
COVID-19 pandemic led to stark rise in depressive and fear disorders globally in 2020: glance
Cases of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders increased by more than a quarter worldwide in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, in step with the first world estimates of impacts of the pandemic on mental health, printed in The Lancet.
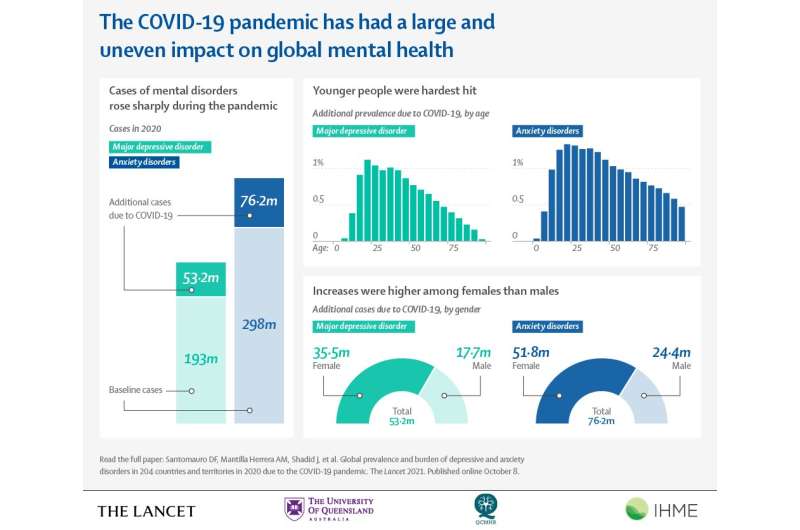
In 2020, instances of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders increased by 28% and 26%, respectively. Girls were affected more than men, and younger of us were more affected than older age groups. Worldwide locations with high COVID-19 infection rates and valuable reductions within the motion of of us—a ruin consequence of measures much like lockdowns and college closures—had essentially the most attention-grabbing increases in prevalence of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders.
Even sooner than the COVID-19 pandemic, valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders—which is willing to develop the risk of varied health outcomes much like suicide—were valuable contributors to the world burden of illness, affecting thousands and thousands of fellows and girls folks of all ages loyal throughout the world.
Lead author Dr. Damian Santomauro, of the Queensland Centre for Psychological Health Research, Faculty of Public Health, University of Queensland, Australia, acknowledged: “Our findings highlight an urgent must enhance mental health programs in present an explanation for to address the rising burden of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders worldwide. Selling mental wellbeing, focused on factors contributing to unlucky mental health which have been made worse by the pandemic, and bettering remedy in case you develop a mental dysfunction must be central to efforts to enhance enhance companies. Even sooner than the pandemic, mental health-care programs in most countries have traditionally been below-resourced and disorganised of their carrier provide. Assembly the added demand for mental health companies as a result of COVID-19 will likely be fascinating, but taking no action could perhaps aloof no longer be an risk.”
Except now, no compare had analysed the world affect of the COVID-19 pandemic on prevalence of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders in 2020. Most aged work consisted of surveys particularly locations over a short duration of time.
The new glance is the first to evaluate world impacts of the pandemic on valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders, quantifying the prevalence and burden of the disorders by age, intercourse, and build in 204 countries and territories in 2020.
A systematic literature overview modified into once performed to determine inhabitants discover details printed between January 1, 2020, and January 29, 2021. Eligible compare reported prevalence of depressive or fear disorders that were advisor of the conventional inhabitants and had a pre-pandemic baseline. Using a illness modelling meta-evaluation tool, details from eligible compare modified into once old to estimate adjustments in prevalence of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders as a result of COVID-19 in step with age, intercourse, and build, along with in locations for which no eligible compare were readily within the market. Estimates of on each day basis COVID-19 infection rate and motion of of us were old as indicators of the affect of the pandemic on populations.
The systematic overview known 5,683 outlandish details sources, of which 48 (one in every of which reported loyal through two areas) met inclusion criteria. Most compare were from Western Europe (22) and high-earnings North America (14), with others from Australasia (5), high-earnings Asia Pacific (5), East Asia (2), and central Europe (1).
