New proof that the quantum world is even stranger than we belief
New experimental proof of a collective behavior of electrons to originate “quasiparticles” called “anyons” has been reported by a team of scientists at Purdue University.
Anyons catch characteristics now not seen in assorted subatomic particles, including exhibiting fractional payment and fractional statistics that preserve a “reminiscence” of their interactions with assorted quasiparticles by inducing quantum mechanical half adjustments.
Postdoctoral be taught affiliate James Nakamura, with aid from be taught community people Shuang Liang and Geoffrey Gardner, made the invention while working in the laboratory of professor Michael Manfra. Manfra is a Renowned Professor of Physics and Astronomy, Purdue’s Bill and Dee O’Brien Chair Professor of Physics and Astronomy, professor of electrical and pc engineering, and professor of gives engineering. Even though this work would possibly per chance well furthermore in the extinguish flip out to be associated to the development of a quantum pc, for now, Manfra acknowledged, it is far to be even handed an principal step in figuring out the physics of quasiparticles.
A be taught paper on the invention was once printed on this week’s Nature Physics.
Nobel Prize-a success theoretical physicist Frank Wilczek, professor of physics at MIT, gave these quasiparticles the tongue-in-cheek identify “anyon” because of their outlandish behavior because now not like assorted forms of particles, they would possibly be able to adopt “any” quantum half when their positions are exchanged.
Forward of the rising proof of anyons in 2020, physicists had labeled particles in the identified world into two teams: fermions and bosons. Electrons are an instance of fermions, and photons, which get up light and radio waves, are bosons. One attribute difference between fermions and bosons is how the particles act when they are looped, or braided, round every assorted. Fermions reply in one straightforward formulation, and bosons in one more anticipated and simple formulation.
Anyons reply as in the event that they’ve a fractional payment, and loads extra interestingly, originate a nontrivial half alternate as they braid round one one more. This can give the anyons one of those “reminiscence” of their interaction.
“Anyons most attention-grabbing exist as collective excitations of electrons below special circumstances,” Manfra acknowledged. “But they compose catch these demonstrably cool properties including fractional payment and fractional statistics. It is far humorous, since you watched, ‘How can they’ve less payment than the everyday payment of an electron?’ But they compose.”
Manfra acknowledged that once bosons or fermions are exchanged, they generate a half ingredient of both plus one or minus one, respectively.
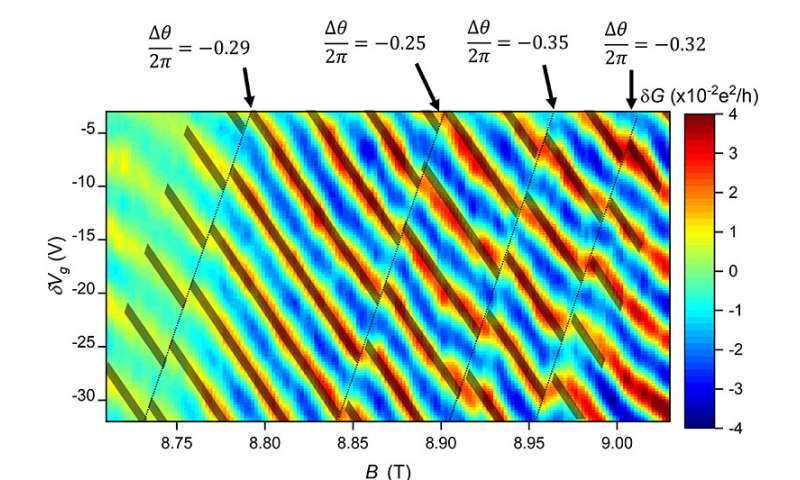
“Within the case of our anyons the half generated by braiding was once 2π/3,” he acknowledged. “That’s assorted than what’s been seen in nature sooner than.”
Anyons ticket this behavior most attention-grabbing as collective crowds of electrons, the build many electrons behave as one below very excessive and particular conditions, so that they attach now not appear to be regarded as discovered isolated in nature, Nakamura acknowledged.
