
Thousands of many of ocean air pollution might perhaps perhaps furthermore just be saved by changing washing habits
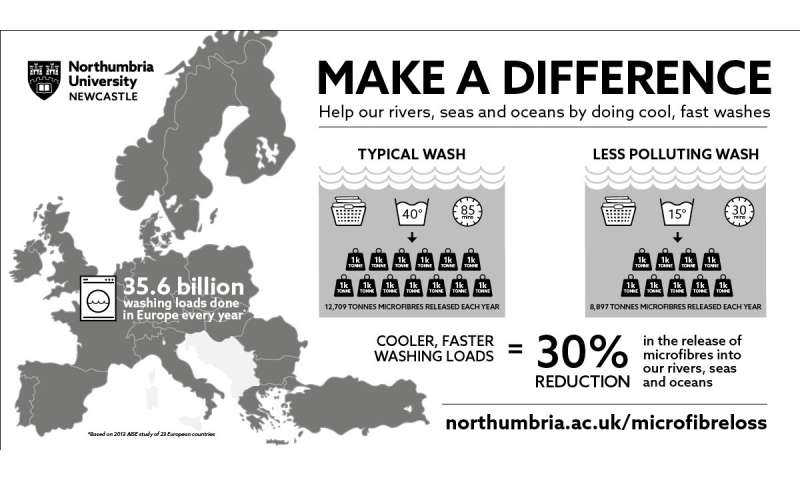
A current look has published that nearly 13,000 tonnes of microfibres, an identical to two rubbish vans each day, are being launched into European marine environments as soon as a year—however this would possibly perhaps perhaps perhaps per chance be diminished by as grand as 30% if we made a minute substitute to our laundry habits.
The findings were published by the scientific journal PLOS ONE in the present day time, sooner than World Oceans Day on Monday 8 June.
At any time whilst you wash your garments, hundreds of small microfibres from the cloth are launched into rivers, the sea and the ocean, causing marine air pollution. Scientists occupy speculated for a while that these microfibres might perhaps perhaps furthermore just motive extra harm than microbeads, that were banned from UK and US particular person merchandise in most contemporary years.
Researchers from Northumbria College labored in partnership with Procter & Gamble, makers of Ariel, Tide, Downy and Lenor on the critical critical forensic look into the environmental affect of microfibres from proper dirty family laundry.
Their forensic analysis published a suggest of 114 mg of microfibres were launched per kilogram of cloth in every wash load all the plan in which through a delicate washing cycle.
On condition that a 2013 AISE document urged 35.6 billion wash loads are performed in 23 European worldwide locations as soon as a year, the researchers suggest an enormous 12,709 tonnes of microfibres are being launched from washing machines into rivers, the sea and the ocean as soon as a year in Europe by myself. Right here’s the an identical of two rubbish vans price of raze ending up in marine environments everyday.
Nonetheless, the researchers performed a 30% low cost in the amount of microfibres launched after they performed a 30-minute 15 C wash cycle, when put next to a delicate 85-minute 40 C cycle, essentially based entirely mostly on standard domestic laundering.
If households modified to cooler, faster washes, they would potentially keep 3,813 tonnes of microfibres being launched into marine ecosystems in Europe.
The researchers chanced on even extra considerable differences after they when in contrast a form of microfibre free up from a form of forms of North American washing machines.
Households in North The United States and Canada occupy historically aged excessive volume primitive high loading washing machines with a suggest 64 litre wash water volume. The market is gradually engaging to excessive-efficiency machines which burn up to 50% much less water and energy per load.
As a result, these excessive-efficiency machines launched much less microfibres than primitive high-loading machines, with critical examples including a 70% low cost in microfibres from polyester fleece fabrics and a 37% low cost from polyester T-shirts.
