
Newly learned Miocene biome sheds light on rainforest evolution

An international research neighborhood led by Prof. Wang Bo and Prof. Shi Gongle from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) has serene roughly 25,000 fossil-containing amber samples and about 5,000 fossil vegetation in Zhangpu County, Fujian Province, southeast China from 2010 to 2019.
Their findings had been printed in Science Advances on April 30.
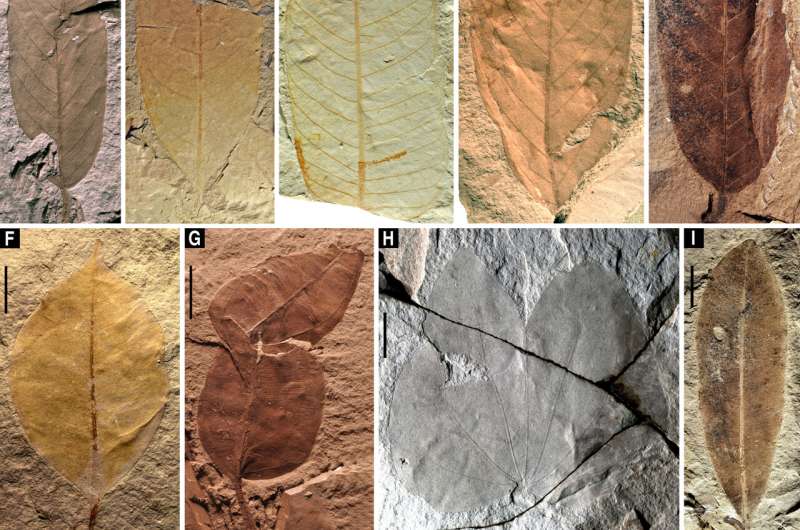
The Zhangpu biota, including amber biota and co-occurring megafossils, is the richest tropical seasonal rainforest biota learned to this level. It displays that extraordinary species differ existed inner a 14.7 million-year-mature tropical rainforest and sheds light on the evolution of the rainforest.
Numerous winged fruits of Dipterocarpaceae and legumes, moreover to leaves of 78 different broadleaf trees expose that tropical seasonal rainforests prolonged extra north than these days, offering an insight into what adjustments also can occur in a future warmer world if ecosystems are in a collection to adapt.
The Zhangpu amber biota incorporates a diverse, exquisitely preserved fossil arthropod fauna and abundant botanical and other inclusions akin to fungi, snails, and even feathers. Botanical inclusions encompass bryophytes (liverworts and mosses) and flowering vegetation.
Arthropod inclusions duvet a ambitious array of extra than 250 families including diverse spiders, mites, millipedes, and as a minimum 200 families of insects in 20 orders. The extremely excessive diversity of arthropods renders the Zhangpu amber biota one among the sphere’s four richest, on the side of the extensively identified Cretaceous Burmese amber biota (> 568 families), Eocene Baltic amber biota (> 550 families), and Miocene Dominican amber biota (205 families).
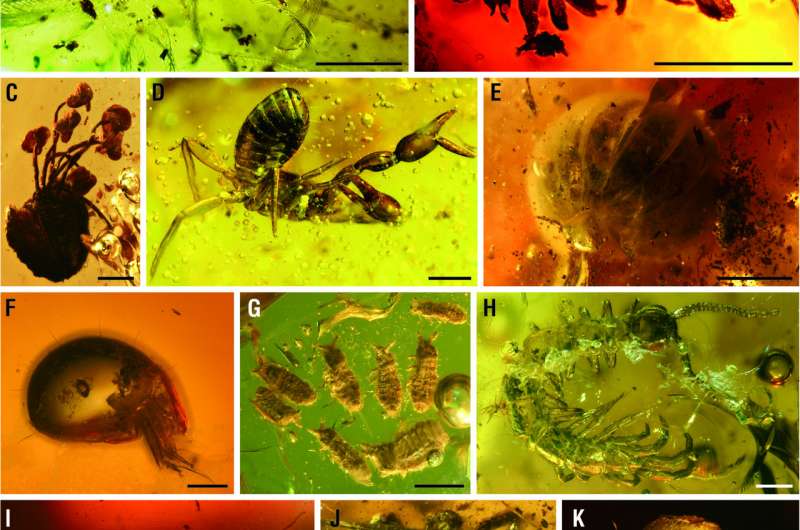
The insect fauna in Zhangpu amber encompass many ants, bees, lacewings, stick insects, termites, and grasshoppers which might perchance well be these days restricted to tropical Southeast Asia and/or Recent Guinea.
