Astronomers hope UN can support defend darkish skies in opposition to megaconstellation threat

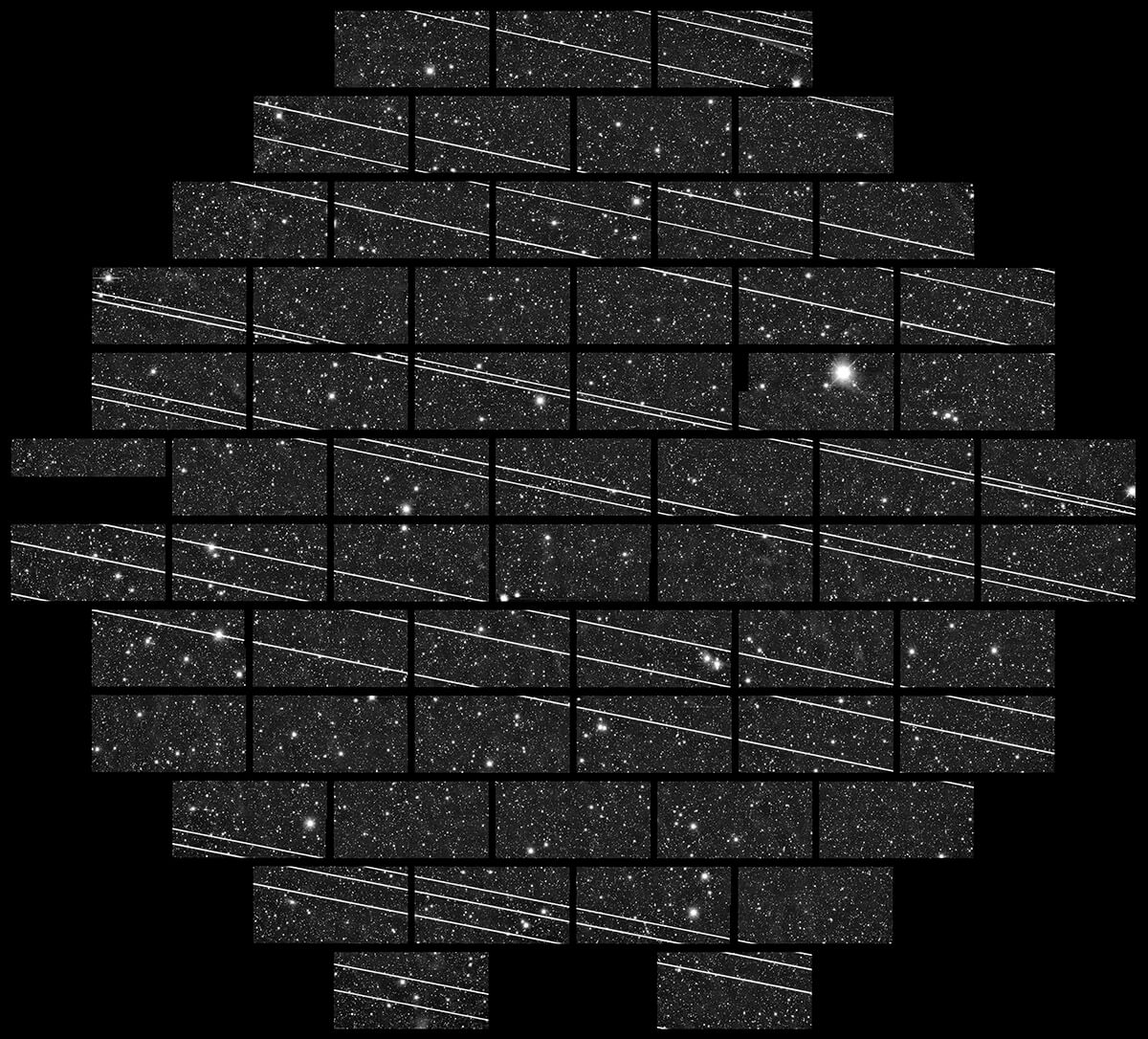
An image from the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory reveals streaks left by Starlink satellites.
(Image: © NSF’s Nationwide Optical-Infrared Astronomy Be taught Laboratory/CTIO/AURA/DELVE)
Astronomers idea to buy their defense of darkness to one other level.
The darkish skies that optical astronomers count on, and many of the relaxation of us take care of, are below threat from satellite megaconstellations like SpaceX’s burgeoning Starlink broadband community, researchers web stressed out.
Many in the astronomy neighborhood web therefore been spurred to motion — learning the matter in ingredient, to illustrate, alerting the public relating to the seriousness of the articulate, and advising satellite operators on the particular strategy to provide their spacecraft dimmer and no more obtrusive. But some scientists for the time being are taking one other step, one which they hope will web even more significant and lasting effects.
Related: The most historical satellites ever launched
That mountainous step started this week with an on-line workshop called “Dark and Peaceful Skies for Science and Society,” which used to be organized jointly by the United International locations Design of job for Outer Design Affairs (UNOOSA) and the Global Mountainous Union. The workshop’s slate on Thursday (Oct. 8) used to be devoted to the arriving megaconstellations, discussing the affect they are able to web on astronomy and ways to mitigate the consequences.