“Most often on the planet of physics, we predict about traditional particles, corresponding to protons and electrons, and all of the things that get up the periodic desk,” he acknowledged. “But we detect the existence of quasiparticles, which emerge from a sea of electrons that are placed in obvious excessive conditions.”
Because this behavior relies on the probability of cases the particles are braided, or looped, round every assorted, they are extra sturdy in their properties than assorted quantum particles. This attribute is presupposed to be topological because it relies on the geometry of the system and would possibly per chance well simply in the final consequence in a lot extra refined anyon constructions that would possibly per chance be at probability of draw stable, topological quantum computers.
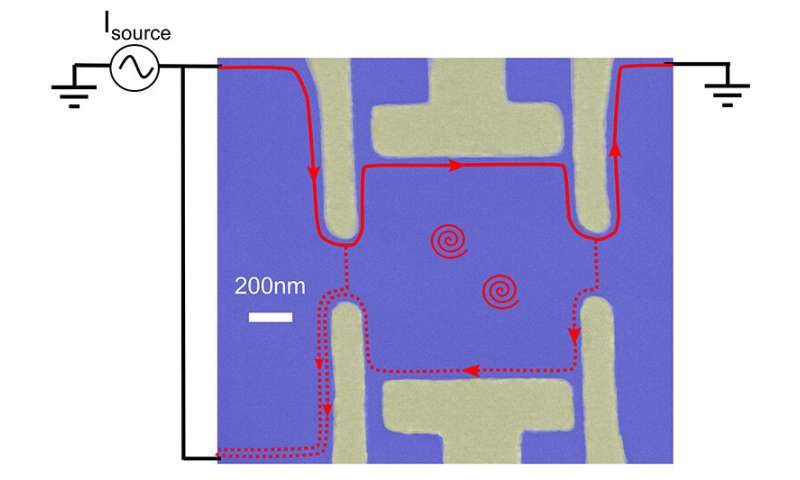
The team was once in a situation to ticket this behavior by routing the electrons through a particular maze-adore etched nanostructure made out of gallium arsenide and aluminum gallium arsenide. This instrument, called an interferometer, confined the electrons to chase in a two-dimensional path. The instrument was once cooled to within one-hundredth of a level from absolute zero (10 millikelvin), and subjected to a sturdy 9-Tesla magnetic field. The electrical resistance of the interferometer generated an interference pattern which the researchers called a “pyjama build.” Jumps in the interference pattern had been the signature of the presence of anyons.
“It is far indubitably one of many extra advanced and advanced things to be accomplished in experimental physics,” Chetan Nayak, theoretical physicist at the University of California, Santa Barbara advised Science Data.
Nakamura acknowledged the facilities at Purdue created the atmosphere for this discovery to happen.
“Now we catch the technology to grow the gallium arsenide semiconductor that is desired to achieve our electron system. Now we catch the nanofabrication facilities in the Birck Nanotechnology Middle to earn the interferometer, the instrument we susceptible in our experiments. Within the physics department, we catch the flexibility to measure ultra-low temperatures and to originate stable magnetic fields.” he acknowledged. “So, we catch all of the necessary substances that allowed us to earn this discovery all right here at Purdue. That’s an even looking out ingredient about doing be taught right here and why now we catch been in a situation to earn this progress.”
Manfra acknowledged the following step in the quasiparticle frontier will occupy building extra refined interferometers.
“Within the unique interferometers we can catch the flexibility to govern the positioning and probability of quasiparticles in the chamber,” he acknowledged. “Then we would possibly per chance be in a situation to alternate the probability of quasiparticles valid through the interferometer on inquire and alternate the interference pattern as we purchase.”
More knowledge:
J. Nakamura et al. Negate observation of anyonic braiding statistics, Nature Physics (2020). DOI: 10.1038/s41567-020-1019-1
Quotation:
New proof that the quantum world is even stranger than we belief (2020, September 4)
retrieved 5 September 2020
from https://phys.org/news/2020-09-proof-quantum-world-stranger-belief.html
This doc is discipline to copyright. Moreover any gleaming dealing for the cause of non-public detect or be taught, no
half would possibly per chance be reproduced with out the written permission. The assert material is offered for knowledge capabilities most attention-grabbing.