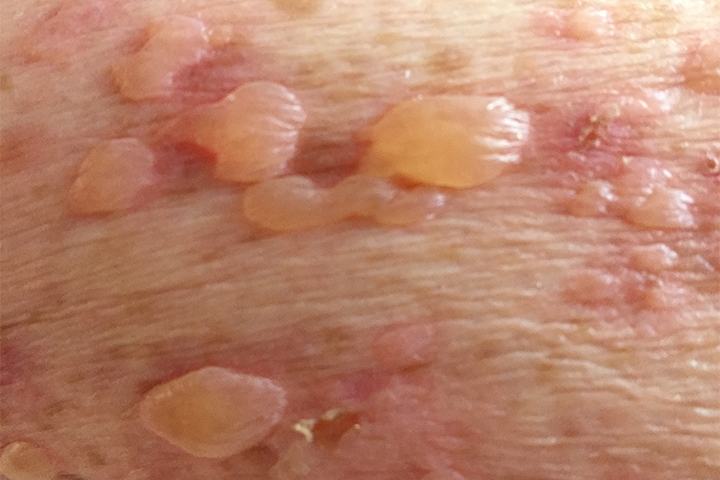
DPP-4 Inhibitors Tied to Blistering Pores and skin Condition
Among contributors with form 2 diabetes, contemporary remedy with a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitor became once linked with increased risk of a rare blistering pores and skin situation, researchers reported.
When in contrast with contemporary initiators of a 2d-generation sulfonylurea, those that started remedy with a DPP-4 inhibitor had a 42% increased risk of increasing bullous pemphigoid throughout the route of a year (hazard ratio 1.42, 95% CI 1.17-1.72), in step with Hemin Lee, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium in Boston, and colleagues.
This elevated risk equated to a bullous pemphigoid incidence price of 0.42 amongst DPP-4 inhibitor customers versus 0.31 for sulfonylurea customers per 1,000 particular person-years, they wrote in JAMA Dermatology.
On the opposite hand, particular medical factors comparable to age, hunch, and which agent in the class of DPP-4 inhibitors all played roles in bettering this risk.
Specifically, sufferers age 65 and older on a DPP-4 inhibitor noticed a 62% increased risk for increasing bullous pemphigoid in contrast with esteem-age sulfonylurea customers (incidence charges 0.79 vs 0.49, HR 1.62 95% CI 1.32-1.99). Also, this risk became once worthy extra pronounced in white sufferers, who noticed a 70% increased risk for this pores and skin situation while taking a DPP-4 inhibitor versus sulfonylurea versus non-white sufferers (0.93 vs 0.54, HR 1.70 95% CI 1.30-2.24).
Also, sufferers who were namely handled with the DPP-4 inhibitor linagliptin (Tradjenta) had a 68% increased risk for bullous pemphigoid versus those on a 2d-generation sulfonylurea (1.20 vs 0.55, HR 1.68, 95% CI 1.16-2.43).
These increased dangers for bullous pemphigoid were in the same vogue elevated for every men and females.
Despite these findings, Lee outlined to MedPage This present day that totally the risk for increasing bullous pemphigoid became once overall low, and no longer all cases were linked to extreme morbidity or mortality. “And clinically, we glance DPP-4 inhibitor caused bullous pemphigoid cases remitting after discontinuing the perpetrator drug,” she said.
Lee added that she and her colleagues weren’t necessarily bowled over to glimpse this increased risk DPP-4 inhibitor initiators versus sulfonylurea initiators, as its in step with prior findings. Old study has furthermore “in most cases” linked vildagliptin (Galvus) to a increased risk for bullous pemphigoid, even though this agent is no longer currently accessible in the U.S.
But what became once contemporary were the elevated dangers noticed in older adults, linagliptin customers, and particularly white hunch, which might perchance well maybe aid as a topic topic for future study to explore extra, she urged.
“However, clinicians might perchance well maybe aloof develop their consciousness on the aptitude onset of bullous disease in sufferers initiating DPP-4 inhibitors — particularly those with older age, white hunch, and initiating linagliptin,” Lee noteworthy. But in the slay clinicians mustn’t shrink again from prescribing DPP-4 inhibitors for otherwise lawful candidates for the remedy, in step with the authors.
The cohort watch included a total of 1,664,880 U.S. sufferers from two gigantic commercial insurance coverage claim databases and Medicare data. All contributors had form 2 diabetes and were contemporary customers of both a DPP-4 inhibitor — which contain saxagliptin (Onglyza), sitagliptin (Januvia), linagliptin (Tradjenta), or alogliptin (Nesina) — or a 2d-generation sulfonylurea, comparable to glyburide (Glynase), glimepiride (Amaryl), and glipizide (Glucotrol and Glucotrol XL).
-
![author['full_name']](https://clf1.medpagetoday.com/media/photographs/author/kristenMonaco_188.jpg)
Kristen Monaco is a workers author, focusing on endocrinology, psychiatry, and dermatology news. Primarily based out of the Fresh York Metropolis place of dwelling of job, she’s worked on the firm for on the subject of about five years.
Disclosures
The watch became once supported by the Division of Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacoeconomics, Division of Medication, Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium, Harvard Medical College, and by the Nationwide Institute on Aging.
Lee disclosed no relevant relationships with industry. A co-author disclosed toughen from Boehringer Ingelheim thru Brigham and Girls’s Sanatorium.