The microbiome and human most cancers
Setting apart microbes and cancers
The position of microorganisms in causing and sustaining cancers has been in dispute for hundreds of years. By the lens of gut- and tumor-connected microbes, Sepich-Poore et al. review our present working out of the microbiota in most cancers, constructing a “microbially aware” framework. The authors argue that folk can also just tranquil be idea to be as a meta-organism, nonetheless how our microbiota influences most cancers is tranquil no longer wisely understood mechanistically. Nevertheless, advances in microbiome learn are enhancing our working out of immuno-oncology and riding unusual diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
Science, this enviornment p. eabc4552
Structured Summary
BACKGROUND
Historical accounts linking most cancers and microbes date as early as four millennia ago. After institution of the germ theory of infectious ailments, clinical learn of microbial influences on most cancers started in 1868, when William Busch reported spontaneous tumor regressions in sufferers with Streptococcus pyogenes infections. Over the next century, dejected reproducibility, incorrect microbiological claims, and severe toxicity led many to low cost the position of bacteria in carcinogenesis and most cancers therapy. On the other hand, these reviews offered the main unpleasant demonstrations of most cancers immunotherapy. Contemporaneously, the viral theory of most cancers flourished, spurred by the 1911 discovery of Rous sarcoma virus, which transformed benign tissue into malignant tumors in chickens. The decades-long search to search out viruses within the support of every and every human most cancers eventually failed, and a lot of cancers were linked to somatic mutations. Now the realm is encountering keen claims of the importance of microbes, at the side of bacteria and fungi, in most cancers and most cancers therapy. This Review seriously evaluates this evidence in gentle of standard most cancers biology and immunology, delineating roles for microbes in most cancers by inspecting advances in proposed mechanisms, diagnostics, and modulation suggestions.
ADVANCES
Few microbes accurate now situation off most cancers, nonetheless many seem complicit in its progress, continuously performing by draw of the host’s immune plot; conversely, several possess immunostimulatory properties. Mechanistic analyses of gut microbiota–immune plot interactions indicate unprecedented effects on antitumor immunity by modulating indispensable and secondary lymphoid tissue activities. Hundreds of these pathways invoke Toll-treasure receptor–initiated cytokine signaling, nonetheless microbial metabolic effects and antigenic mimicry with most cancers cells are additionally indispensable. In preclinical units, microbial metabolites additionally support a watch on phenotypes of tumor somatic mutations and modulate immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy.
Rising evidence means that intratumoral bacteria exist and are provocative, with overlapping immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, electron microscopy, and sequencing info in ~10 most cancers forms. Preliminary reviews extra imply that fungi and bacteriophages contribute to gastrointestinal cancers. On the other hand, the abundance of intratumoral microbial cells is low relative to most cancers cells, and data of their real looking repertoire and potency remains exiguous. Further validation of their occurrence and affect is required in various cohorts and therapeutic contexts.
The immunomodulatory effects of host microbiota possess reinvigorated efforts to alternate their composition as a plot of immunotherapy. Despite wide preclinical evidence, translation of microbiota modulation approaches into folk has no longer yet materialized into commercialized therapies. Synthetic biology approaches are additionally gaining traction, with engineered bacterial most cancers therapies in preclinical and clinical trial settings.
OUTLOOK
An even bigger working out of the roles of microbes in most cancers offers a likelihood to beef up every stage of the most cancers care cycle, nonetheless indispensable challenges dwell. Concerted efforts to characterize most cancers-connected microbiota amongst tumor, stool, and blood samples with gold-fashioned contamination controls would vastly abet this progress. This would possibly per chance per chance per chance be analogous to The Most cancers Genome Atlas’s position in characterizing the most cancers somatic mutation panorama. Natty-scale clinical trials are for the time being making an strive out the efficacy of microbiota modulation approaches, starting from dietary changes to intratumorally injected, engineered bacteria. These bacterial most cancers therapies, if receive and effective, can also vastly rating bigger the most cancers therapy armamentarium. Altogether, integrating the host-centric and microbial viewpoints of most cancers can also just beef up affected person outcomes whereas offering a nuanced working out of most cancers-host-microbial evolution.
