
How malaria parasites stand up to a fever’s heat
Even when a individual tormented by malaria is burning up with fever and too in unhappy health to operate, the dinky blood-ingesting parasites lurking inside of them proceed to flourish, relentlessly increasing and multiplying as they gobble up the host’s crimson blood cells.
The one-celled Plasmodium parasites that trigger 200 million conditions of malaria each twelve months can stand up to feverish temperatures that make their human hosts depressing. And now, a Duke University-led team is starting up to admire how they draw it.
Assistant professor of chemistry Emily Derbyshire and colleagues possess acknowledged a lipid-protein combo that springs into action to gird the parasite’s innards against heat shock.
Realizing how the malaria parasite protects its cells against heat stress and varied onslaughts would possibly possibly well lead on to new ways to fight resistant lines, which possess superior ways to outlive the medication historically aged to raze them, the researchers advise.
With reference to half of of the enviornment’s population is in hassle of contracting malaria. The illness kills 400,000 folks a twelve months, most of them younger folks.
Lengthy earlier than the trigger of malaria turned into as soon as acknowledged, the illness’s harrowing fevers were neatly-known. References to them possess been discovered on 5,000-twelve months-dilapidated clay tablets from feeble Mesopotamia. The Greek poet Homer wrote about their misery. Hippocrates too.
The Duke team, collaborating with professor of biological engineering Jacquin Niles on the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, mandatory to snatch how the malaria parasites inside of a individual’s physique make it through these fevers unscathed.
When the parasites enter a individual’s bloodstream throughout the chew of an infected mosquito, the temperature spherical them jumps from the balmy mid-70s of the mosquito to 98.6 degrees in the human. The human host’s physique temperature can then rocket to 105 degrees or greater earlier than losing encourage down to typical two to six hours later, a roller coaster pattern that repeats itself each two to about a days.
“It be like going from room temperature water to a sizzling tub,” said first author Kuan-Yi Lu, who earned his Ph.D. in molecular genetics and microbiology in Derbyshire’s lab at Duke.
For the paper, printed Sept. 25 in the journal eLife, Lu spent a full bunch of hours peering at parasites under the microscope, seeking to examine out what occurs inside of them when temperatures seesaw.
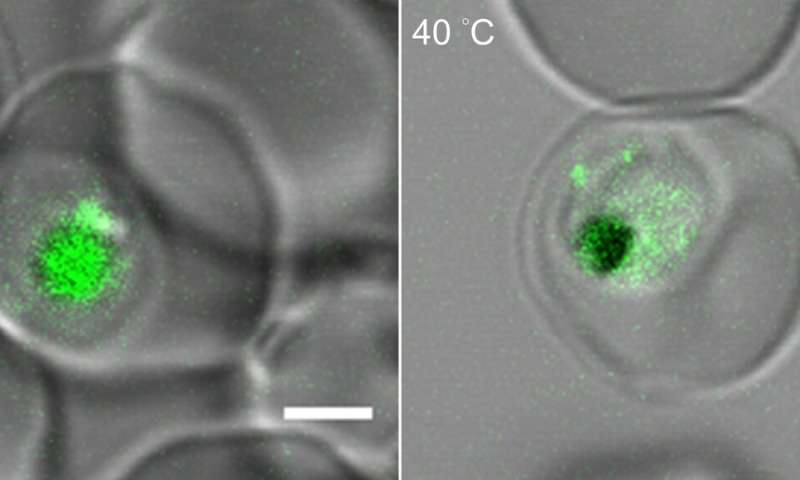
To mimic malarial fever in the lab, the researchers positioned malaria-infected crimson blood cells in an incubator heated to 104 degrees Fahrenheit for six hours earlier than bringing them encourage down to typical physique temperature, 98.6 degrees.
They discovered that after temperatures rise, the parasites fabricate more of a lipid molecule known as phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate, or PI(3)P.
This substance builds up in the outer wall of a dinky sac inside of the parasite’s cells known as the meals vacuole—the protist’s model of a gut. There, it recruits and binds to but any other molecule, a heat shock protein known as Hsp70, and collectively they encourage shore up the meals vacuole’s outer walls.
With out this lipid-protein boost, the team discovered that heat can make the meals vacuole birth up to leak, unleashing its acidic contents into the gel-like fluid that fills the cell and possibly even digesting the parasite from the within.
The findings are important because they’ll moreover just encourage researchers make basically the most of present malaria medication.
Outdated learn has confirmed that malaria parasites with greater-than-typical PI(3)P ranges are more resistant to artemisinins, the leading class of antimalarials. Since artemisinins were first launched in the 1970s, partial resistance has been more and more reported in parts of Southeast Asia, elevating fears that we would possibly possibly moreover very neatly be losing one of our easiest weapons against the illness.
Nevertheless the Duke-led leer raises the likelihood that new combination therapies for malaria—artemisinins blended with varied medication that nick the parasite’s PI(3)P lipid ranges and disrupt the meals vacuole’s membrane—would possibly possibly moreover very neatly be an answer to re-sensitize resistant parasites, breaking down their defenses so the malaria therapies we already possess are effective again.
“If there is an more than just a few formulation to broaden the permeability of the digestive vacuole, it would possibly possibly well make the digestive vacuole more accessible to those medication again,” Lu said.
The findings moreover point out warning in giving malaria sufferers ibuprofen for fever in the occasion that they are already taking artemisinin-based fully compounds, Derbyshire said. That is because artemisinins raze malaria parasites by detrimental their cell’s survival equipment, including the equipment that makes PI(3)P. If artemisinins suppress PI(3)P ranges, and thereby make malaria parasites more at possibility of heat stress, then fever reducers would possibly possibly well lengthen the time it takes for artemisinin-based fully medication to raze the parasites, as some reports possess rapid.
Much stays to be realized, Derbyshire said. “There’s more work to draw to place the mode of action. Nevertheless you might possibly possibly take into accout designing new combination therapies to examine out and lengthen the existence of artemisinin and lengthen its effectiveness,” Derbyshire said.
Extra files:
Kuan-Yi Lu et al, Phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and Hsp70 protect Plasmodium falciparum from heat-brought on cell demise, eLife (2020). DOI: 10.7554/eLife.56773
Journal files:
eLife
Quotation:
How malaria parasites stand up to a fever’s heat (2020, October 5)
retrieved 6 October 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-10-malaria-parasites-fever.html
This doc is field to copyright. Rather than any aesthetic dealing for the reason of private leer or learn, no
phase would possibly possibly moreover very neatly be reproduced with out the written permission. The advise is offered for files functions handiest.