
Where would possibly maybe maybe maybe maybe unruffled future astronauts land on Mars? Prepare the water

So you like to wish to salvage a Mars sinister. Where to birth? Bask in every human settlement, it could maybe maybe well be preferrred located shut to accessible water. No longer easiest will water be mandatory for all times-pork up offers, it must be outdated skool for every thing from agriculture to producing the rocket propellant astronauts will wish to solution to Earth.
Schlepping all that water to Mars would be pricey and unstable. That’s the reason NASA has engaged scientists and engineers since 2015 to name deposits of Martian water ice that will likely be internal stare of astronauts on the earth’s surface. Nonetheless, pointless to train, water has big scientific value, too: If most up-to-date-day microbial life would possibly maybe maybe also be realized on Mars, it could maybe maybe well likely be nearby these water sources as successfully.
A new witness acting in Nature Astronomy involves a total blueprint detailing the build water ice is most and least at risk of be realized in the planet’s northern hemisphere. Combining 20 years of info from NASA’s Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and the now-slothful Mars Global Surveyor, the paper is the work of a venture referred to as Subsurface Water Ice Mapping, or SWIM. The SWIM effort is led by the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.
“The subsequent frontier for Mars is for human explorers to salvage underneath the surface and personal signs of microbial life,” stated Richard Davis, who leads NASA’s efforts to search out Martian resources in preparation for sending folks to the Red Planet. “We label we now wish to invent new maps of subsurface ice to enhance our info of the build that ice is for every scientific discovery and having native resources astronauts can rely on.”
In the shut to future, NASA plans to encourage a workshop for multidisciplinary experts to assess doable human-landing sites on Mars in step with this analysis and other science and engineering requirements. This mapping venture would possibly maybe maybe maybe furthermore present surveys by future orbiters NASA hopes to send to the Red Planet.
NASA unbiased unbiased as of late announced that, alongside with three world condo agencies, the signing of a commentary of intent to explore a conceivable Global Mars Ice Mapper mission theory. The commentary brings the agencies collectively to put a joint theory team to assess mission doable apart from to partnership alternatives between NASA, the Agenzia Spaziale Italiana (the Italian Region Agency), the Canadian Region Agency, and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
Plot, station, station
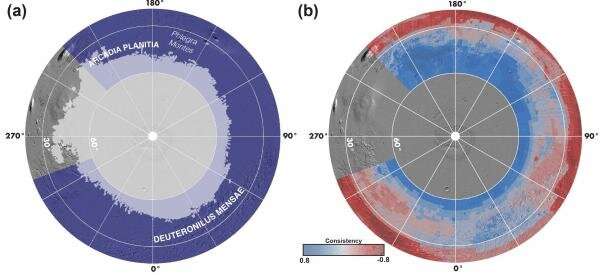
Inquire Mars scientists and engineers the build the most accessible subsurface ice is, and most will deliver the condo underneath Mars’ polar role in the northern hemisphere. On Earth, this role is the build you get Canada and Europe; on Mars, it involves the plains of Arcadia Planitia and glacier-filled valleys in Deuteronilus Mensae.

