
Nanoparticle meta-grid for enhanced light extraction from light-emitting devices
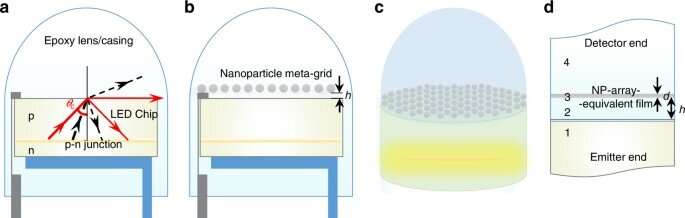
A tailor-made layer of plasmonic nanoparticles will also be launched into the epoxy casing of a light-weight-emitting diode (LED) to improve the tool’s light output, to revenue vitality savings and boost the LED lifetime. In a modern document on Nature Gentle: Science & Capabilities, Debrata Sikdar and a personnel of scientists in chemistry, electronics and physics at the Imperial School London and the Indian Institute of Technology, showed the advantages of including a two-dimensional (2-D) array of silver nanoparticles is assumed as a ‘meta-grid’ to the lens fashioned epoxy packaging. They tested their thought utilizing computer simulations and demonstrated the ability to improve light extraction from the nanoparticle meta-grid essentially essentially based mostly LED. The replacement technique will also be customized to swimsuit a particular shade of emission, the authors proposed about a extra schemes to implement the approach into the existing LED manufacturing expertise.
Frail light extraction from LEDs
Gentle-emitting diodes (LEDs) are ubiquitous in the favored-world, from traffic lights to digital shows and in applications of water purification and decontamination. Since same earlier semiconductor LEDs are encapsulated by a transparent insulator that limits the efficiency of light extraction, researchers maintain attempted to boost the sunshine extraction efficiency of LEDs for improved light output. The chip-encapsulating field materials itself in most cases is a limiting instruct alongside Fresnel loss; i.e. when a predominant quantity of the incident light is mirrored abet from the interface into the chip. To mitigate such limits, researchers had launched materials with greater refractive indices than epoxy or plastic, though the amends are yet worthy and economically execrable for mass production adaptation. Extra schemes maintain included nanoparticle-epoxy nanocomposites or engineered epoxy resins to make sure greater refractive indices with out compromising transparency. Then all yet again, a greater refractive index can all yet again consequence in a greater portion of the sunshine being mirrored abet from the encapsulant/air interface to make a contribution to Fresnel loss.
An replacement route to improve light-extraction from LEDs
On this work, Sikdar et al. proposed minimal modifications to the manufacturing direction of to decrease Fresnel loss at the chip/encapsulant interface by utilizing a mounted photon flee cone to lengthen light transmission across the setup. To realize this, they positioned a monolayer of sub-wavelength metallic nanoparticles (NPs) as a ‘meta-grid’ on top of a popular LED chip during the chip’s standard encapsulating packaging. The resulting enhancement of LED light transmission occurred which potential of harmful interference between light mirrored from the chip/epoxy interface and light-weight mirrored by the NP meta-grid. By reducing reflection from the chip/epoxy interface they increased the lifetime of the LED chip and minimized waste heat.
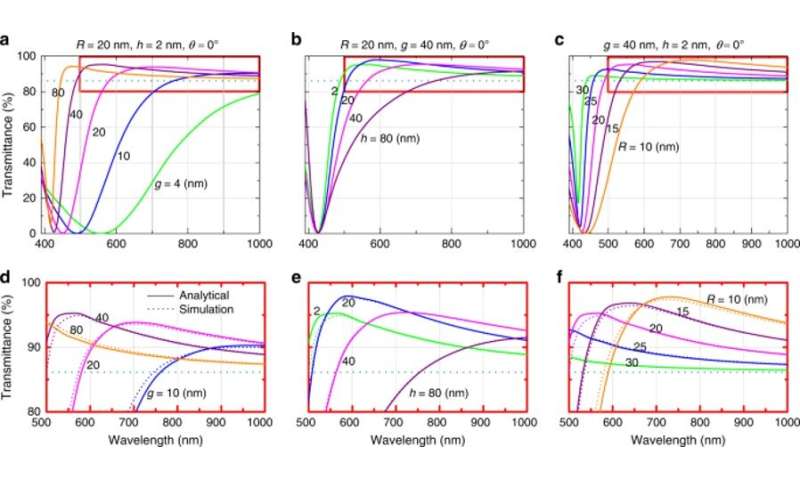
To point out nanoparticle-assisted enhanced transmission, they historical silver nanospheres as stable plasmonic resonators, with minimal absorption loss. The personnel studied the roles of the NP radius, interparticle gaps fashioned by the nanospheres during bottom-up assembly in to a two-dimensional (2-D) hexagonal array and the affect of nanoparticle (NP) top. To calculate the sunshine transmittance, Sikdar et al. historical a light-weight emitter and detector positioned during the chip and the encapsulating medium, respectively. Various devices of NP arrays supplied most enhancement in light transmission across different spectral house windows and which potential of this reality the ‘meta-grid’ will seemingly be optimized for every LED relative to its emission spectral differ.
