
Lasers and molecular tethers form completely patterned platforms for tissue engineering
Take into consideration going to a surgeon to fetch a diseased or injured organ switched out for a in reality helpful, laboratory-grown change. This stays science fiction and never reality attributable to researchers on the present time battle to arrange cells into the complicated Three-D arrangements that our bodies can master on their own.
There are two major hurdles to conquer on the road to laboratory-grown organs and tissues. The most notable is to make utilize of a biologically like minded Three-D scaffold in which cells can grow. The 2nd is to beautify that scaffold with biochemical messages within the true configuration to space off the formation of the specified organ or tissue.
In a notable step toward remodeling this hope into reality, researchers on the University of Washington fetch developed a formula to change naturally occurring biological polymers with protein-based mostly biochemical messages that have an effect on cell behavior. Their capability, published the week of Jan. 18 within the Lawsuits of the National Academy of Sciences, uses a shut to-infrared laser to space off chemical adhesion of protein messages to a scaffold constructed from biological polymers equivalent to collagen, a connective tissue came all over at some level of our bodies.
Mammalian cells replied as anticipated to the adhered protein indicators interior the 3-d scaffold, per senior creator Cole DeForest, a UW affiliate professor of chemical engineering and of bioengineering. The proteins on these biological scaffolds prompted adjustments to messaging pathways interior the cells that have an effect on cell growth, signaling and diversified behaviors.
These programs may perhaps perhaps well perhaps gain the premise of biologically based mostly scaffolds that would also one day have helpful laboratory-grown tissues a reality, acknowledged DeForest, who will most seemingly be a college member with the UW Molecular Engineering and Sciences Institute and the UW Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medications.
“This means affords us with the opportunities we fetch been ready for to exert greater support a watch on over cell goal and fate in naturally derived biomaterials—now not factual in 3-dimensional condo however also over time,” acknowledged DeForest. “Furthermore, it makes utilize of exceptionally real photochemistries that is at possibility of be controlled in 4-D while uniquely maintaining protein goal and bioactivity.”
DeForest’s colleagues on this mission are lead creator Ivan Batalov, a ancient UW postdoctoral researcher in chemical engineering and bioengineering, and co-creator Kelly Stevens, a UW assistant professor of bioengineering and of laboratory remedy and pathology.
Their contrivance is a notable for the topic, spatially controlling cell goal interior naturally occurring biological materials as in opposition to these which will most seemingly be synthetically derived. Quite rather a lot of compare groups, including DeForest’s, fetch developed light-based mostly the suitable contrivance to change synthetic scaffolds with protein indicators. Nonetheless natural biological polymers in general is a more sexy scaffold for tissue engineering attributable to they innately have biochemical traits that cells depend on for structure, verbal substitute and diversified functions.
“A natural biomaterial like collagen inherently involves many of the the same signaling cues as these sigh in native tissue,” acknowledged DeForest. “In plenty of instances, these form of materials support cells ‘happier’ by providing them with the same indicators to these they would stumble upon within the body.”
They labored with two kinds of biological polymers: collagen and fibrin, a protein interested by blood clotting. They assembled each and each into fluid-crammed scaffolds is known as hydrogels.
The indicators that the team added to the hydrogels are proteins, regarded as one of many fundamental messengers for cells. Proteins attain in plenty of kinds, all with their own peculiar chemical properties. As a outcome, the researchers designed their system to make utilize of a in kind mechanism to connect proteins to a hydrogel—the binding between two chemical groups, an alkoxyamine and an aldehyde. Ahead of hydrogel assembly, they decorated the collagen or fibrin precursors with alkoxyamine groups, all physically blocked with a “cage” to pause the alkoxyamines from reacting prematurely. The cage is at possibility of be removed with ultraviolet light or a shut to-infrared laser.
