
Molecular swap permits photomechanical leaping of polymers
Leaping movement is gradually observed in nature, in conjunction with for mammals, bugs and the assorted land creatures; this fluid motion objectives for like a flash mobility, a faster arrival time at a shuttle space over colossal barriers and tough terrain. The qualitative properties of the jump such as route and top are regulated by mere fractions of doable and kinetic energy. As correctly as, an organism can decide to repeat its leaping motions as determined by its have free will.
To implement a identical develop of leaping habits into robotic systems, there could perchance also just tranquil be tailored designs that generate an instantaneous energy transfer to a substrate with ample gathered energy. Most of the most up-to-date leaping robots within the discipline adapt by kicking or pushing the substrates with their legs; here is gradually powered by motorized actuators or battery-powered systems. On the other hand, these systems add undesirable weight to the leaping robots and are also laborious to repair onto a miniaturized physique.
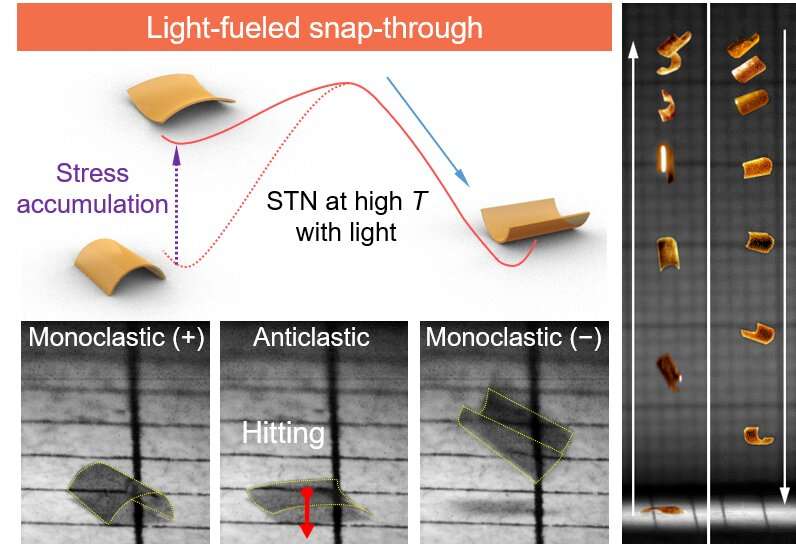
A photoactive liquid crystalline polymer is succesful of leaping motion for the rationale that anisotropic photomechanical response of the photoactive molecular machine permits the liquid crystalline polymer to build up and free up picture-brought about energy effectively. The photoactive molecular machine, an azobenzene moiety, is aligned with liquid crystal molecules that present directional picture-brought about contraction from photoisomerization of the azobenzene. 270° dapper zigzag nematic molecular geometry at top and bottom of the photoactive liquid crystalline polymer induces a non-isometric bi-trusty suppose below actinic light irradiation with simultaneous heating. The bi-trusty structure is identified to build up energy under the energy barrier in portray to deform between two trusty constructions. All over the technique of deformation, the gathered energy begins to exceed the energy barrier and continues to an instantaneous free up, the so known as ‘snap-by.’ Instantaneous energy free up in photoactive liquid crystalline polymer generates the leaping motion by impact with the substrate. Remarkably, the utmost leaping top reaches 15.5 physique lengths with the utmost instantaneous toddle of 880 BL s-1.
A ambitious bellow for a leaping robot is on-ask of persevering with leaping. Unlike motorized leaping robots, it’s miles sophisticated to implement continuous or directional leaping for a leaping robot with a monolithic physique for the rationale that perspective between the robot and actuation supply modifications repeatedly. The bidirectional light irradiation permits the photoactive liquid crystalline polymer to leap repeatedly in two assorted suggestions: hitting and kicking basically basically based photomechanical leaping. Regardless of the touchdown route or curvature of the soft robot, on-ask of sunshine irradiation from top or bottom present for leaping motions in soft robots.
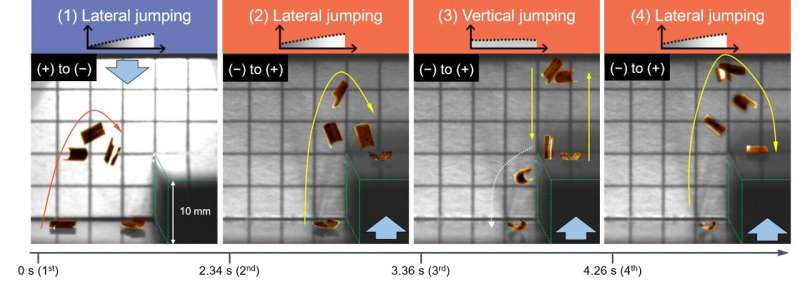
Additionally, the photomechanical leaping could even be guided by producing a beam depth gradient. The gradient light depth breaks symmetry of photoisomerization in a monolithic photoactive liquid crystalline polymer which generates directionality of kinetic energy. By combining bi-directional light irradiation with a beam depth gradient, the miniaturized photoactive liquid crystalline polymer can attain at its shuttle space, even overcoming colossal barriers.
This unprecedent approach will present insights into contactless leaping maneuverability in miniaturized soft robots.
More info:
Jisoo Jeon et al, Continuous and programmable photomechanical leaping of polymer monoliths, Materials On the present time (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2021.04.014
Citation:
Molecular swap permits photomechanical leaping of polymers (2021, May perhaps perhaps also 21)
retrieved 22 May perhaps perhaps also 2021
from https://phys.org/info/2021-05-molecular-permits-photomechanical-polymers.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any aloof dealing for the rationale of non-public scrutinize or review, no
segment can be reproduced with out the written permission. The order material is equipped for info applications simplest.