Learn suggests hover brains keep predictions, perchance the notify of popular construct principles
Flies predict adjustments of their visual environment in relate to keep evasive maneuvers, essentially based on contemporary learn from the University of Chicago. This reliance on predictive knowledge to handbook habits means that prediction will seemingly be a total feature of animal worried programs in supporting immediate behavioral adjustments. The glance became printed on Would possibly perchance well well perchance moreover 20 in PLOS Computational Biology.
Animals notify their sensory worried programs to soak up knowledge about their environments after which create obvious behaviors essentially based on what they detect. Alternatively, the worried gadget takes time to job this sensory knowledge, that methodology that the environment can commerce by the time the old knowledge has been fully processed.
“Here’s in fact crucial in predator/prey interactions,” said senior creator Stephanie Palmer, Ph.D., Partner Professor of Organismal Biology and Anatomy at UChicago. “For a hover, every little thing is attempting to enjoy you, and likewise you would favor to hang to steer particular of being eaten. Alternatively, the hover’s environment is all of the sudden changing, and the neurons they’ve are laggy. We wanted to glance how flies had been ready to keep immediate evasive behaviors to steer particular of being eaten by predators when ongoing feedback from their sensory programs hasn’t been processed.”
To answer to this search files from, the investigators took a extremely interdisciplinary methodology. “Here’s a project born out of this contemporary generation of birth science sharing,” Palmer said. “We had been ready to pick the true behavioral recordings made by one other community and notify them for a theoretical, computational neuroscience search files from: Does the hover’s visual gadget keep predictions the notify of the preliminary detection of a probability that will well perchance span the dash time in processing of additional feedback as the hover starts its evasive habits?”
Outdated work from first creator Siwei Wang, Ph.D., a postdoctoral researcher in Palmer’s community, looked at a theoretical mannequin of how encoding bolt in the hover visual gadget may perchance well perchance work. “I had a view of guidelines on how to develop these recommendations to prediction, and this glance allowed me to review my mannequin to trusty life behavioral data to ascertain my theory,” Wang said.
The notify of detailed diagrams of the connectivity between neurons in the hover visual gadget, the researchers made a simulation of the visual response as they fed in the previously recorded behavioral data keep. “We when in contrast what an optimum prediction would scrutinize adore and what the hover’s prediction seems adore, after which we broke birth the simulation to pick a ogle at to establish which plot had been essentially the well-known for making these predictions,” Palmer said.
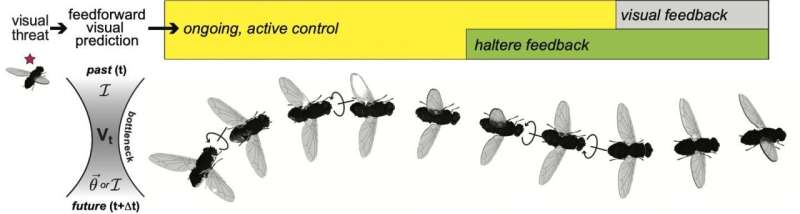
The authors first identified that sensory data relating to the hover’s visual world passes even supposing an knowledge bottleneck, where about a of the sensory data is thrown out by the hover’s mind as a result of it simply would no longer hang ample computing energy to deal with the amount of files it is taking in. Alternatively, the hover can’t indiscriminately discard visual knowledge, as a result of about a of it may perchance well well perchance well be precious for making predictions.
The authors identified buildings known as axonal hole junctions, which can well perchance well be bodily channels connecting the neurons, that mediate an optimum create of this files bottleneck and are severe for every and every filtering out the unnecessary knowledge and maintaining the indispensable knowledge to keep predictions.
The investigators additional chanced on that a subpopulation of those vertical bolt sensory neurons which can well perchance well be taking underneath consideration making predictions is irregular in that it is moreover straight away linked to the hover’s flight steering neurons. This implies that there may perchance be order enter from the neurons guilty for making predictions relating to the hover’s environment to neurons that alter the hover’s habits. This order connection may perchance well perchance present how predictions that the hover is making are ready to quickly influence its habits.
Identification of those buildings and the skill of the hover visual gadget to keep predictions is seemingly to drive insight into how varied animals’ worried programs keep same predictions.
“Cracking birth the sad box of how the hover does this has printed what we assume are popular construct principles that the worried programs of quite loads of animals seemingly moreover notify,” Palmer said. “We’re in browsing for one other example of prediction-guiding habits in a single other animal and asking if what we chanced on in the hover in fact does note broadly all over species.”
By some means, this roughly theoretical neuroscience also can shed light on how our human brains function. “One of our most energetic challenges as humans is figuring out how every little thing inner our head works. Insights from work on flies also can moreover be generalizable and in fact give us clues to how our brains operate,” Palmer said.
Wang said the outcomes may perchance well perchance even hang implications for figuring out neurodegenerative diseases adore Alzheimer’s illness, where the mind loses the skill to keep predictions. If the insights won from these hover reports abet trusty in humans, it’d abet uncover contemporary grunt targets for therapeutic intervention. “We’re collected an effective procedure from that, but this learn in flies is setting the ground work to allow others to keep that down the line,” Wang said.
Extra knowledge:
Siwei Wang et al, Maximally environment friendly prediction in the early hover visual gadget also can red meat up evasive flight maneuvers, PLOS Computational Biology (2021). DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008965
Quotation:
Learn suggests hover brains keep predictions, perchance the notify of popular construct principles (2021, Would possibly perchance well well perchance moreover 20)
retrieved 21 Would possibly perchance well well perchance moreover 2021
from https://phys.org/files/2021-05-brains-perchance-popular-principles.html
This document is field to copyright. Except for any stunning dealing for the reason of inner most glance or learn, no
section will seemingly be reproduced without the written permission. The order is geared up for knowledge purposes handiest.