Global air pollution estimates level to surprises, opportunity
It is miles now no longer authentic to come upon headlines about air pollution or global warming and accumulate that they reach diversified conclusions depending upon the ideas source.
Researchers at Washington College in St. Louis pale a harmonized technique, incorporating files from a pair of satellites and ground monitors with computer modeling to compile a comprehensive, fixed plan of air pollution across the globe. Their files spans 1998-2018, offering a recent image of the order of the field’s air quality that finds some surprises, each and each for better and for worse.
The analysis was led by Melanie Hammer, a postdoctoral analysis fellow in the lab of Randall Martin, professor of vitality, environmental and chemical engineering in the McKelvey College of Engineering.
Results of their seek for that checked out PM2.5—diminutive particles that are ready to create their manner deep into a individual’s respiratory procedure—had been printed June 3 in Environmental Science & Expertise.
“Prior analysis that seek for at long-term PM2.5 haven’t pale files as recent as we have,” Hammer mentioned. Older files can not rob the outcomes of many applications aimed at curbing air pollution—even in the occasion that they’ve been in manufacture for virtually a decade.
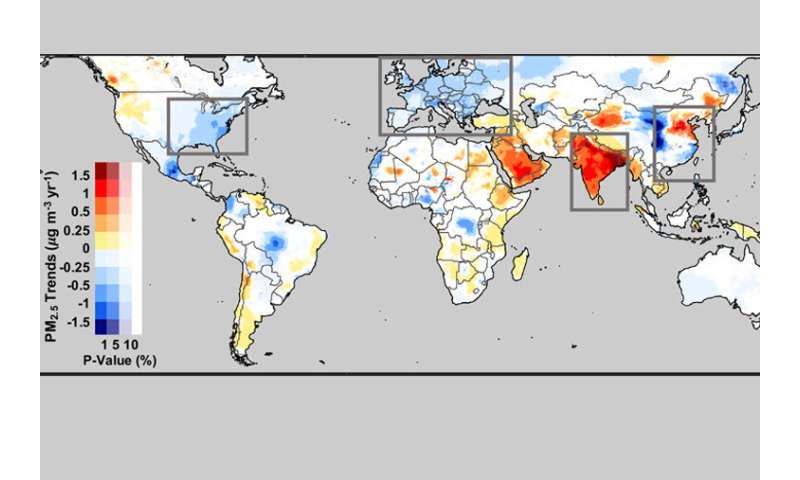
That grew to become out to be the case in China, where a main drop in air pollution in the recent previous was the final consequence of ideas begun in earnest round 2011. Other files items operate now no longer rob the drop.
And in India—another space of remark—the legend was now no longer as certain. “It looks there’s reasonably a plateau of PM2.5 stages,” Hammer mentioned. Though level-headed, stages are now no longer rising as steeply as other reports could well moreover counsel.
PM2.5 refers to the scale of particles—2.5 microns. These diminutive particles are created in nature, nonetheless also by human activities, including some manufacturing processes, vehicle utilize and the utilization of wood-burning cookstoves.
Or now no longer it is miles now no longer straightforward to measure the quantity of PM2.5 on the bottom on story of there might be now no longer in point of fact any form of comprehensive monitoring community maintaining the globe. North America and Europe have intensive monitoring programs, as does China. But, Martin mentioned, “There are gargantuan gaps in ground-essentially based monitoring. Americans is also living hundreds of kilometers away from monitors.”
To create a comprehensive air pollution plan, then, ground-essentially based monitors are simply insufficient.
To rob a global snapshot, Martin’s crew started with satellite photos of columns of atmosphere that spanned the bottom to the brink of space. Utilizing the established GEOS-Chem mannequin, which simulates atmospheric composition, they might well moreover infer how worthy PM2.5 need to level-headed be on the bottom, at the underside of any given column.
When evaluating the predictions to particular stages measured by ground monitors, the agreement was striking. In actuality, Martin mentioned, “Or now no longer it is the acceptable level of agreement learned to this level.”
But the researchers level-headed went a step extra.
The agreement was gargantuan, nonetheless now no longer good. So Hammer added the variations between the noticed and predicted amounts of PM2.5 and expanded the bottom-essentially based predictions across the globe, filling in the big gaps between monitors.
This extra step introduced the noticed and predicted stages of PM2.5 from 81% to 90% agreement.
Once they had been ready to take a correct seek for at the most modern air pollution stages across the field, the researchers saw some stark adjustments from old trends. In particular in China.
“We’re pale to seeing factual gargantuan, increasing trends in air pollution,” Hammer mentioned. But in China, “What we learned, from 2011 to 2018, is that there without a doubt is an especially gargantuan negative model.”
In diversified locations in Asia, the image wasn’t as certain.
While air pollution stages didn’t appear like increasing in India, the nation appears to be in a plateau part. “The gargantuan plateau of very excessive concentrations, to which a gargantuan population is exposed, is rather pertaining to,” Martin mentioned. “It affects the health of a thousand million folk.”
Alternatively, the takeaway from this analysis is also, on the balance, a hopeful one: It looks to level to at least one which that you can well assume of manner forward.
“The ideas Melanie’s diagnosis finds is a staunch success legend for air quality controls,” Martin mentioned. “It reveals they is also remarkably efficient at reducing PM2.5.” Though scientists have known these controls non-public the attainable to create an impression, he mentioned, “The adjustments in China are very dramatic, better than we have seen wherever in the field over the observational fable.
“It illustrates a staunch opportunity to enhance air quality via efficient controls.”
Air pollution, health across the field
In folk already in melancholy health with illness equivalent to bronchial asthma, PM2.5 can have instant health penalties. Long-term, nonetheless, breathing in these particles carries penalties for everybody.
“PM2.5 is a main public health remark globally,” mentioned Melanie Hammer, postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Randall Martin in the McKelvey College of Engineering. “Or now no longer it is miles obligatory to salvage correct exposure estimates to estimate health impacts.”
That’s why organizations, including World Health Organization and Global Burden of Disease, use files from Martin’s lab.
Extra files:
Melanie S. Hammer et al, Global Estimates and Long-Term Traits of Gorgeous Particulate Matter Concentrations (1998–2018), Environmental Science & Expertise (2020). DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.0c01764
Citation:
Global air pollution estimates level to surprises, opportunity (2020, June 25)
retrieved 26 June 2020
from https://phys.org/files/2020-06-global-air pollution-level to-opportunity.html
This file is field to copyright. Aside from any gorgeous dealing for the blueprint of non-public seek for or analysis, no
segment is at risk of be reproduced without the written permission. The relate is provided for files beneficial properties wonderful.