The Thursday discussions will consequence in a articulate that will be submitted to the United International locations’ Committee on the Aloof Uses of Outer Design, said workshop attendee Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer and satellite tracker primarily primarily based at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
“The lengthy-term hope is that we are capable of persuade the UN to articulate guidelines about keeping the night sky that can replicate a more cost effective compromise between the satellite operators and the desires of astronomers,” McDowell told Design.com. Those guidelines will then be picked up by national governments as licensing rules, if all goes in response to position, he added.
Related: SpaceX’s Starlink satellite megaconstellation launches in pictures
Such guidelines will lend a hand operators to assemble their spacecraft to be as sad as probably and to withhold them at altitudes lower than 360 miles (600 kilometers), McDowell said. (In higher orbits, satellites take the sun for longer stretches and are therefore seen through more of the night. It also takes longer for dull satellites in higher orbits to tumble reduction to Earth.)
This kind is a new one for the astronomy neighborhood, which has no longer gotten fervent significant in role-governance disorders, he added. Neophytes though they are in this role, McDowell and his colleagues assign no longer need unrealistic expectations relating to the race of development.
“Or no longer it is the very starting up of a lengthy battle,” McDowell said. “And so for the time being, we’re going to web a few years, I judge, where we will in actuality compare significant impacts on flooring-primarily primarily based astronomy.”
Those impacts are expected to come reduction primarily from three mountainous commercial constellations, all of which would perchance well be designed to beam web provider from low-Earth orbit (LEO): SpaceX’s Starlink, OneWeb’s community and Project Kuiper, which will be flee by Amazon. SpaceX and Amazon idea to withhold their craft attain or below the 360-mile line, but OneWeb’s constellation will waft significant higher, about 750 miles (1,200 km) up.
Amazon has said that Project Kuiper will consist of about 3,200 spacecraft. SpaceX has permission from the U.S. Federal Communications Commission to loft 12,000 Starlink satellites and has proposed a “Abilities 2” machine that will be 30,000 solid. OneWeb’s structure, in the period in-between, envisions as regards to 48,000 spacecraft sooner or later.
For standpoint: Humanity has launched fewer than 10,000 objects to the final frontier for the reason that fracture of day of the role age in 1957, in response to UNOOSA.
Starlink: SpaceX’s satellite web venture
Or no longer it is unclear how a bunch of these web satellites will basically attain role. SpaceX has already launched as regards to 800 Starlinks and plans to continue lofting 60-satellite batches relatively in most cases for the foreseeable future. Amazon hasn’t launched any Kuiper craft but, nonetheless. OneWeb has orbited 74, however the firm unbiased no longer too lengthy previously went through monetary catastrophe and used to be sold by a neighborhood co-led by the UK national authorities.
So there is a range of probably outcomes, most of which will terror astronomers. For instance, McDowell characterized the affect of 10,000 LEO web satellites on mighty observations as “severe” and that of 100,000 spacecraft, a tally that can consequence in case your total corporations hit their most formidable targets, as “catastrophic.”
The impacts would perchance no longer be spread evenly across mighty campaigns, either. For instance, projects that must web a examine shut to the horizon spherical twilight, corresponding to hunts for attain-Earth asteroids, will be hit in particular laborious, McDowell said.
Astronomers web had productive conversations with SpaceX, which has worked to slash reduction the brightness of its 570-lb. (260 kilograms) Starlink craft. (The first few Starlink batches were surprisingly vivid, which galvanized researchers’ mission.) As an illustration, the firm has added “visors” to Starlink spacecraft to withhold daylight off their most reflective surfaces and is orienting the satellites to sad them from a flooring observer’s standpoint.
McDowell said that he appreciates such efforts, which is mostly certain that that Starlink satellites are too faint to gape with the naked deem for basically the most portion. (They’ll calm articulate up as vivid streaks after they fling into a calm telescope’s field of gaze, nonetheless.)
However the articulate is greater than SpaceX, Amazon, OneWeb or any diversified firm, he stressed out. And that is reasons why he and his colleagues are appealing in this new course.
“The moral respond is to get the UN and web some most efficient practices agreed,” McDowell said.
UN guidelines would perchance well also support mitigate one other doable affect of the arriving megaconstellations — an increasingly more cluttered orbital atmosphere. And they would come in in in particular at hand when mountainous satellite networks race global, which is lag to happen in some unspecified time in the future. Indeed, McDowell said he had unbiased no longer too lengthy previously seen the foremost detailed proposal for a Chinese megaconstellation.
Mike Wall is the creator of “Out There” (Immense Central Publishing, 2018; illustrated by Karl Tate), a guide relating to the behold for alien existence. Note him on Twitter @michaeldwall. Note us on Twitter @Spacedotcom or Fb.
Be half of our Design Forums to withhold talking role on the most up-to-date missions, night sky and more! And whenever you web a data tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].