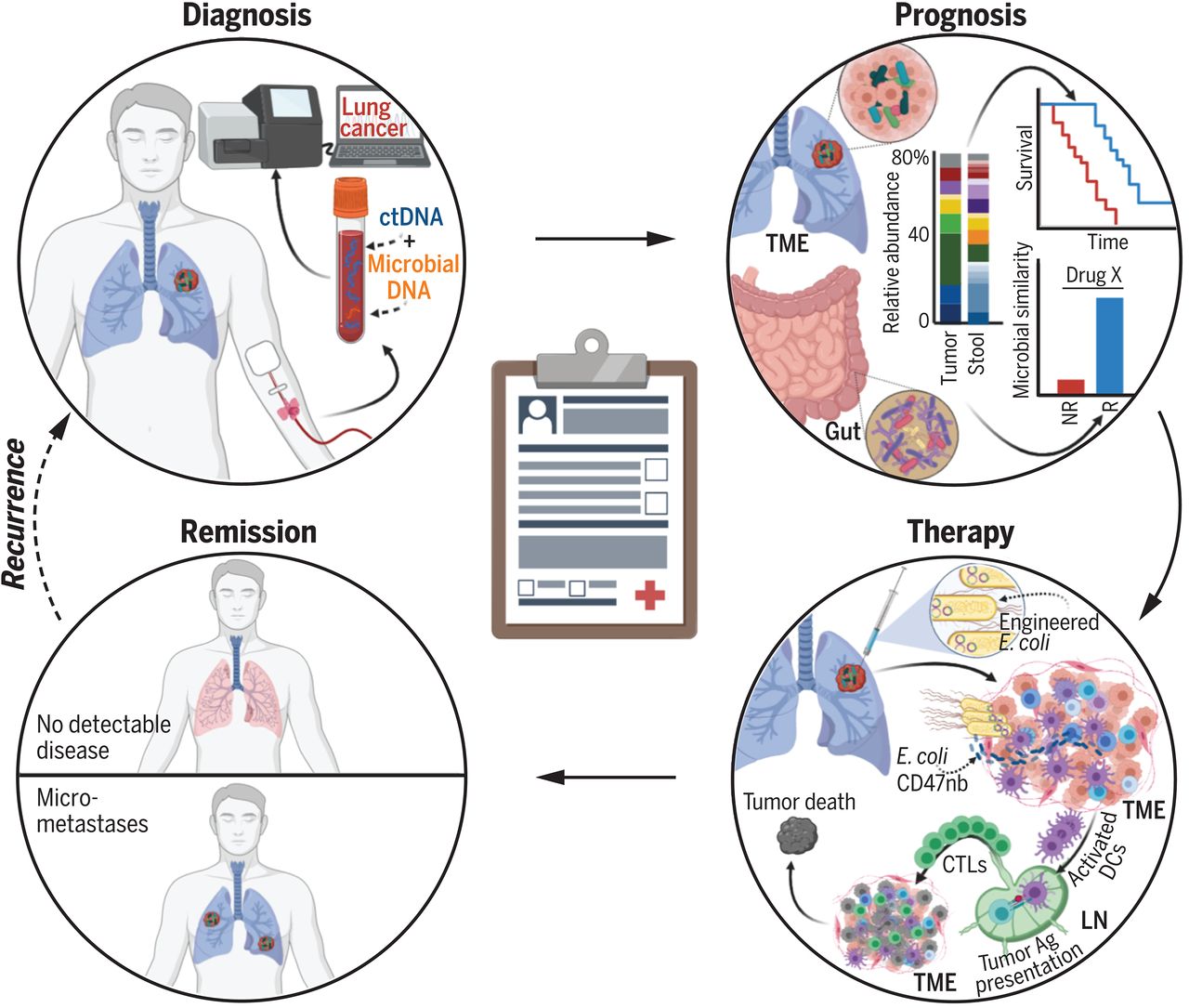
Opportunities for microbes to affect cancer care.
Diagnosis: Cancer-specific, blood-borne microbial DNA may complement cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA). Prognosis: Gut and intratumoral microbiota may stratify patient outcomes (NR, nonresponder; R, responder; TME, tumor microenvironment). Therapy: Intratumor injection of CD47 nanobody (CD47nb)–producing Escherichia coli may create systemic antitumor immunity by enhancing dendritic cell (DC) phagocytosis, lymph node (LN) antigen (Ag) presentation, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity.
” data-hide-link-title=”0″ data-icon-position=”” href=”https://science.sciencemag.org/content/sci/371/6536/eabc4552/F1.large.jpg?width=800&height=600&carousel=1″ rel=”gallery-fragment-images-2103377982″ title=”Opportunities for microbes to affect cancer care. Diagnosis: Cancer-specific, blood-borne microbial DNA may complement cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA). Prognosis: Gut and intratumoral microbiota may stratify patient outcomes (NR, nonresponder; R, responder; TME, tumor microenvironment). Therapy: Intratumor injection of CD47 nanobody (CD47nb)–producing Escherichia coli may create systemic antitumor immunity by enhancing dendritic cell (DC) phagocytosis, lymph node (LN) antigen (Ag) presentation, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) activity.”>
Diagnosis: Most cancers-particular, blood-borne microbial DNA can also just complement cell-free tumor DNA (ctDNA). Prognosis: Intestine and intratumoral microbiota can also just stratify affected person outcomes (NR, nonresponder; R, responder; TME, tumor microenvironment). Therapy: Intratumor injection of CD47 nanobody (CD47nb)–producing Escherichia coli can also just damage systemic antitumor immunity by enhancing dendritic cell (DC) phagocytosis, lymph node (LN) antigen (Ag) presentation, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) command.
Summary
Microbial roles in most cancers formation, diagnosis, prognosis, and remedy were disputed for hundreds of years. Present reviews possess provocatively claimed that bacteria, viruses, and/or fungi are pervasive amongst cancers, key actors in most cancers immunotherapy, and engineerable to address metastases. Despite these findings, the selection of microbes identified to accurate now situation off carcinogenesis remains exiguous. Critically evaluating and constructing frameworks for such evidence in gentle of standard most cancers biology is a very unprecedented process. In this Review, we delineate between causal and complicit roles of microbes in most cancers and hint total themes of their affect by draw of the host’s immune plot, herein outlined because the immuno-oncology-microbiome axis. We extra review evidence for intratumoral microbes and approaches that manipulate the host’s gut or tumor microbiome whereas projecting the next portion of experimental discovery.