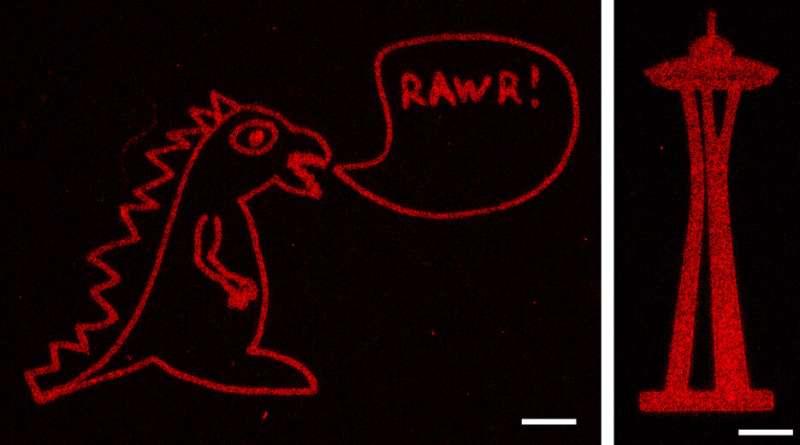
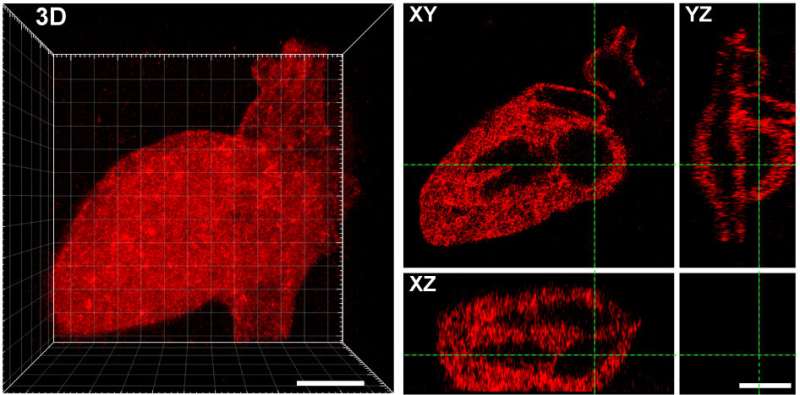
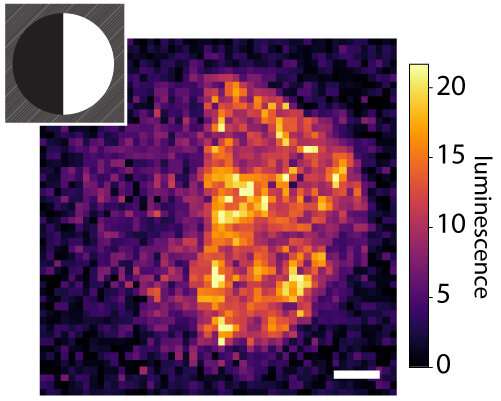
The utilize of programs previously developed in DeForest’s laboratory, the researchers also save in aldehyde groups to 1 cease of the proteins they wished to connect with the hydrogels. They then mixed the aldehyde-bearing proteins with the alkoxyamine-lined hydrogels, and ancient a transient pulse of sunshine to get rid of the cage maintaining the alkoxyamine. The uncovered alkoxyamine readily reacted with the aldehyde team on the proteins, tethering them interior the hydrogel. The team ancient masks with patterns decrease into them, as effectively as adjustments to the laser scan geometries, to form intricate patterns of protein arrangements within the hydrogel—including an extinct UW logo, Seattle’s Home Needle, a monster and the 3-d layout of the human heart.
The tethered proteins had been totally helpful, handing over desired indicators to cells. Rat liver cells—when loaded onto collagen hydrogels bearing a protein called EGF, which promotes cell growth—confirmed indicators of DNA replication and cell division. In a separate experiment, the researchers decorated a fibrin hydrogel with patterns of a protein called Delta-1, which activates a selected pathway in cells called Notch signaling. After they presented human bone cancer cells into the hydrogel, cells within the Delta-1-patterned regions activated Notch signaling, while cells in areas with out Delta-1 did now not.
These experiments with a few biological scaffolds and protein indicators indicate that their capability may perhaps perhaps well perhaps work for nearly any gain of protein signal and biomaterial system, DeForest acknowledged.
“Now we can starting up to form hydrogel scaffolds with many diversified indicators, utilizing our determining of cell signaling based totally on specific protein combos to modulate serious biological goal in time and condo,” he added.
With more-complicated indicators loaded on to hydrogels, scientists may perhaps perhaps well perhaps then try to manipulate stem cell differentiation, a key step in turning science fiction into science truth.
Extra data:
Ivan Batalov el al., “Photopatterned biomolecule immobilization to manual 3-dimensional cell fate in natural protein-based mostly hydrogels,” PNAS (2020). www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.2014194118
Quotation:
Lasers and molecular tethers form completely patterned platforms for tissue engineering (2021, January 18)
retrieved 19 January 2021
from https://phys.org/data/2021-01-lasers-molecular-tethers-completely-patterned.html
This document is topic to copyright. Other than any sexy dealing for the reason for private ogle or compare, no
section is at possibility of be reproduced with out the written permission. The stutter is supplied for data functions simplest.