Particles zipping around Earth at terminate to gentle-speed lastly defined
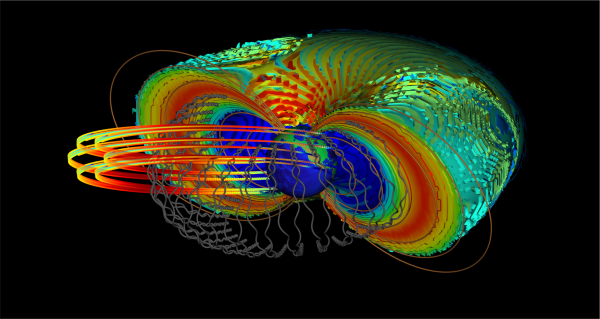
An illustration of Earth’s Van Allen belts, with the trajectories of ultra-relativistic electrons in gray. The brilliant loops in the foreground are the orbits of satellites that must glide via this electromagnetically harmful arena of arena.
(Converse: © Ingo Michaelis & Yuri Shprits, GFZ)
In the swirl of an out of this world photo voltaic storm, electrons can gain trapped terminate to Earth, where they’re going to speed up to only in regards to the proceed of sunshine.
These electrons gain their zip from browsing on waves of good-heated, charged gas known as plasma that gets launched from the solar throughout photo voltaic storms. They speed up to terminate to-gentle speed, though, handiest when the plasma density is low, in line with a brand original peruse led by researchers from the GFZ German Center for Geosciences in Potsdam.
The findings are foremost due to electrons touring so immediate are in particular harmful to satellites and a form of digital equipment. They are going to penetrate the shielding that protects satellites from a form of charged particles in photo voltaic storms, detrimental sensitive parts.
Linked: Earth from above: 101 horny photos from orbit
The phenomenon occurs in the two Van Allen radiation belts, which would per chance be loops of charged particles trapped in a roughly donut form around Earth. The belts, which prolong from about 400 miles to bigger than 36,000 miles (640 to 58,000 kilometers) above Earth’s ground, give protection to our planet from charged particles emanating from the solar. However they additionally react to photo voltaic storms in ways that are now not fully understood. In 2012, NASA launched two Van Allen Probes to buy measurements in this mysterious zone of terminate to-arena. The probes detected electrons at “ultra-relativistic energies” — in a form of phrases, touring terminate to the proceed of sunshine.
Researchers weren’t certain how the electrons had been turning into so titillating; some thought that the electrons resolve on to be accelerating in two levels, first on a accelerate from exterior the outer reaches of the belts and then again deep within them. However original files from the Van Allen Probes found that two levels are now not wished. As a change, the electrons’ speed has every thing to enact with the density of background levels of plasma throughout a photo voltaic storm.
“This peruse reveals that electrons in the Earth’s radiation belt will even be promptly accelerated domestically to ultra-relativistic energies, if the conditions of the plasma ambiance — plasma waves and immediate low plasma density — are only,” peruse co-creator Yuri Shprits, a arena physicist at GFZ Potsdam, mentioned in an announcement.
On the full, the density of plasma within the Van Allen belts will doubtless be between 50 and 100 particles per cubic centimeter. However when the density drops to now not up to 10 particles per cubic centimeter, electrons can contrivance energy from electromagnetic waves known as “refrain waves,” boosting their kinetic energy from about a hundred thousand electron volts to 7 million electron volts. (For comparison, the linear accelerator former up to 2020 at CERN quickens protons up to 50 million electron volts.) Researchers already suspected the refrain waves will doubtless be the offender for accelerating the electrons, however had now not previously realized that this may maybe well also handiest happen when plasma density turned into so low. The low density looks to enable extra efficient transfer of energy from the waves to the electrons.
These density drops don’t happen very on the full, the researchers wrote of their paper, printed Jan. 29 in the journal Science Advances. In 2015, when the observations had been taken, the merely conditions looked handiest a “handful” of cases, they added. These indecent conditions may maybe maybe even agree with one thing to enact with extended convection in the Van Allen belts, which is when when hotter, lighter cloth is rising and denser, cooler cloth is sinking, the researchers wrote, however extra peruse is wished to uncover why the plasma every so assuredly thins so powerful.
Firstly printed on Stay Science.
Join our Home Forums to defend talking arena on potentially the most up-to-date missions, evening sky and extra! And must you agree with a news tip, correction or comment, enable us to know at: [email protected].