
Contemporary watch shows microplastics was ‘hubs’ for pathogens, antibiotic-resistant micro organism

Or no longer it’s estimated that a median-sized wastewater therapy plant serving roughly 400,000 residents will discharge up to 2,000,000 microplastic particles into the ambiance day to day. Yet, researchers are silent studying the environmental and human health impact of these extremely-ravishing plastic particles, no longer up to 5 millimeters in length, define in all the pieces from cosmetics, toothpaste and garments microfibers, to our food, air and keen water.
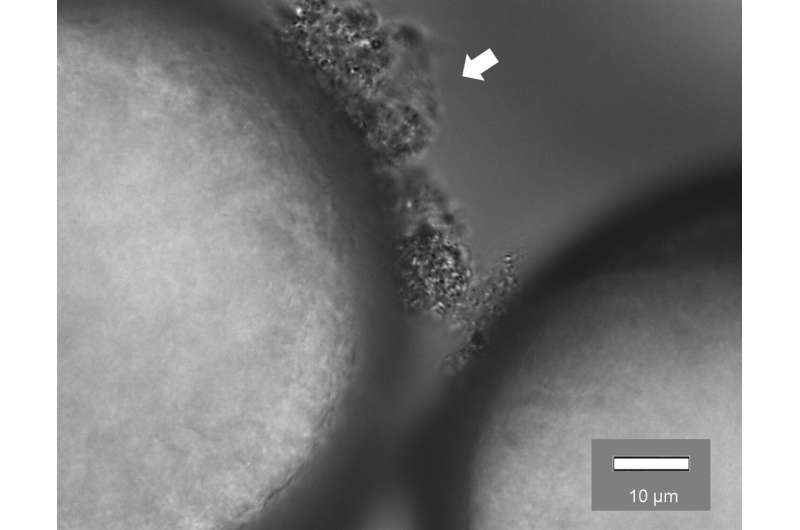
Now, researchers at Contemporary Jersey Institute of Abilities occupy shown that ubiquitous microplastics can turn out to be ‘hubs’ for antibiotic-resistant micro organism and pathogens to grow when they wash down household drains and enter wastewater therapy vegetation—forming a slimy layer of buildup, or biofilm, on their surface that lets in pathogenic microorganisms and antibiotic damage to glue and comingle.
In findings published in the Journal of Dangerous Materials Letters, researchers realized sure lines of micro organism elevated antibiotic resistance by up to 30 times while residing on microplastic biofilms that might perhaps perchance manufacture within activated sludge devices at municipal wastewater therapy vegetation.
“A preference of latest stories occupy centered on the negative impacts that hundreds of thousands of plenty of microplastic damage a Three hundred and sixty five days is having on our freshwater and ocean environments, however till now the feature of microplastics in our cities’ and cities’ wastewater therapy processes has largely been unknown,” stated Mengyan Li, companion professor of chemistry and environmental science at NJIT and the watch’s corresponding author. “These wastewater therapy vegetation will also be hotspots where varied chemicals, antibiotic-resistant micro organism and pathogens converge and what our watch shows is that microplastics can attend as their carriers, posing coming near risks to aquatic biota and human health in the occasion that they bypass the water therapy process.”
“Most wastewater therapy vegetation aren’t designed for the elimination of microplastics, so that they’re continuously being launched into the receiving ambiance,” added Dung Ngoc Pham, NJIT Ph.D. candidate and first author of the watch. “Our draw used to be to evaluation whether or no longer microplastics are enriching antibiotic-resistant micro organism from activated sludge at municipal wastewater therapy vegetation, and if that is the case, learn more relating to the microbial communities enthusiastic.”
In their watch, the group silent batches of sludge samples from three home wastewater therapy vegetation in northern Contemporary Jersey, inoculating the samples in the lab with two in model commercial microplastics—polyethylene (PE) and polystyrene (PS). The group used a combination of quantitative PCR and next-generation sequencing tactics to establish the species of micro organism that are inclined to grow on the microplastics, tracking genetic adjustments of the micro organism along the reach.
The evaluation revealed that three genes in explicit—sul1, sul2 and intI1— identified to relief resistance to customary antibiotics, sulfonamides, were realized to be up to 30 times bigger on the microplastic biofilms than in the lab’s control assessments utilizing sand biofilms after correct three days.
When the group spiked the samples with the antibiotic, sulfamethoxazole (SMX), they chanced on it extra amplified the antibiotic resistance genes by up to 4.5-fold.
“Beforehand, we belief the presence of antibiotics might perhaps perchance almost definitely be necessary to toughen antibiotic-resistance genes in these microplastic-associated micro organism, however it no doubt appears microplastics can naturally allow for uptake of these resistance genes on their dangle.” stated Pham. “The presence of antibiotics does occupy a gigantic multiplier attain alternatively.”
Eight diversified species of micro organism were realized extremely enriched on the microplastics. Amongst these species, the group observed two emerging human pathogens most ceaselessly linked with respiratory an infection, Raoultella ornithinolytica and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia, continuously hitchhiking on the microplastic biofilms.
The group whine the most in model stress realized on the microplastics by far, Novosphingobium pokkalii, is doubtless a key initiator in forming the sticky biofilm that draws such pathogens—as it proliferates it might perhaps well perhaps make contributions to the deterioration of the plastic and salvage bigger the biofilm. On the identical time, the group’s watch highlighted the feature of the gene, intI1, a cellular genetic ingredient essentially accountable for enabling the alternate of antibiotic resistance genes amongst the microplastic-sure microbes.
“We might perhaps perchance judge of microplastics as tiny beads, however they give a large surface dwelling for microbes to reside,” explained Li. “When these microplastics enter the wastewater therapy plant and mix in with sludge, micro organism admire Novosphingobium can by probability put to the skin and secrete glue-admire extracellular substances. As other micro organism put to the skin and grow, they might be able to even swap DNA with every other. That is how the antibiotic resistance genes are being unfold amongst the neighborhood.”
“Now we occupy evidence that the micro organism developed resistance to other antibiotics this reach as properly, reminiscent of aminoglycoside, beta-lactam and trimethoprim,” added Pham.
Now, Li says the lab is extra studying the feature of Novosphingobium in biofilm formation on microplastics. The group can be in quest of to better perceive the extent to which such pathogen-carrying microplastics might perhaps perchance almost definitely be bypassing water therapy processes, by studying resistance of microplastic biofilms all the plan in which thru wastewater therapy with disinfectants reminiscent of UV gentle and chlorine.
“Some states are already pondering fresh rules on utilizing microplastics in user products. This watch raises requires extra investigation on microplastic biofilms in our wastewater programs and pattern of effective reach for casting off microplastics in aquatic environments,” stated Li.
More data:
Dung Ngoc Pham et al, Microplastics as hubs enriching antibiotic-resistant micro organism and pathogens in municipal activated sludge, Journal of Dangerous Materials Letters (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.hazl.2021.100014
Citation:
Contemporary watch shows microplastics was ‘hubs’ for pathogens, antibiotic-resistant micro organism (2021, March 19)
retrieved 19 March 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-03-microplastics-hubs-pathogens-antibiotic-resistant-micro organism.html
This story is enviornment to copyright. Other than any shapely dealing for the reason of private watch or research, no
allotment might perhaps perchance almost definitely be reproduced without the written permission. The state is supplied for data purposes handiest.