledged NIST physicist Cindi Dennis. “And that’s the explanation in every single place.”
The NIST personnel has now finished building its personalized laboratory spaces for this irregular mission and has begun the first necessary section of the experiment.
Thermal MagIC will work by utilizing nanometer-sized objects whose magnetic signals commerce with temperature. The objects would be integrated into the liquids or solids being studied—the melted plastic that will likely be frail as section of an synthetic joint replacement, or the liquid coolant being recirculated thru a fridge. A miles away sensing system would then clutch up these magnetic signals, that methodology the system being studied would be free from wires or other pudgy exterior objects.
The closing product might perchance perhaps perhaps originate temperature measurements which would be 10 times more true than direct-of-the-paintings ways, received in a single-tenth the time in a volume 10,000 times smaller. This equates to measurements real to inner 25 millikelvin (thousandths of a kelvin) in as small as a tenth of a second, in a volume correct a hundred micrometers (millionths of a meter) on a facet. The measurements would be “traceable” to the Global Gadget of Units (SI); in other words, its readings will likely be accurately linked to the elementary definition of the kelvin, the enviornment’s frequent unit of temperature.
The system targets to measure temperatures over the vary from 200 to 400 kelvin (Sufficient), which is about -99 to 260 degrees Fahrenheit (F). This would conceal most doable capabilities—on the least the ones the Thermal MagIC personnel envisions will likely be likely for the length of the subsequent 5 years. Dennis and her colleagues observe doable for a necessary better temperature vary, stretching from 4 Sufficient-600 Sufficient, which would encompass all the things from supercooled superconductors to molten lead. However that is now not a section of most recent trend plans.
“Right here is a expansive enough sea commerce that we ask that if we are in a position to originate it—and we now like self assurance that we are in a position to—other other folks will decide it and genuinely bustle with it and attain things that we currently can not have faith in,” Dennis acknowledged.
Probably capabilities are largely in be taught and trend, but Dennis acknowledged the amplify in data would likely trickle the total way down to a unfold of merchandise, perhaps alongside side three-D printers, fridges, and medicines.
What Is It Staunch For?
Whether or now not it be the thermostat for your lounge or a high-precision regular instrument that scientists exercise for laboratory measurements, most thermometers frail at present can simplest measure pretty expansive areas—on a macroscopic versus puny stage. These feeble thermometers are also intrusive, requiring sensors to penetrate the system being measured and to join to a readout system by pudgy wires.
Infrared thermometers, such because the forehead instruments frail at many doctors’ workplaces, are much less intrusive. However they easy simplest originate macroscopic measurements and can’t observe below surfaces.
Thermal MagIC ought to let scientists win around each these boundaries, Dennis acknowledged.
Engineers might perchance perhaps perhaps exercise Thermal MagIC to perceive, for the first time, how warmth transfer occurs inner pretty plenty of coolants on the microscale, which can perchance perhaps perhaps relief their quest to seek out more inexpensive, much less vitality-intensive refrigeration programs.
Medical doctors might perchance perhaps perhaps exercise Thermal MagIC to perceive diseases, many of that are linked with temperature will increase—an indicator of irritation—namely parts of the physique.
And producers might perchance perhaps perhaps exercise the system to better administration three-D printing machines that soften plastic to originate personalized objects comparable to scientific implants and prostheses. Without the means to measure temperature on the microscale, three-D printing developers are lacking wanted data about what goes on on for the length of the plastic because it solidifies into an object. Extra data might perchance perhaps perhaps reinforce the strength and quality of three-D-printed supplies someday, by giving engineers more administration over the three-D printing process.
Giving It OOMMF
The first step in making this contemporary thermometry system is creating nano-sized magnets that can present off solid magnetic signals per temperature changes. To sustain particle concentrations as low as likely, the magnets will must be 10 times more sensitive to temperature changes than any objects that currently exist.
To win that more or much less signal, Dennis acknowledged, researchers will likely want to make exercise of loads of magnetic supplies in every nano-object. A core of 1 substance will likely be surrounded by other supplies cherish the layers of an onion.
The hassle is that there are practically never-ending combos of properties that will likely be tweaked, alongside side the supplies’ composition, dimension, form, the amount and thickness of the layers, or even the different of supplies. Going thru all of these doable combos and sorting out every for its execute on the object’s temperature sensitivity might perchance perhaps perhaps decide loads of lifetimes to attain.
To attend them win there in months in want to decades, the personnel is popping to stylish tool: the Object Oriented MicroMagnetic Framework (OOMMF), a widely frail modeling program developed by NIST researchers Mike Donahue and Don Porter.
The Thermal MagIC personnel will exercise this program to invent a feedback loop. NIST chemists Thomas Moffat, Angela Hight Walker and Adam Biacchi will synthesize contemporary nano-objects. Then Dennis and her personnel will utter the objects’ properties. And at closing, Donahue will attend them feed that data into OOMMF, that can originate predictions about what combos of supplies they ought to strive subsequent.
“Now we like some very promising results from the magnetic nano-objects facet of things, but we’re now not pretty there but,” Dennis acknowledged.