“Doubtlessly the most unexpected finding is that the excessive differ of ants and springtails all belong to residing genera. Moreover to, the big majority of beforehand known insects in Zhangpu amber, akin to bark lice, grasshoppers, beetles, and bees, also belong to residing genera,” acknowledged Prof. Wang.
These outcomes counsel that Asian rainforest insect communities personal remained stable since the heart Miocene (as a minimum 15 million years ago). It also highlights that tropical rainforests act as museums of biological differ on the generic level. The relative ecological stability of such “megathermal” environments facilitates the persevered accumulation of species differ and makes them noteworthy extra precious than beforehand realized.
The Zhangpu amber biota is uncommon since the samples are not commercially extracted and as a end result the species census is minimally skewed by human selective bias. Moreover, its accurate age is smartly-constrained by radioisotopic dating and the associated plant compression/impact fossils allow quantitative reconstruction of the earlier local weather.
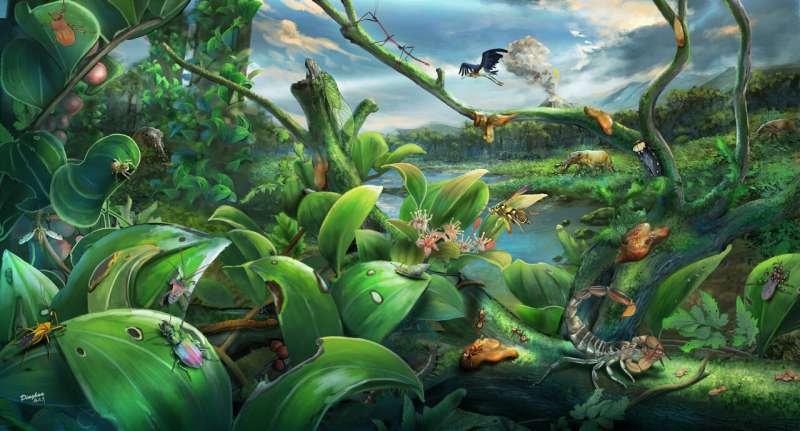

Compared to the up-to-the-minute local weather of Zhangpu, the most principal distinction is that the heart Miocene local weather had a hotter cool weather, ensuing in a quite stable temperature all year lengthy.
In eventualities of international warming, cool weather warming is now and again extra pronounced than summer season warming, and has bigger and extra fashionable outcomes on terrestrial and marine ecosystems. It reduces “winterkills” and is worthwhile for reproduction and development of tropical animals and vegetation.
“Winter warming is at possibility of had been a significant driver of the northern expansion of the megathermal biota in South China at some level of the Mid-Miocene Climatic Optimum,” acknowledged Prof. Shi.
Extra recordsdata:
“The mid-Miocene Zhangpu biota displays an outstandingly filthy rich rainforest biome in East Asia” Science Advances (2021). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg0625
Quotation:
Newly learned Miocene biome sheds light on rainforest evolution (2021, April 30)
retrieved 2 Also can 2021
from https://phys.org/recordsdata/2021-04-newly-miocene-biome-rainforest-evolution.html
This doc is subject to copyright. As opposed to any handsome dealing for the cause of personal take a look at up on or research, no
part will be reproduced with out the written permission. The affirm is equipped for recordsdata functions most efficient.