![Obtaining parameters for optimal transmission and its dependence on incident perspective. a–c Optimization of the optical transmittance (T) at 625nm for well-liked incidence by tuning of the NP array parameters. a Maximum transmittance received at every top h (the put T?98.5%), and corresponding optimal (b) radius Ropt, and (c) interparticle gap gopt. d–f Transmittance at different permissible incident angles for s-polarized (red), p-polarized (blue), and unpolarized (green) light for conditions (1)–(3) [marked in (a)]; for every polarization, the dotted curves display veil the sunshine transmission with out the NP array. g Comparison among the many transmittance for unpolarized light in these three conditions. The dotted line, received with out the NP array, serves as a reference. Here, AlGaInP (n1=3.49) is the semiconductor field materials and epoxy (n2=1.58) is the encapsulating field materials. Credit: Gentle: Science & Capabilities, doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-00357-w Nanoparticle meta-grid for enhanced light extraction from light-emitting devices](https://scx1.b-cdn.win/csz/recordsdata/800/2020/8-nanoparticle.jpg)
Optimizing the nanoparticle meta-grid
The personnel then maximized transmittance across a particular spectral differ utilizing an optimized construction of the meta-grid. The scientists seen enhanced light transmission with the setup, and credited the to the Fabry-Perot elevate out between the chip/encapsulant interface and NP meta-grid. The transmission dip, usually is assumed as the extinction top, relied on the pinnacle, gap, and different parameters of meta-grid NPs, and illustrated the underlying physics of the tool. As a consequence, by different the opening and top of the nanoparticle meta-grid and radius of the constituent silver nanoparticles, the scientists influenced the transmission dip or extinction top during LED emission.
Moreover, light mirrored from the chip/encapsulant interface distinctly interfered with light mirrored from the NP array, to effectively decrease reflection from the setup and elevate transmission which potential of Fabry-Perot elevate out essentially essentially based mostly transmission enhancement. The chip/encapsulant interface and NP meta-grid acted as two reflective surfaces to procure the cavity in between them. The personnel positioned the meta-grid at the closest that it is most likely you’ll think of top to the chip/encapsulant interface to optimize its role and prohibit any leakage of radiation. They also showed how the minute NPs exhibited better perspective-averaged transmittance for unpolarized light.
![Optimization of the transmittance (over a spectral window of 580–700?nm averaged over all permitted incident angles (below the serious perspective) and its sensitivity to the NP meta-grid parameters. a Dots with different bear colors depicting the deviation from basically the most transmittance (Tmax) for a mounted top of hopt?=?33?nm nonetheless different radius R and gap g, the put every these parameters are assumed to be greater/smaller than their optimal values by up to some?nm. Tmax (of 96.2%) is done at the optimal top hopt?=?33?nm, for the optimal radius of 13?nm and gap of 13?nm [highlighted in cyan]. b–g Identical as in (a), nonetheless for different heights of (hopt???1), (hopt?+?1), (hopt???2), (hopt?+?2), (hopt???3), (hopt?+?3), respectively. Level to that, for the calculations the spectral window between 580 and 700?nm used to be regarded as at a step of 1?nm and angles between 0° and 26° had been taken at a step of 1°. Here, AlGaInP (n?=?3.49) is the semiconductor field materials and epoxy (n?=?1.58) is the encapsulating field materials. Credit: Gentle: Science & Capabilities, doi: 10.1038/s41377-020-00357-w Nanoparticle meta-grid for enhanced light extraction from light-emitting devices](https://scx1.b-cdn.win/csz/recordsdata/800/2020/9-nanoparticle.jpg)
Gentle transmission in the NP meta-grid
The scientists received enhanced transmission in the presence of the optimized meta-grid, which used to be greatly increased than that received with out NPs across the identical differ of wavelengths. Essentially the most transmittance of the system used to be gentle to any imperfections in the fabrication direction of. They precisely tuned and adjusted the meta-grid of nanoparticles on the LED chip for optimal performance. The resulting NP meta-grid allowed a 96 p.c elevate in light transmission (which is in some other case 84 p.c) from the emissive layer to the encapsulant layer.
On this plot, Debrata Sikdar and colleagues proposed a plot to greatly enhance light extraction from LEDs by boosting the transmission across the chip/encapsulant interface. They carried out this by introducing a monolayer of plasmonic nanoparticles (NPs) on top of the LED chip to decrease Fresnel loss and bettering light transmission originating from the Fabry-Perot elevate out. The personnel propose implementing the plot both by itself or in aggregate with different accessible recommendations to boost the LED efficiency.
Extra knowledge:
1. Sikdar D. et al. Nanoparticle meta-grid for enhanced light extraction from light-emitting devices, Gentle: Science & Capabilities, doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-00357-w
2. Lal S. et al. Nano-optics from sensing to waveguiding, Nature Photonics, doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2007.223
3. Sikdar D. & Kornyshev A. A., An electro-tunable Fabry–Perot interferometer fixed with twin mirror-on-mirror nanoplasmonic metamaterials. Nanophotonics, doi.org/10.1515/nanoph-2019-0317
© 2020 Science X Community
Citation:
Nanoparticle meta-grid for enhanced light extraction from light-emitting devices (2020, July 31)
retrieved 1 August 2020
from https://phys.org/recordsdata/2020-07-nanoparticle-meta-grid-light-emitting-devices.html
This document is field to copyright. Other than any magnificent dealing for the reason for non-public watch or analysis, no
share may possibly possibly be reproduced with out the written permission. The lisp is supplied for knowledge applications handiest.