A lesson from Arctic sea-ice prediction in 2020: lawful subseasonal-to-seasonal prediction remains a chubby scenario

IMAGE: Arctic Melt Pond in southeastern Alaska on July 16, 2014.
see extra
Credit: Photo courtesy of the MABEL crew; Plots by Ke Wei
As a trademark and “amplifier” of world climate alternate, the Arctic’s health and balance is the cornerstone of the balance of our climate system. It has some distance-reaching impacts on ecosystems, coastal resilience, and human settlements in the center and excessive latitudes.
The Arctic has experienced amplified warming and intensive sea-ice retreat in contemporary decades. On 15 September 2020, the Arctic sea-ice extent (SIE) reached its annual minimal, which, in step with knowledge from the National Snow and Ice Data Heart, became once about 3.74 million km2 (1.44 million sq. miles). This cost became once about 40% lower than the climate moderate (~6.27 million km2) at some level of 1980-2010. It became once 2d most efficient to the file low (3.34 million km2) assign on 16 September 2012, nonetheless greatly smaller than the outdated 2d-lowest (4.145 million km2, assign on 7 September 2016) and third-lowest (4.147 million km2, assign on 14 September 2007) values, making 2020 the 2d-lowest SIE year of the satellite tv for laptop generation (42 years of files).
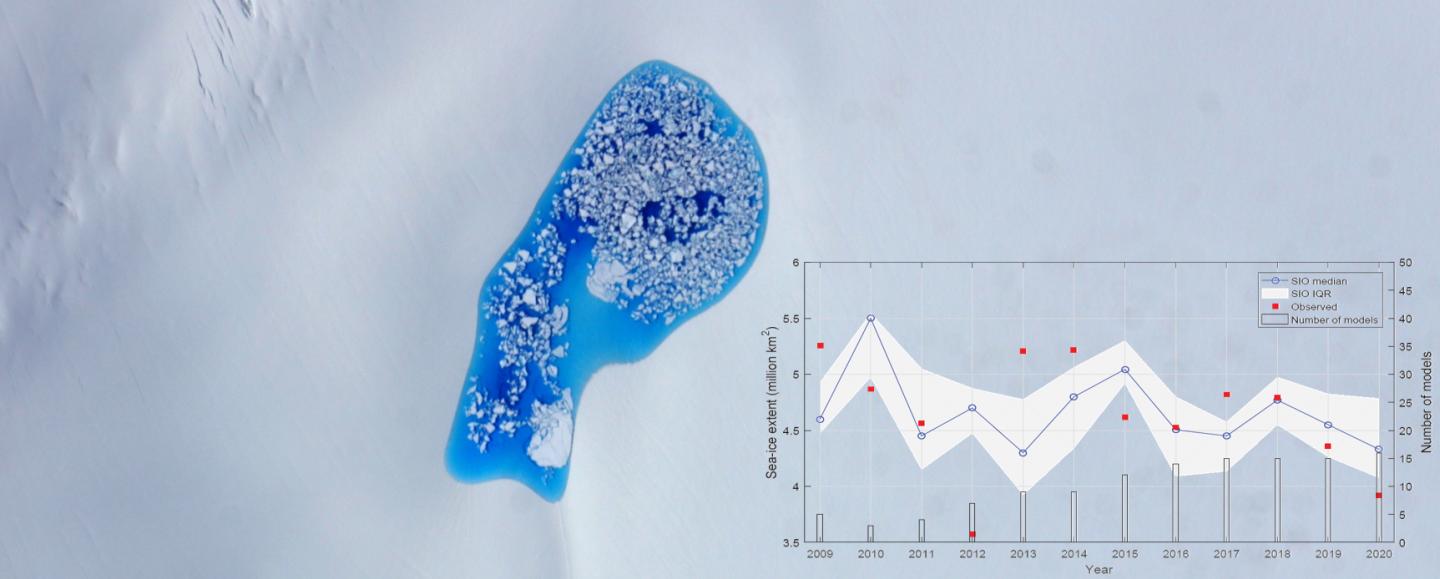
In 2020, a whole of 39 institutions and organizations worldwide submitted their Sea Ice Outlook of the pan-Arctic September SIE. From the June to August SIO, the median of all predictions remained rather stable (4.33 million km2 in June, 4.36 million km2 in July, and 4.3 million km2 in August), which have been much elevated than the noticed cost of three.92 million km2. This indicates that most forecasting programs puffed up the coverage of sea ice in September 2020.
Just precise prediction of Arctic SIE is restful a worldwide scenario. Currently, a commentary published in Atmospheric and Oceanic Science Letters summarized the predictions from 2009 to 2020, and chanced on that most years’ noticed values (8 out of 12) fell open air the predicted interquartile vary of dynamical fashions, indicating that it’s restful a chubby scenario to precisely predict the Arctic SIE on subseasonal-to-seasonal (S2S) time scales, especially in crude years.
“Arctic sea-ice analysis require an improved skill to create extra lawful predictions and close a nearer idea of the physics of sea-ice processes”, says Prof. Wei, creator of this commentary.
Within the next run, extra efforts needs to be made to assimilate sea-ice, atmospheric and oceanic observations to generate a skillful initialization. Within the period in-between, sea-ice prediction relies on a skillful atmospheric mannequin to plot a excessive-quality atmospheric forecast. Lastly, S2S programs could perchance perchance simply restful have the skill to employ adjustments in sea-ice properties due to world warming, which produces youthful and thinner sea ice along with extra soften ponds. Thus, improved descriptions of sea-ice processes in sea-ice mannequin substances of prediction programs are wished.
Global warming is pushing the Arctic to a unhealthy tipping level whereby domino-love irreversible processes could perchance perchance very properly be triggered. On account of this fact, it’s some distance fundamental to salvage better Arctic sea-ice prediction programs to support because the navigation lights to files us via this uncharted future climate.
###
Disclaimer: AAAS and EurekAlert! are no longer chargeable for the accuracy of files releases posted to EurekAlert! by contributing institutions or for the utilization of any knowledge via the EurekAlert system.