Discovery of latest geologic route of calls for modifications to plate tectonic cycle
Geoscientists on the College of Toronto (U of T) and Istanbul Technical College be pleased chanced on a novel route of in plate tectonics which reveals that extensive harm occurs to areas of Earth’s crust lengthy earlier than it can presumably quiet be geologically altered by known plate-boundary processes, highlighting the necessity to amend recent understandings of the planet’s tectonic cycle.
Plate tectonics, an licensed theory for over 60 years that explains the geologic processes occurring below the bottom of Earth, holds that its outer shell is fragmented into continent-sized blocks of actual rock, known as “plates,” that mosey over Earth’s mantle, the rocky inner layer above the planet’s core. Because the plates float round and collide with one another over million-years-lengthy classes, they originate all the pieces from volcanoes and earthquakes to mountain ranges and deep ocean trenches, on the boundaries where the plates collide.
Now, using supercomputer modelling, the researchers existing that the plates on which Earth’s oceans sit are being torn apart by big tectonic forces even as they float about the globe. The findings are reported in a witness published this week in Nature Geoscience.
The bearing in mind to this point centered finest on the geological deformation of those drifting plates at their boundaries after that they had reached a subduction zone, such because the Marianas Trench in the Pacific Ocean where the gigantic Pacific plate dives below the smaller Philippine plate and is recycled into Earth’s mantle.
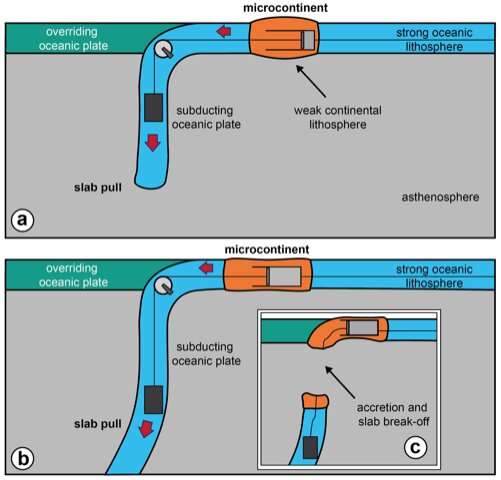
The novel study reveals great earlier harm to the drifting plate extra a ways from the boundaries of two colliding plates, centered round zones of microcontinents—continental crustal fragments that be pleased damaged off from necessary continental heaps to blueprint accelerate islands on the total a few hundred kilometers from their fatherland.
“Our work discovers that a in point of fact a form of fragment of the plate is being pulled apart thanks to the subduction route of, and at a remarkably early fragment of the tectonic cycle,” talked about Erkan Gün, a Ph.D. candidate in the Division of Earth Sciences in the Faculty of Arts & Science at U of T and lead creator of the witness.
The researchers timeframe the mechanism a “subduction pulley” where the load of the subducting portion that dives below another tectonic plate, pulls on the drifting ocean plate and tears apart the feeble microcontinent sections in an early fragment of potentially necessary harm.
“The harm occurs lengthy earlier than the microcontinent fragment reaches its destiny to be consumed in a subduction zone on the boundaries of the colliding plates,” talked about Russell Pysklywec, professor and chair of the Division of Earth Sciences at U of T, and a coauthor of the witness. He says another manner to search out out about at it is miles to think the drifting ocean plate as an airport baggage conveyor, and the microcontinents are admire items of baggage travelling on the conveyor.
“The conveyor system itself is on the total tearing apart the baggage as it travels around the carousel, earlier than the baggage even reaches its owner.”
The researchers arrived on the outcomes following a mysterious observation of necessary extension of rocks in alpine regions in Italy and Turkey. These observations quick that the tectonic plates that brought the rocks to their recent place were already highly damaged earlier than the collisional and mountain-constructing events that most steadily trigger deformation.
“We devised and performed computational Earth fashions to study a route of to chronicle for the observations,” talked about Gün. “It turned out that the temperature and tension rock histories that we measured with the digital Earth fashions match closely with the enigmatic rock evolution seen in Italy and Turkey.”
In accordance to the researchers, the findings refine some of the most fundamental functions of plate tectonics and call for a revised figuring out of this foremost theory in geoscience.
“In total we possess—and divulge—that the ocean plate conveyor is just too actual to be damaged as it drifts world broad, nevertheless we impart otherwise,” talked about Pysklywec.
Extra data:
Erkan Gün et al, Pre-collisional extension of microcontinental terranes by a subduction pulley, Nature Geoscience (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-021-00746-9
Quotation:
Discovery of latest geologic route of calls for modifications to plate tectonic cycle (2021, Also can 11)
retrieved 12 Also can 2021
from https://phys.org/data/2021-05-discovery-geologic-plate-tectonic.html
This tale is subject to copyright. Other than any pretty dealing for the motive of non-public witness or study, no
fragment will most likely be reproduced without the written permission. The vow is offered for data capabilities finest.