The meta-evaluation indicates that increased COVID-19 infection rate and reduced motion of of us were linked to increased prevalence of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders, suggesting that countries hit hardest by the pandemic in 2020 had essentially the most attention-grabbing increases in prevalence of the disorders.
In the absence of the pandemic, mannequin estimates counsel there would have been 193 million instances of valuable depressive dysfunction (2,471 instances per 100,000 inhabitants) globally in 2020. Nonetheless, the evaluation reveals there were 246 million instances (3,153 per 100,000), a rise of 28% (a further 53 million instances). Larger than 35 million of the extra instances were in ladies folks, compared with close to 18 million in men.
Model estimates counsel there would have been 298 million instances of fear disorders (3,825 per 100,000 inhabitants) globally in 2020 had the pandemic no longer took location. The evaluation indicates there were essentially an estimated 374 million instances (4,802 per 100,000) for the length of 2020, a rise of 26% (a further 76 million instances). Virtually 52 million of the extra instances were in ladies folks, compared with spherical 24 million in men.
Youthful of us were more plagued by valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders in 2020 than older age groups. The extra prevalence of these disorders peaked among these aged 20-24 years (1,118 extra instances of valuable depressive dysfunction per 100,000 and 1,331 extra instances of fear disorders per 100,000) and declined with rising age.
Co-author Alize Ferrari, GBD mental disorders team lead at the Queensland Centre for Psychological Health Research, Faculty of Public Health, University of Queensland, Australia, acknowledged: “The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated many novel inequalities, and social determinants of mental health. Sadly, for rather about a reasons, ladies folks were always more more likely to be worse plagued by the social and financial consequences of the pandemic. Further caring and family responsibilities are inclined to drop on ladies folks, and on memoir of ladies folks are more more likely to be victims of home violence, which increased at diverse phases of the pandemic.
“Faculty closures and wider restrictions limiting adolescence’s capacity to be taught and work along with their peers, mixed with the increased risk of unemployment, also intended that adolescence were also more closely impacted by valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders for the length of the pandemic. It is wanted that policymakers remove underlying factors much like these into memoir as portion of measures to enhance mental health companies.”
The authors acknowledge that their glance modified into once diminutive by an absence of high quality details on the results of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in loads of parts of the world, in particular low- and heart-earnings countries. This capability that, they are saying extrapolated estimates generated for countries the build details modified into once lacking must be interpreted with warning, and make contact with for improved details coverage and quality globally. Most readily within the market details modified into once in step with self-reported symptom scales that the majority effective estimate probable instances of valuable depressive dysfunction and fear disorders. Extra details from diagnostic mental health surveys advisor of the conventional inhabitants—of which most attention-grabbing three lined the glance duration—will enhance belief of the pandemic’s results on mental health. The prevalence of varied mental disorders—much like drinking disorders—could perhaps additionally have been plagued by the COVID-19 pandemic, and the authors sing these must be assessed as new mental health surveys are undertaken.
Writing in a linked Commentary, Dr. Maxime Taquet and Professor Paul Harrison, from the University of Oxford, and Professor Emily Holmes, from Uppsala University and the Karolinska Institute, who weren’t angry about the glance, acknowledged: “The valuable world insight into the burden of depressive and fear disorders for the length of the pandemic by Santomauro and colleagues starkly highlights the affect of the pandemic on mental health globally.” They echo the glance authors’ calls for action to enhance mental health programs, announcing: “The glance could perhaps aloof as a result of this truth urgently incentivise more compare to search out out the fuller geographic distribution of unhappy and fear, the prevalence of depressive and fear disorders, and the underpinning mechanisms to enhance mental health within the context of the COVID-19 pandemic globally.”
Extra details:
World prevalence and burden of depressive and fear disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, The Lancet (2021). doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(21)02143-7 , www.thelancet.com/journals/lan … (21)02143-7/fulltext
Quotation:
COVID-19 pandemic led to stark rise in depressive and fear disorders globally in 2020: glance (2021, October 9)
retrieved 11 October 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/details/2021-10-covid-pandemic-stark-depressive-fear.html
This doc is enviornment to copyright. Except for any elegant dealing for the explanation of within most glance or compare, no
portion would be reproduced without the written permission. The allege is supplied for details applications most attention-grabbing.