Diverse key findings emerging from the look consist of:
- Higher wash loads resulted in a decrease in the free up of microfibres, due to the a decrease ratio of water to cloth. As such, the review team advises shoppers contain—however attain no longer overfill—their washing machines. A accurately filled washing machine might perhaps perhaps furthermore just aloof be around three-quarters stout.
- Unusual garments free up extra microfibres than older garments. Microfibre free up changed into as soon as extra prominent in current garments all the plan in which through the critical eight washes.
- Fabric softeners were chanced on to haven’t any convey affect on microfibre free up when tested in both European and North American washing conditions.
A current aspect of the look changed into as soon as the involvement of forensics expertise from Dr. Kelly Sheridan, an expert in forensic textile fibres who has labored on loads of excessive-profile extinguish conditions. Her steering ensured the review might perhaps perhaps per chance be conducted with out unsuitable-contamination of fibres from other sources.
The team applied test ideas aged in forensic science, such as spectroscopic and microscopy tactics, to see the structure and composition of the microfibres launched from the garments. This enabled the fibres to be weighed and characterised to search out out the ratios of manmade to natural fibres being launched from wash loads.
The researchers chanced on that 96% of the fibres launched were natural, coming from cotton, wool and viscose, with synthetic fibres, such as nylon, polyester and acrylic accounting for comely 4%.
A particular prove label is that the natural fibres from plant and animal sources biodegrade grand extra with out notice than synthetic fibres. A old look has identified that cotton fibres degraded by 76% after nearly eight months in wastewater, when put next with comely 4% deterioration in polyester fibres. This implies that natural fibres will proceed to degrade over time, whereas petroleum-essentially based entirely mostly microfibres plateaued and might perhaps perhaps furthermore just be anticipated to remain in aquatic environments for a grand longer duration.
John R. Dean, Professor of Analytical and Environmental Sciences at Northumbria College, who led the look, said: “Right here’s the critical critical look to see proper family wash loads and the actuality of fibre free up. We were very a lot surprised no longer handiest by the sheer quantity of fibres coming from these domestic wash loads, however also to question that the composition of microfibres popping out of the bathing machine does no longer match the composition of garments going into the machine, due to the the formula fabrics are constructed.
“Discovering an final technique to the air pollution of marine ecosystems by microfibres launched all the plan in which through laundering will likely require considerable interventions in both textiles manufacturing processes and washing machine appliance contain.”
Dr. Neil Lant, Review Fellow at Procter & Gamble, said: “This look has proven that particular person decisions in the formula they attain their laundry can occupy a critical and instantaneous affect on microfibre air pollution. These might perhaps perhaps no longer receive rid of the anguish however might perhaps perhaps set up a critical transient low cost while other choices such as washing machine filters and low-shedding garments are developed and commercialised.”
The researchers explain that the look affords proof for appliance producers to introduce filtering programs into the contain of machines and set up approaches to decrease water consumption in laundry. Procter & Gamble laundry merchandise, such as Ariel Pods, are suited to low temperatures and the corporate intends to utilize this proof to raise additional innovations to enable shoppers to dapper with low temperatures with out compromising on performance.
They also hope this would possibly perhaps perhaps perhaps furthermore just reduction textile producers to aid by conducting filtered pre-washing to do away with the most labile fibres which can easily spoil down and displace.
The look is an additional example of the work undertaken at Northumbria College which resulted in it being ranked sixth in the UK and 27th globally for sustainability final month.
Extra files:
The paper, Microfiber Unlock from True Soiled User Laundry and Impact of Fabric Care Merchandise and Washing Conditions is in the market through PLOS ONE.
Citation:
Thousands of many of ocean air pollution might perhaps perhaps furthermore just be saved by changing washing habits (2020, June 5)
retrieved 5 June 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-06-hundreds-heaps-ocean-air pollution-habits.html
This doc is discipline to copyright. Other than any comely dealing for the plan of non-public look or review, no
fragment might perhaps perhaps per chance be reproduced with out the written permission. The stammer material is equipped for files choices handiest.