Fungus creates a immediate tune for carbon
 PNAS” width=”600″>
PNAS” width=”600″>Minute algae in Earth’s oceans and lakes decide in sunlight and carbon dioxide and flip them into sugars that withhold the relaxation of the aquatic food internet, gobbling up about as noteworthy carbon as your total world’s bushes and flowers blended.
Original compare presentations a in actuality crucial piece has been lacking from the primitive clarification for what occurs between this first “fixing” of CO2 into phytoplankton and its eventual launch to the setting or descent to depths the build it now not contributes to global warming. The lacking piece? Fungus.
“Generally, carbon moves up the food chain in aquatic environments in a thoroughly different plot than we recurrently mediate it does,” mentioned Anne Dekas, an assistant professor of Earth machine science at Stanford College. Dekas is the senior creator of a paper printed June 1 in Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences that quantifies how noteworthy carbon goes into parasitic fungi that assault microalgae.
Underwater merry-slide-round
Researchers except now gather predicted that most carbon fixed into colonies of onerous-shelled, single-celled algae identified as diatoms then funnels straight into bacteria—or dissolves like tea within the surrounding water, the build or now not it’s largely taken up by other bacteria. Primitive thinking assumes carbon escapes from this microbial loop mainly thru greater organisms that graze on the bacteria or diatoms, or thru the CO2 that returns to the setting because the microbes breathe.
This streak is a really out of the ordinary within the context of climate swap. “For carbon sequestration to happen, carbon from CO2 desires to slide up the food chain into giant ample objects of biomass that it’ll sink down into the backside of the ocean,” Dekas mentioned. “That’s how or now not it’s in actuality removed from the setting. If it true cycles for long classes within the outside of the ocean, it can perhaps be launched relief to the air as CO2.”
It turns out fungus creates an underappreciated negate lane for carbon, “shunting” as noteworthy as 20 p.c of the carbon fixed by diatoms out of the microbial loop and into the fungal parasite. “As an alternative of going thru this merry-slide-round, the build the carbon could well within the slay slide relief to the setting, you are going to need gotten a extra bid path to the increased phases within the food internet,” Dekas mentioned.
The findings moreover gather implications for industrial and recreational settings that form out substandard algal blooms. “In aquaculture, so as to set up the principle gash, like fish, wholesome, fungicides will in all probability be added to the water,” Dekas mentioned. That will pause fungal infection of the fish, but it indubitably could well remove a natural check on algal blooms that price the industry some $8 billion per three hundred and sixty five days. “Except we heed the dynamics between these organisms, we can gather to mild be comely cautious about the administration insurance policies we’re the utilization of.”
Microbial interactions
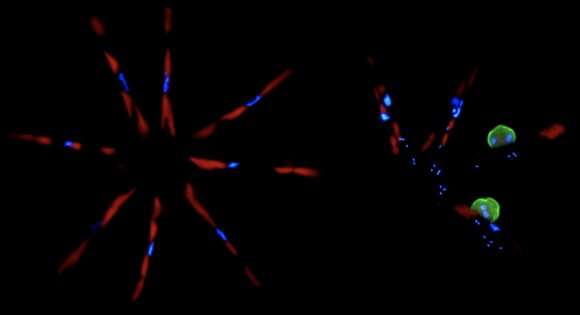
The authors based their estimates on experiments with populations of chytrid fungi called Rhizophydiales and their host, a form of freshwater algae or diatom named Asterionella formosa. Coauthors in Germany labored to isolate these microbes, as smartly as bacteria learned in and round their cells, from water mild from Lake Stechlin, about 60 miles north of Berlin.
“Keeping apart one microorganism from nature and growing it within the laboratory is complex, but setting apart and sustaining two microorganisms as a pathosystem, in which one kills the other, is a true space,” mentioned lead creator Isabell Klawonn, who labored on the compare as a postdoctoral pupil in Dekas’ lab at Stanford. “Only a pair of mannequin programs are therefore on hand to collect a study such parasitic interactions.”
Scientists surmised as early because the 1940s that parasites played a in actuality crucial role in controlling the abundance of phytoplankton, and so that they seen epidemics of chytrid fungus infecting Asterionella blooms in lake water. Technological advances gather made it likely to make a decision apart these invisible worlds in supreme and measurable ingredient—and commence to take into myth their have an effect on in a noteworthy bigger characterize.
“We’re realizing as a neighborhood that or now not it is now not true the capabilities of an particular person microorganism that is crucial for working out what occurs within the setting. It be how these microorganisms work together,” Dekas mentioned.
The authors measured and analyzed interactions within the Lake Stechlin pathosystem the utilization of genomic sequencing; a fluorescence microscopy approach that involves attaching fluorescent dye to RNA within microbial cells; and a highly in actuality educated instrument at Stanford—one of handiest a pair of dozen within the world—called NanoSIMS, which creates nanoscale maps of the isotopes of parts that are cloak in materials in vanishingly minute amounts. Dekas mentioned, “To win these single-cell measurements to reward how photosynthetic carbon is flowing between negate cells, from the diatom to the fungus to the linked bacteria, or now not it’s the handiest approach to accomplish it.”
The true amount of carbon diverted to fungus from the microbial merry-slide-round could well differ in other environments. However the discovery that it can perhaps be as high as 20 p.c in even one setting is most considerable, Dekas mentioned. “Whenever you happen to’re changing this methodology by bigger than a pair of p.c in any route, it’ll gather dramatic implications for biogeochemical biking. It makes a giant difference for our climate.”
More data:
Isabell Klawonn et al, Characterizing the “fungal shunt”: Parasitic fungi on diatoms gather an impact on carbon waft and bacterial communities in aquatic microbial food webs, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (2021). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2102225118
Citation:
Fungus creates a immediate tune for carbon (2021, June 4)
retrieved 5 June 2021
from https://phys.org/data/2021-06-fungus-immediate-tune-carbon.html
This document is enviornment to copyright. Besides any gorgeous dealing for the motive of deepest sight or compare, no
portion will in all probability be reproduced with out the written permission. The vow is supplied for data capabilities handiest.