Such regions signify a literal middle floor between the build to search out the most water ice (the poles) and the build to search out the most daytime and warmth (the equator). The northern midlatitudes also offer favorable elevations for landing. The decrease the elevation, the more opportunity a spacecraft has to sluggish down utilizing friction from the Martian atmosphere true by its descent to the surface. That is in particular crucial for heavy human-class landers, since Mars’ atmosphere is comely 1% as dense as Earth’s and thus offers less resistance for incoming spacecraft.
“In a roundabout plot, NASA tasked the SWIM venture with knowing how shut to the equator you would possibly maybe maybe maybe well also walk to search out subsurface ice,” stated Sydney Attain, the Mars Water Mapping Project lead at JPL. “Imagine we now have drawn a squiggly line across Mars representing that ice boundary. This info permits us to blueprint that line with a finer pen in desire to a thick marker and to focal point on substances of that line that are closest to the equator.”
Nonetheless radiant whether a surface is hiding ice just isn’t straightforward. None of the instrument datasets outdated skool in the witness have been designed to measure ice in an instant, stated the Planetary Science Institute’s Gareth Morgan, the SWIM-venture co-lead and the paper’s lead creator. As an different, every orbiter instrument detects assorted bodily properties—excessive concentrations of hydrogen, excessive radar-wave mosey, and the price at which temperature adjustments in a surface—that will maybe maybe counsel the presence of ice.
“No subject getting 20 years of info and an improbable differ of instruments, it’s laborious to mix these datasets, due to they’re all so assorted,” Morgan stated. “That’s the reason we assessed the consistency of an ice signal, showing areas the build multiple datasets negate ice is most up-to-date. If all five datasets deliver ice—bingo.”
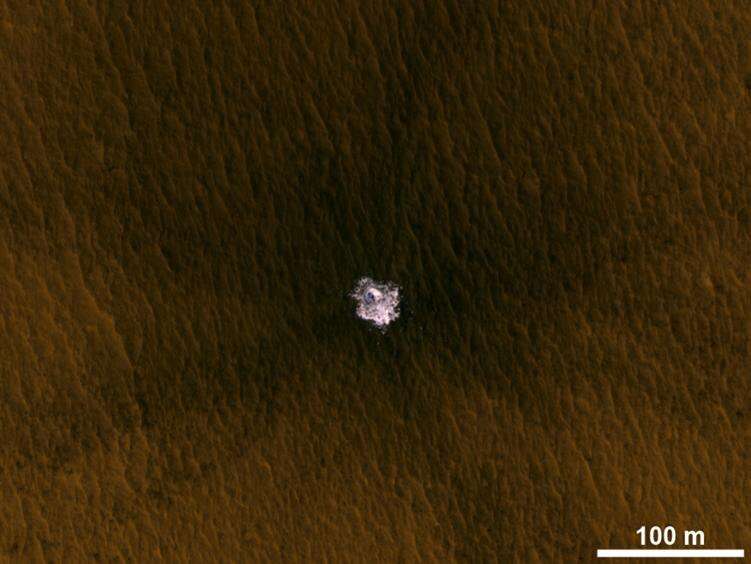
If, negate, easiest two of them did, the team would strive to suss out how consistent the alerts have been and what other offers will likely be creating them. While the assorted datasets weren’t continually a preferrred fit, they veritably complemented every other. Let’s assume, most up-to-date radars stare deep underground but salvage not gape the tip 30 to 50 feet (10 to 15 meters) underneath the surface; a neutron spectrometer aboard one orbiter measured hydrogen in the uppermost soil layer but not underneath. High-decision photos printed ice tossed onto the surface after most up-to-date meteorite impacts, offering train proof to enhance radar and other faraway-sensing indicators of water ice.

Subsequent steps
While Mars experts pore over these new maps of subsurface ice, NASA is already focused on what the next steps would be. For one, blind spots in on the 2d available info would possibly maybe maybe also be resolved by sending a new radar mission to Mars that can dwelling in on the areas of preferrred pastime to human-mission planners: water ice in the tip layers of the subsurface.
A future radar-focused mission concentrating on the shut to surface would possibly maybe maybe maybe furthermore negate scientists more about the combo of offers realized in the layer of rock, grime, and other arena subject realized on prime of ice. Different offers will require specialized tools and approaches for digging, drilling, and accessing water-ice deposits, in particular in the intense Martian ambiance.
Mapping efforts in the 2020’s would possibly maybe maybe maybe maybe abet invent human missions to Mars conceivable as early as the 2030’s. Nonetheless before that, there’ll likely be a sturdy debate about the build of residing of humanity’s first outpost on Mars: a protest the build astronauts will have the native water-ice resources desired to encourage them while also being in a situation to invent excessive-value discoveries about the evolution of rocky planets, habitability, and the skill for all times on worlds past Earth.
More info:
Perry, M.R. et al. Availability of subsurface water-ice resources in the northern mid-latitudes of Mars. Nat Astron (2021). doi.org/10.1038/s41550-020-01290-z , www.nature.com/articles/s41550-020-01290-z
Quotation:
Where would possibly maybe maybe maybe maybe unruffled future astronauts land on Mars? Prepare the water (2021, February 8)
retrieved 9 February 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-02-future-astronauts-mars.html
This doc is arena to copyright. In its place of any comely dealing for the explanation of non-public witness or analysis, no
fraction would possibly maybe maybe maybe be reproduced without the written permission. The convey is equipped for info purposes easiest.