Recent long-timeframe satellite tv for computer diagnosis shows “plum” rainy season wetter now than ever sooner than

IMAGE: (upper) Adjustments in rainfall phases between the 2000’s and the 2010’s. (lower) Frequency of precipitation (0.5mm/hr) and heavy precipitation (10.0mm/hr) right in the course of the Meiyu-Baiu season over the years….
leer extra
Credit: Tokyo Metropolitan University
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have analyzed long-timeframe precipitation radar recordsdata from satellites and stumbled on severely enhanced rainfall over the latest decade right in the course of the annual Meiyu-Baiu rainy season in East Asia. The tips spans 23 years and supplies unparalleled insight into how rainfall patterns have modified. They confirmed that the increased rainfall used to be driven by the decadal increased transport of moisture from the tropics and frequent occurrence of the upper tropospheric trough over the entrance.
From the 2nd half of of June to the first half of of July each and every 365 days, East Asia is topic to a particularly rainy spell identified because the Meiyu (in China) or Baiu (in Japan) season or “plum rains,” from the ripening of plums along the Yangtze River. They are prompted by the so-called Meiyu-Baiu entrance, the set apart the drift of moist air across the Asian monsoon space meets anti-cyclonic flows across the rim of the western North Pacific subtropical high (WNPSH). Although they invent important obligatory water to the gap, no longer too long ago, it appears that the floods they residing off have taken a deadly flip, with neatly-liked destruction; flooding in China and Japan in 2020 used to be particularly devastating. For scientists and policymakers, it’s key that this be set apart inner the framework of a greater portray: are these merely anomalies, or are they here to forestall?
Although studied in important depth, the bulk of review exhaust rainfall gauge measurements and observations of cloud job spherical land. An overall portray of rainfall all over the gap used to be missing, particularly analyses which spanned long classes of time. Now, a staff led by Assistant Professor Hiroshi Takahashi have examined satellite tv for computer recordsdata that contains radar measurements of precipitation. They mixed two gadgets of recordsdata, the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) and the World Precipitation Measurement Mission (GPM). The elephantine residing of recordsdata spans 23 years and covers each and every the sea and the land with equal precision. By careful diagnosis of the time series, they confirmed a predominant elevation in rainfall over the past decade. In specific, they confirmed that there used to be a obvious enlarge within the different of excessive precipitation events, the form that can residing off natural mess ups.
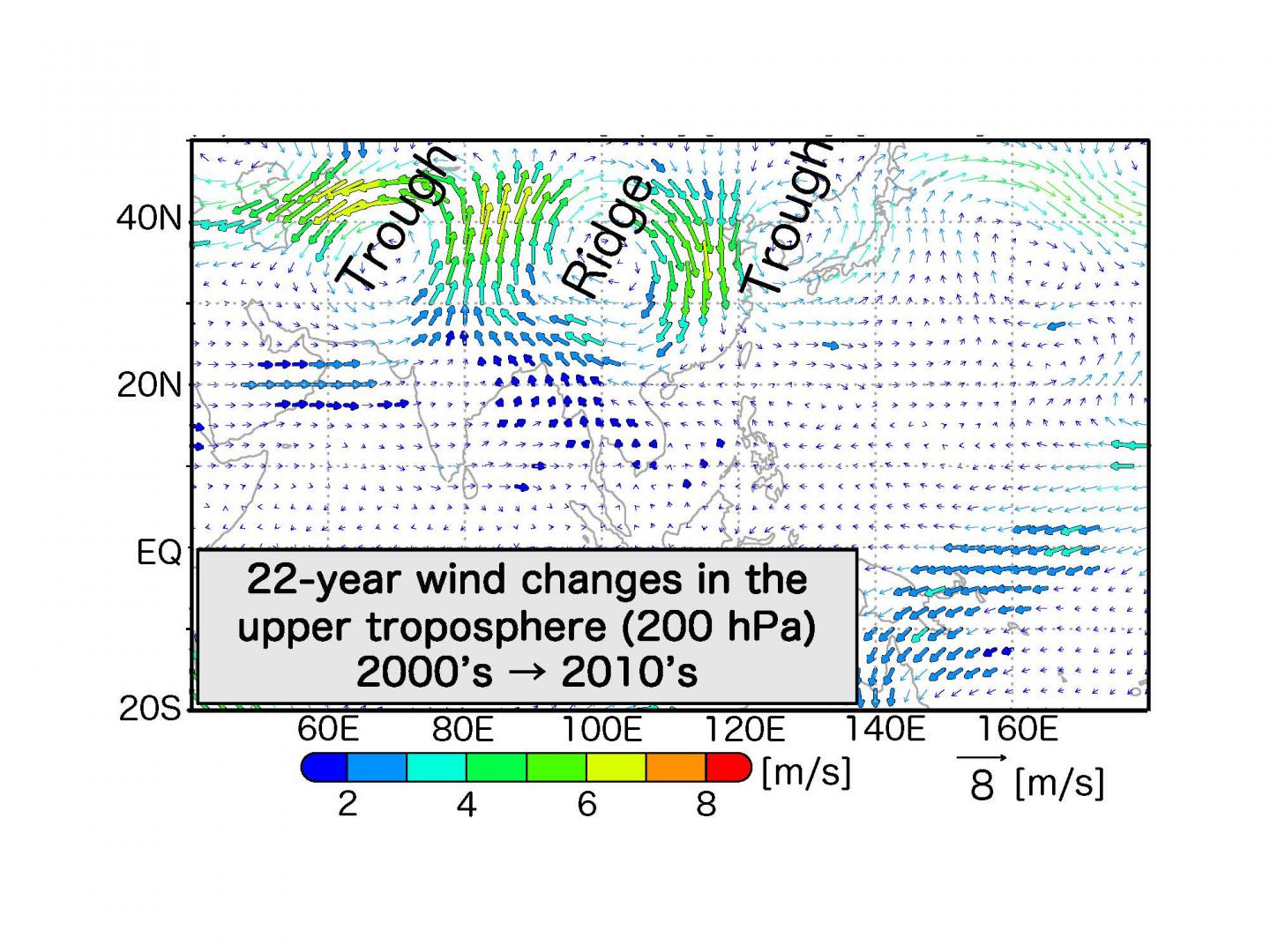
The are waiting for is why it has modified. The staff fervent in two aspects of the growth of rainfall, the transport of moisture and adjustments within the drift of air within the upper troposphere. Initially, they confirmed that there used to be increased transport of water vapor along the rim of the WNPSH, largely as a consequence of decreased tropical cyclone job, a pattern viewed each and every in decade-to-decade comparisons and the devastating season of 2020. Furthermore, they confirmed there had been anomalous circulations within the upper troposphere, developing a “trough” that drove air upwards across the western edge of the Meiyu-Baiu entrance, strongly correlated with enhanced rainfall.
By a elephantine diagnosis of recordsdata encompassing a a lot bigger condominium and a longer time span than sooner than, the staff’s findings set apart the new adjustments within the Meiyu-Baiu season in East Asia inner the framework of a globally altering native weather. They hope that new standards for common rainfall are reflected in new standards of peril prevention.
###
This work used to be supported by a KAKENHI Grant-in-Succor from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (No. 19H01375), the Ambiance Study and Expertise Construction Fund of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Company of Japan (Grant No. JPMEERF20192004), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company/Earth Statement Study Heart (PI No. ER2GPF012).
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! are no longer to blame for the accuracy of news releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing institutions or for the exhaust of any recordsdata in the course of the EurekAlert system.