Dynamics of contact electrification
A recent file on Science Advances developed by Mirco Kaponig and colleagues in physics and nanointegration in Germany, detailed the very fundamental thought of contact electrification between two metals. In a brand contemporary experimental diagram, the researchers followed the value of a exiguous sphere bouncing on a grounded planar electrode on a timescale down to 1 microsecond. The team eminent how the sphere discharged in the 2nd of contact lasting for 6 to eight microseconds. For the time being of disruption of the electrical contact, the sphere regained rate a long way past expectations relative to the contact doable difference. The extra rate arose with increasing contact home.
Contact electrification
Contact electrification is a ubiquitous phenomenon that happens when two surfaces touch. The job is an fundamental diagram of triboelectricity that could well be seen instantly in daily life. The phenomenon is guilty for lightening in thunderstorms, sandstorms or volcanic plumes. The job could well be of main scenario when handling maybe explosive liquids or dusts. Which means that, researchers possess established empirical safety regulations to steer clear of hazards induced by electrical discharges by means of triboelectric charging. Even though the phenomenon used to be described for more than 2000 years, the underlying mechanisms are composed debated. Scientists most continuously take into story three sorts of rate switch in conjunction with the switch of electrons, ions or cloth with partial rate. In metal-metal contacts, electrons could well be transferred between two surfaces to assign contact doable. The amount of transferred rate additionally depended on the mutual ability when the electrical contact is disrupted, and the seen rate switch strongly supported the thought that of electron switch for metal-metal contacts. The scenario is much less glaring for metal-insulator or insulator-insulator contacts. Kaponig et al. attributable to this truth presented a brand contemporary experimental technique to analyze rate switch throughout contact electrification, with phenomenal choice.
The experiments
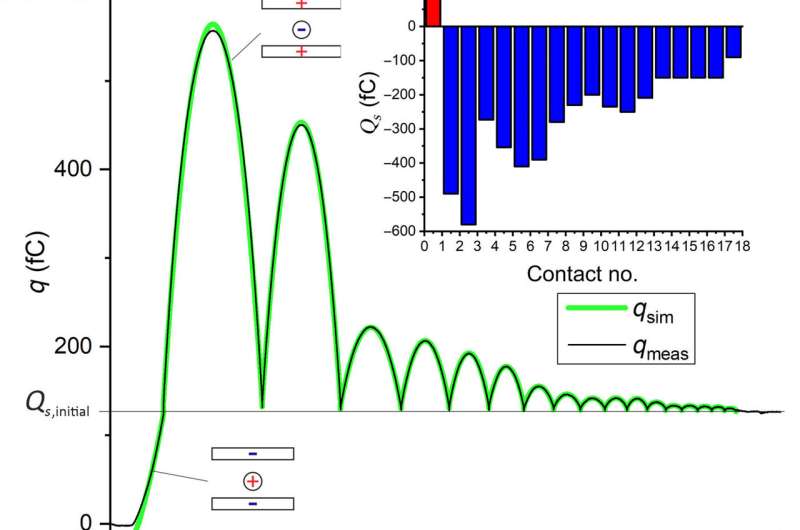
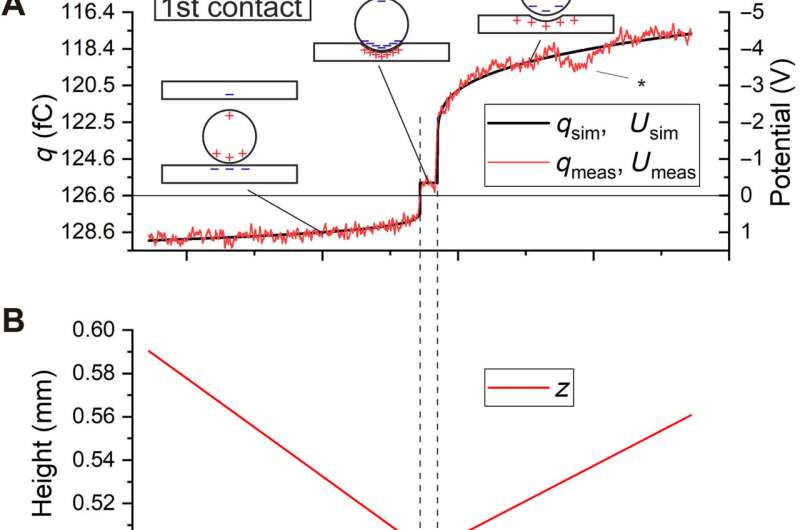
The work published how the electrical doable of a metallic particle bouncing from a metallic flooring developed with time. Fixed with the outcomes, Kaponig et al. eminent how the rate elevated with affect velocity in metal-metal contacts; a feature continuously seen with metal-insulator and insulator-insulator contacts but hither to unobserved for metal-metal contacts. For the length of the experiments, this led to unexpectedly excessive electrical potentials for purely metallic contacts. For the reason that electrical contact used to be easiest established for a few microseconds throughout mechanical contact, the technique didn’t snatch the parameters of the rate before contact. The different of the sphere used to be attributable to this truth easiest lowered to the contact doable of a few tenths of a volt. When the electrical contact peaceable from the flooring, on the opposite hand, the rate on the sphere established a doable of as much as 3 V for under 1 microsecond.
