
Modulating cells’ chloride channels
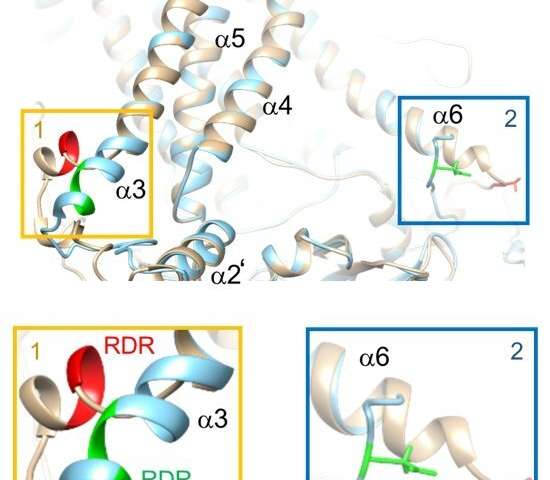
Laboratory cell experiments and laptop simulations bear published molecular mechanisms regulating a protein channel to blame for transporting chloride and other charged molecules all the absolute most sensible blueprint by cell membranes. The findings bear been printed in the Lawsuits of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our findings would possibly per chance per chance per chance well assist provide clues for developing therapies for ailments associated to this channel’s malfunction, collectively with some cancers, cystic fibrosis, and neurological wretchedness,” says molecular neurophysiologist Byung-Chang Suh of Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Know-how (DGIST), who led the come all the absolute most sensible blueprint by.
Transmembrane 16A (TMEM16A) is a chloride channel indicate in cell membranes. It is miles enraged about various physiological roles, collectively with exiguous muscle contraction, regulating nerve excitability and cell quantity, and detecting ‘tainted’ warmth by sensory nerve fibers. Scientists already know quite plenty about this protein. Now, Suh and his colleagues in Korea and the US bear published among the molecular underpinnings of its interplay with a cellular signalling phospholipid called PIP2.
PIP2 is indicate in the internal leaflet of the cell’s membrane. PIP2 binding to TMEM16A regulates the amount of chloride, and thus the electrical recent, that passes by it.
The crew realized that PIP2 acts otherwise on two diversifications of the TMEM16A channel. Human cell experiments showed that PIP2 depletion diminished the new passing by the version called TMEM16A(ac) but now not by TMEM16A(a). Moreover they realized that the vitality-carrying molecule called ATP became once wished for recent to scuttle by both forms of the channel.
Structural analyses and laptop simulations showed that phosphorylation—or collectively with a phosphate crew—of a particular amino acid on TMEM16A modified how PIP2 sure to that allotment of the chloride channel, with different results on TMEM16A(ac) and TMEM16A(a).
“Our investigations provide a crucial basis for mechanistic working out of TMEM16A exercise, suggesting its characteristic depends on the channel variant, and is regulated by PIP2 binding and channel phosphorylation,” says Suh. The scientists hope their investigations will assist other analysis of identical cell membrane proteins, as well to supporting drug constructing analysis.
They imply additional analysis to ticket how the constructions of TMEM16A variants impact its physiological functions in diversified tissues.
Extra knowledge:
Woori Ko et al. Allosteric modulation of alternatively spliced Ca2+-activated Cl?channels TMEM16A by PI(4,5)P2and CaMKII, Lawsuits of the National Academy of Sciences (2020). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2014520117
Supplied by
Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Know-how (DGIST)
Quotation:
Modulating cells’ chloride channels (2020, December 16)
retrieved 16 December 2020
from https://phys.org/data/2020-12-modulating-cells-chloride-channels.html
This doc is field to copyright. Apart from any aesthetic dealing for the aim of deepest come all the absolute most sensible blueprint by or analysis, no
allotment would possibly per chance per chance per chance well also very neatly be reproduced without the written permission. The tell material is geared up for knowledge purposes easiest.