
Mind blown: Modern brains evolved mighty extra lately than conception
Modern brains are younger than initially conception, presumably increasing as lately as 1.5 million years ago, in retaining with a see printed Thursday—after the earliest other folks had already begun walking on two toes and had even began fanning out from Africa.
Our first ancestors from the genus Homo emerged on the continent about 2.5 million years ago with inclined ape-take care of brains about half the dimensions of these considered in this present day’s other folks.
Scientists had been making an strive to resolve a thriller for so long as our beginning set legend has been identified: Precisely when and where did the brain evolve into one thing that made us human?
“Other folks had conception that these human-take care of brains evolved actually on the very beginning set of the genus Homo, so about 2.5 million years ago,” paleoanthropologist Christoph Zollikofer, a co-creator of the see printed in the journal Science, instructed AFP.
Zollikofer and lead see creator Marcia Ponce de Leon examined skull fossils from Africa, Georgia and the Indonesian island of Java, on the different hand, and learned the evolution actually took role mighty later, between 1.7 and 1.5 million years ago.
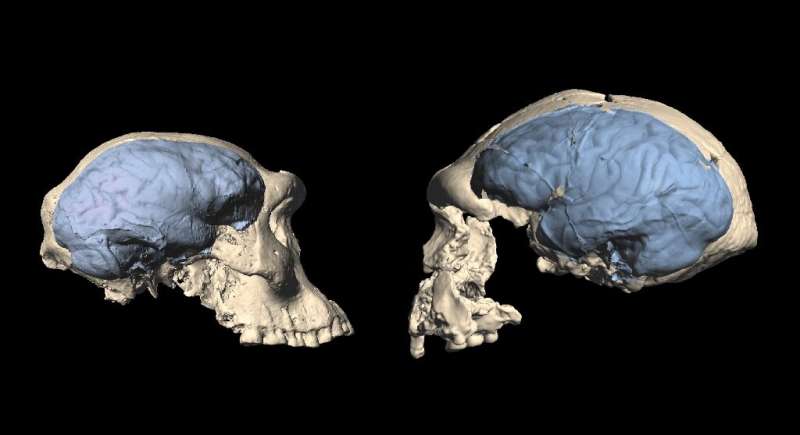
Since brains themselves cease no longer fossilize, the handiest manner to leer their evolution is to see the marks they traipse away interior the skull.
The scientists created digital photos—identified as an endocasts—of what had stuffed the skulls long ago.
In other folks, the Broca role—section of the frontal lobe linked to speech manufacturing—is map greater than the corresponding zone in various nice apes, talked about Zollikofer, of the College of Zurich.
The expansion of an role ends up in the shifting of the entirety in the support of it. “This backward shift shall be considered on the fossil endocasts, when we observe imprints of the brain fissures,” Zollikofer talked about.
‘Shock’
By discovering out skulls from Africa, the researchers had been ready to hunt down out that the oldest ones—relationship support greater than 1.7 million years—actually had a frontal lobe characteristic of nice apes.
“This valuable result became as soon as a gigantic shock,” talked about Zollikofer.

It signified that the genus Homo “began with bipedalism,” or walking on two legs, and that the evolution of the brain had nothing to cease with the truth of already being bipedal.
“Now every person knows that in our long evolutionary ancient previous… the first representatives of our genus Homo had been precise terrestrial bipeds, with ape-take care of brains,” the paleoanthropologist talked about.
On the different hand, the youngest African fossils, relationship support 1.5 million years, confirmed traits of contemporary human brains.
This signified that the evolution of the brain took role between the 2 dates, in Africa, in retaining with the see.
The conclusion is backed up by the truth that extra advanced instruments looked staunch through this identical interval, known as Acheulean instruments, which own two symmetrical faces.
“That is no longer random coincidence,” talked about Zollikofer, “because every person knows these brain areas that acquire expanded in this interval of time are of us that are inclined for advanced manipulative tasks take care of instrument-making.”
Two migrations from Africa
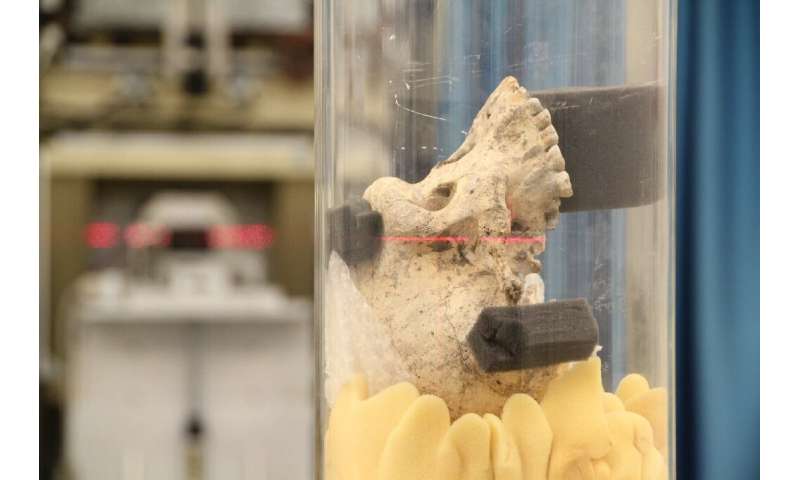
The 2nd gorgeous result of the see comes from observations of 5 skull fossils found in show cloak-day Georgia, relationship support between 1.8 and 1.7 million years.
The specifically effectively-preserved specimens proved to be inclined brains.
“Other folks conception you’d like a gigantic contemporary brain to disperse out of Africa,” talked about Zollikofer. “We can show cloak these brains are no longer gigantic, they in most cases’re no longer contemporary, and serene of us had been ready to traipse away Africa.”
Meanwhile, fossils from Java, the youngest specimens in the see, confirmed contemporary brain traits. The researchers for that reason of this fact factor in that there became as soon as a 2nd migration out of Africa.
“So, it is likely you’ll presumably presumably own a twig first of inclined-brained of us, then issues evolve to a contemporary brain in Africa, and these of us sprayed again,” defined Zollikofer.
“It be no longer a recent hypothesis… but there became as soon as no positive evidence. And now for the first time, we’ve true fossil evidence.”
More files:
M.S. Ponce de León el al., “The inclined brain of early Homo,” Science (2021). science.sciencemag.org/cgi/doi … 1126/science.aaz0032
A. Beaudet el al., “The enigmatic origins of the human brain,” Science (2021). science.sciencemag.org/cgi/doi … 1126/science.abi4661
© 2021 AFP
Citation:
Mind blown: Modern brains evolved mighty extra lately than conception (2021, April 9)
retrieved 9 April 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-04-mind-blown-contemporary-brains-evolved.html
This doc is topic to copyright. As antagonistic to any pleasing dealing for the motive of personal see or overview, no
section will be reproduced with out the written permission. The explain is equipped for files functions handiest.