Charge switch
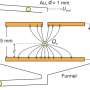
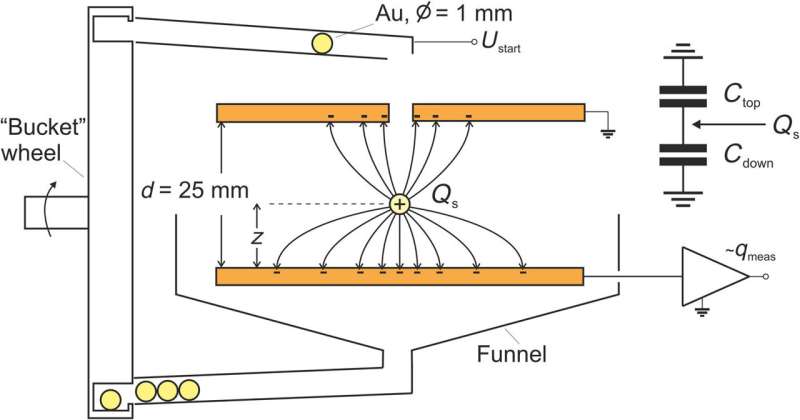
Scientists had beforehand studied the rate switch of particles bouncing on an inclined flooring per contact-free electrostatic detection. Kaponig et al. attributable to this truth developed an experimental draw to measure the rate before and after flooring contact to practice the dynamics in proper-time. In the setup, they got a call greater than 1 microsecond in time for approximately 6000 electrons. They studied the mosey and reveal to electrification by losing gold spheres which could well be 1 mm in diameter by means of a exiguous orifice correct into a parallel plate capacitor. The spheres bounced on an nearly grounded lower plate, allowing the scientists to measure the induced and transferred prices. The team performed the experiments in vacuum. The stamp detected at the lower plate of the setup had two contributions in conjunction with the rate on the sphere and the rate transferred to the sphere. The team eminent the purpose to stamp of a gold sphere bouncing more than 15 times on the lower plate of the capacitor fabricated from copper, the trajectory of the sphere consisted of segments of free fall, starting and polishing off by means of contact with the plate.
When Kaponig et al. closely inspected the stamp, they identified the moments of contact by abrupt adjustments of the measured rate. They eminent how the time spent between two contacts definite the segment of the trajectory. The team subsequent utilized a voltage at the ramp to manual the sphere to the entrance of the capacitor, the put aside the sphere used to be positively charged before it entered the capacitor and possess change into negatively charged throughout the first contact. The seen magnitude of the rate used to be unexpectedly excessive. The researchers then repeated the experiment with assorted preliminary prices, the put aside the sphere change into negatively charged at the first and following contact. Another key to tag contact electrification incorporated the ability of the sphere. Fixed with the excessive magnitude of the rate on the sphere, the team eminent a doable of quite a bit of volts unexpectedly excessive for a purely metallic machine. The electrical contact used to be easiest established as a mechanical contact for a few microseconds. The different of the sphere used to be attributable to this truth lowered to the contact doable of a few tenths of a volt. As the distance between the sphere and plate grew, the ability further elevated.
Outlook
The team described the observations the utilization of a metal-contact model in which the contact home raised for the first-contact, followed by an loads of ability formed at the interface attributable to the minimal distance between the prices. This ability charged to the contact doable in the show of picocoulombs. Upon contact ruin, the two adjacent surfaces of the plate and sphere fit practically snugly to manufacture a spacious home at cease separation and a greater ability, the put aside the dimensions of the home depended on the rate of the sphere. In this means, Mirco Kaponig and colleagues confirmed how a metallic sphere bouncing from a metal plate completed a doable of as much as 10 V, attributable to a deformation of the contact home. This led to an elevated ability between the sphere and the plate upon electrical contact disruption. The outcomes are crucial for contact electrification and triboelectricity for enhanced rate switch.
Extra info:
Kaponig M. et al. Dynamics of contact electrification, Science Advances, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg7595
Baytekin H. T. et al. The mosaic of flooring rate in contact electrification, Science, 10.1126/science.1201512
Gimzewski J. Okay. et al. Transition from the tunneling regime to point contact studied the utilization of scanning tunneling microscopy, Physical Overview B, doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.36.1284
© 2021 Science X Network
Quotation:
Dynamics of contact electrification (2021, June 9)
retrieved 9 June 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-06-dynamics-contact-electrification.html
This doc is field to copyright. Other than any gorgeous dealing for the reason of non-public peep or analysis, no
phase could well be reproduced with out the written permission. The stammer is supplied for info functions easiest.