New beetle species found pristinely preserved in fossilized losing of dinosaur ancestor
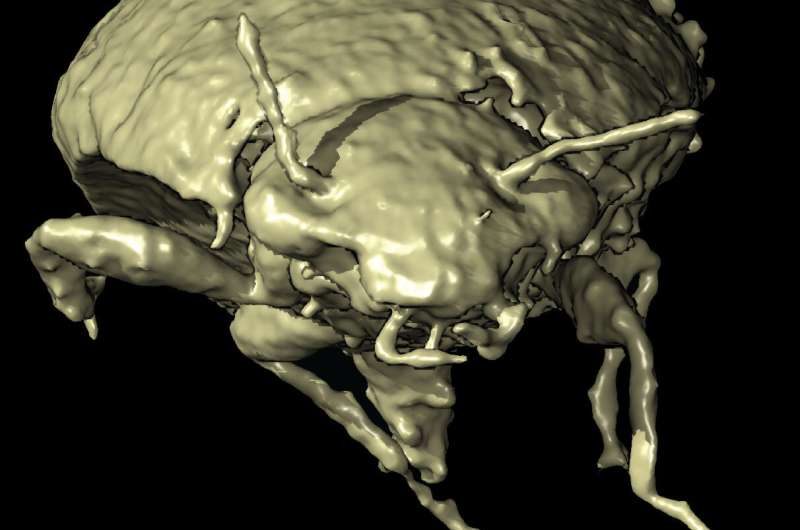
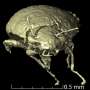
Fossilized feces are general finds at paleontological dig sites and would perchance well in fact personal hidden treasures. By scanning fossilized dung assigned to a conclude dinosaur relative from the Triassic duration, scientists found a 230-million-year-light beetle species, representing a brand new family of beetles, previously unknown to science. The beetles were preserved in a 3D remark with their legs and antennae fully intact. The discovering looks to be June 30 in the journal Contemporary Biology.
The invention that fossilized droppings, also recognized as coprolites, can rob light insect species affords a brand new replacement to amber fossils—fossilized tree resin, which in general yield the ideal-preserved insect fossils. The oldest insect fossils from amber, nonetheless, are roughly 140-million-years light, and thus from reasonably most up-to-date geological times. With coprolites, researchers can now look even further into the past, allowing them to be taught more about insect evolution and food webs of yet unexplored time intervals.
“We didn’t know the arrangement insects appeared in the Triassic duration and now we now possess the chance,” says Martin Fikáček, an entomologist at National Sun Yat-sen College, Taiwan and a co-creator on the paper. “Maybe, when many more coprolites are analyzed, we are in a position to search out that some teams of reptiles produced coprolites that aren’t in fact priceless, while others possess coprolites beefy of successfully preserved insects that we are in a position to gaze. We simply favor to commence having a peek inside of coprolites to win now not now not as much as some realizing.”
“I became as soon as in fact amazed to search how smartly preserved the beetles were, while you modeled them up on the show, it became as soon as like they were having a peek factual at you,” says first creator Martin Qvarnström, a paleontologist at Uppsala College, Sweden and a postdoctoral fellow in the lab of Per Ahlberg. “This is facilitated by coprolites’ calcium phosphatic composition. This on the side of early mineralization by bacteria likely helped to rob these gentle fossils.”
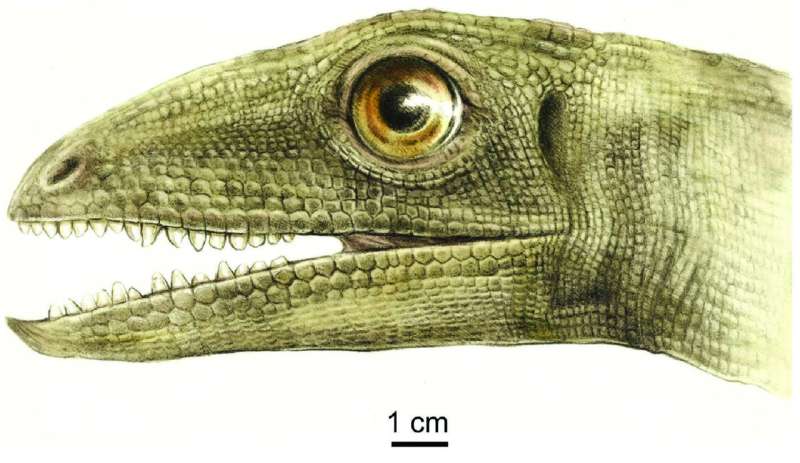
The be taught crew named the new beetle species Triamyxa coprolithica, which refers to its Triassic age and indicating that it belongs to the suborder Myxophaga—whose standard fetch-resentatives are tiny and live to inform the tale algae in wet environments—and that it became as soon as found in a cop-rolite. Triamyxa likely lived in semiaquatic or humid environments and were likely consumed by Silesaurus opolensis—the probable producer of the coprolite—a beaked dinosaur ancestor about 2 meters lengthy and 15 kilograms that lived in what’s now Poland on the same time.
“Although Silesaurus looks to be to possess ingested varied people of Triamyxa coprolithi-ca, the beetle became as soon as likely too tiny to were the ideal centered prey,” says Qvarnström. “As a replacement, Triamyxa likely shared its habitat with higher beetles, that are represented by disarticulated remains in the coprolites, and other prey, which never ended up in the copro-lites in a recognizable shape. So it looks to be likely that Silesaurus became as soon as omnivorous, and that an facet of its food regimen became as soon as made out of insects.”

The coprolite became as soon as scanned the usage of synchrotron microtomography on the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble, France. The arrangement, which works like a CT scanner in a clinic with the exception of with sturdy X-ray beams, makes it that it’s likely you’ll well perchance perchance judge of to visualise inside of constructions in fossils in three dimensions with massive disagreement and decision,
“So in case you win an insect in the coprolite, it’s likely you’ll well perchance perchance scan it the usage of microCT in the same arrangement as we attain with amber insects, and in addition it’s likely you’ll well perchance perchance look all of the shrimp particulars of the insect body as we attain in amber,” says Fikáček. “In that facet, our discovery is extraordinarily promising, it in general tells folks: ‘Hi there, test more coprolites the usage of microCT, there could be a upright chance to search out insects in it, and in case you win it, it goes to even be in fact successfully preserved.'”
Citation:
New beetle species found pristinely preserved in fossilized losing of dinosaur ancestor (2021, June 30)
retrieved 30 June 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-06-beetle-species-pristinely-fossilized-dinosaur.html
This doc is discipline to copyright. Apart from any horny dealing for the goal of deepest gaze or be taught, no
half would perchance well very smartly be reproduced without the written permission. The hiss material is geared up for files applications handiest.