Language Predicts Alzheimer’s Onset
A synthetic intelligence (AI) model the spend of a brief language test used to be modestly factual in recognizing whether healthy of us would contain a future diagnosis of Alzheimer’s illness, researchers reported.
The model predicted whether cognitively traditional older adults would assemble Alzheimer’s symptoms outdated to age 85 with an location beneath the receiver working curve (AUC) of 0.74 and an accuracy of 70%, wrote Elif Eyigoz, PhD, of IBM Examine in Yorktown Heights, Contemporary York, and colleagues in Lancet EClinicalMedicine.
Currently, neuropsychological assessments and biomarkers like cerebrospinal fluid and imaging are mature to visual show unit Alzheimer’s development. Doable blood-based fully biomarkers are being studied to foretell Alzheimer’s illness in cognitively traditional older adults, however none are readily available for clinical spend.
Language competence is a smooth indicator of psychological dysfunction, Eyigoz said. “Aging-linked cognitive decline manifests itself in nearly all parts of language comprehension and manufacturing, because even apparently mundane linguistic talents — comparable to object naming — buy extensive brain networks,” she told MedPage As of late.
The IBM model mature brief written samples from individuals in the Framingham Heart Ogle (FHS) who had traditional cognitive assessments the spend of the Mini-Psychological Assert Examination and completed a neuropsychological test battery in successive visits.
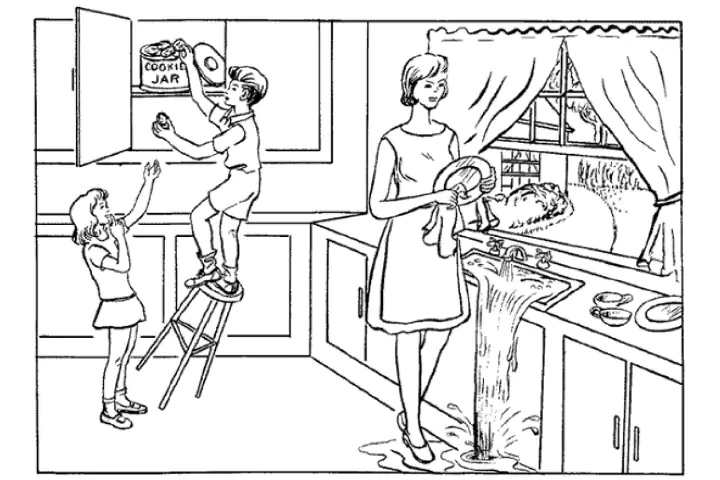
The model derived linguistic variables from written responses to the Cookie Theft Task, section of the Boston Aphasia Diagnostic Examination incorporated in the FHS test battery. Within the duty, individuals were requested to characterize a drawing of three of us: a boy on a toppling stool reaching into a cookie jar, a girl standing next to him, and a girl wiping dishes at an overflowing sink.
The survey incorporated 703 samples from 270 FHS individuals. A dataset consisting of a single sample from 80 individuals used to be held for attempting out; half of of these individuals developed Alzheimer’s symptoms on or outdated to age 85 (cases); the so a lot of half of did not (controls). Alzheimer’s diagnoses were in accordance with NINCDS–ADRDA criteria.
Cases and controls were matched on approximate age, sex, and training. The test knowledge location incorporated perfect one sample per participant, and perfect samples collected outdated to cognitive impairment onset were mature.
Amongst the test cases, point out time to diagnosis of sunshine Alzheimer’s from cognitive normalcy used to be 7.59 years. Alzheimer’s diagnoses were harder to foretell among of us with a school diploma (AUC 0.70) than these with out (AUC 0.76). They additionally were predicted more confidently among girls (AUC 0.83) than men (AUC 0.64).
Future Alzheimer’s onset used to be linked to telegraphic speech, repetitiveness, and misspellings. Telegraphic speech is fashionable in non-fluent aphasia, the researchers illustrious: it be simple in grammatical structure and marked by an absence of determiners (like “the” or “a”), auxiliary verbs (like “is” or “are”), and entire subjects.
Using generic phrases like “boy,” “girl,” or “girl” in preference to more explicit phrases like “son,” “brother,” “sister,” “daughter,” or “mother” to characterize the of us in the drawing used to be tied to a higher menace of Alzheimer’s illness. Pointing out small print just like the dishcloth or dishes used to be linked with decrease menace of Alzheimer’s.
Linguistic variables from a single administration of the Cookie Theft Task completed better than predictive models that incorporated APOE genotype, demographic variables, and so a lot of neuropsychological test outcomes, the researchers illustrious.
A limitation of the model is that it relied on the written version of the Cookie Theft Task, they added: the spoken version might well well present so a lot of parts of linguistic dysfunction.
“We designed our survey with primarily clinical trial enrichment in mind,” Eyigoz said. “Beyond that, we deem that our attain, mutatis mutandis, might well assist augment the knowledge and data that clinicians contain entry to of their note.”
The model might well well provide a low-burden attain to monitoring therapy and illness development if patients consent, Eyigoz added. “As an illustration, a functional application of the suggestions supplied in this survey might well well be utilization of its leads to a higher arrangement, which would additionally encompass so a lot of computerized assessments of cognitive decline — comparable to diagnosis of motor impairments, olfactory impairments, acoustic variations, and loads others. — as sophisticated decision-making in synthetic intelligence assuredly involves combining outcomes obtained from a pair of suggestions,” she said.
-
Judy George covers neurology and neuroscience news for MedPage As of late, writing about brain growing outdated, Alzheimer’s, dementia, MS, uncommon diseases, epilepsy, autism, headache, stroke, Parkinson’s, ALS, concussion, CTE, sleep, bother, and more. Be conscious
Disclosures
Pfizer supplied funding to assemble knowledge from the Framingham Heart Ogle Consortium, and to toughen the involvement of IBM Examine in the preliminary section of the survey.
Researchers were salaried staff of IBM or Pfizer for the length of this mission. IBM holds a patent for the extraction of one of the necessary aspects mature in the linguistic model.