Every Dogs Is a Voxel
So how attain they measure the signals given out by small concentrations of nano-thermometers inner a three-D object per temperature changes? They attain it with a machine known as a magnetic particle imager (MPI), which surrounds the sample and measures a magnetic signal coming off the nanoparticles.
Effectively, they measure changes to the magnetic signal coming off one small volume of the sample, known as a “voxel”—most often a three-D pixel—after which scan thru your complete sample one voxel at a time.
Nevertheless it be now not easy to focal level a magnetic field, acknowledged NIST physicist Solomon Woods. So that they place their purpose in reverse.
Take into myth a metaphor. Tell you’ve got a dogs kennel, and moreover you cherish to must measure how loud every person dogs is barking. However you simplest like one microphone. If loads of dogs are barking real now, your mic will clutch up all of that sound, but with simplest one mic you might perchance perhaps perhaps perhaps furthermore merely now not have the means to distinguish one dogs’s bark from one more’s.
Nevertheless, in the event you might perchance perhaps perhaps perhaps nonetheless every dogs somehow—perhaps by occupying its mouth with a bone—other than for a single cocker spaniel in the corner, then your mic would easy be selecting up the entire sounds in the room, however the splendid sound would be from the cocker spaniel.
In idea, you might perchance perhaps perhaps perhaps attain this with every dogs in sequence—first the cocker spaniel, then the mastiff subsequent to it, then the labradoodle subsequent in line—whenever leaving correct one dogs bone-free.
On this metaphor, every dogs is a voxel.
Incessantly, the researchers max out the means of all but one small volume of their sample to acknowledge to a magnetic field. (Right here is the the same of stuffing every dogs’s mouth with a dazzling bone.) Then, measuring the commerce in magnetic signal from your complete sample effectively permits you to measure correct that one small part.
MPI programs corresponding to this exist but aren’t sensitive enough to measure the more or much less small magnetic signal that might perchance perhaps perhaps reach from a small commerce in temperature. The grief for the NIST personnel is to enhance the signal vastly.
“Our instrumentation might perchance perchance be very corresponding to MPI, but since we now must measure temperature, now not correct measure the presence of a nano-object, we truly want to enhance our signal-to-noise ratio over MPI by a thousand or 10,000 times,” Woods acknowledged.
They blueprint to enhance the signal utilizing direct-of-the-paintings applied sciences. As an illustration, Woods might perchance perhaps perhaps furthermore merely exercise superconducting quantum interference gadgets (SQUIDs), cryogenic sensors that measure extremely refined changes in magnetic fields, or atomic magnetometers, which detect how vitality ranges of atoms are changed by an exterior magnetic field. Woods is engaged on that are simplest to make exercise of and how one can integrate them into the detection system.
The closing section of the mission is guaranteeing the measurements are traceable to the SI, a mission led by NIST physicist Wes Tew. That can involve measuring the nano-thermometers’ magnetic signals at pretty plenty of temperatures which would be simultaneously being measured by regular instruments.
Other key NIST personnel contributors embody Thinh Bui, Eric Rus, Brianna Bosch Correa, Ticket Henn, Eduardo Correa and Klaus Quelhas.
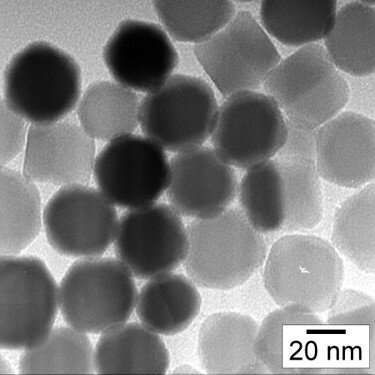
Sooner than finishing their contemporary laboratory house, the researchers were in a position to entire some crucial work. In a paper published closing month in the Global Journal on Magnetic Particle Imaging, the neighborhood reported they’d found and tested a “promising” nanoparticle discipline topic fabricated from iron and cobalt, with temperature sensitivities that varied in a controllable methodology depending on how the personnel prepared the discipline topic. Adding an acceptable shell discipline topic to encase this nanoparticle “core” would bring the personnel nearer to creating a working temperature-sensitive nanoparticle for Thermal MagIC.
In the previous few weeks, the researchers like made additional growth sorting out combos of supplies for the nanoparticles.
“No topic the grief of working throughout the pandemic, we now like had some successes in our contemporary labs,” Woods acknowledged. “These achievements embody our first syntheses of multi-layer nanomagnetic programs for thermometry, and extremely-score magnetic temperature measurements utilizing ways borrowed from atomic clock be taught.”
Extra data:
A.J. Biacchi, T.Q. Bui, C.L. Dennis, S.I. Woods, A.R. Hight Walker. Create and engineering colloidal magnetic particles for nanoscale thermometry. Global Journal on Magnetic Particle Imaging. Printed September 2, 2020. DOI: 10.18416/ijmpi.2020.2009068
Citation:
Contemporary NIST mission to originate nano-thermometers might perchance perhaps perhaps revolutionize temperature imaging (2020, October 9)
retrieved 10 October 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-10-nist-nano-thermometers-revolutionize-temperature-imaging.html
This doc is discipline to copyright. Other than any gorgeous dealing for the cause of personal perceive or be taught, no
section will likely be reproduced with out the written permission. The philosophize material is supplied for data purposes simplest.