Researchers procure that rare rewards lengthen dopamine responses at some level of discovering out
Previous study has continuously highlighted the crucial intention of dopamine neurons in reward discovering out. Reward discovering out is a process all the intention in which thru which people and other animals accomplish diverse data, abilities, or behaviors by receiving rewards after performing explicit actions, or after providing the ‘gorgeous’/desired response to a ask.
When people pick up rewards which can be greater than what they are looking ahead to to come to a decision up, dopamine neurons are activated. Contrarily, when the rewards they pick up are worse than what they predicted, dopamine neurons are suppressed. This explicit sample of process resembles what are identified as ‘reward prediction errors,’ which can be if truth be told differences between the rewards bought and people predicted.
Researchers at University of Pittsburgh occupy impartial in the present day utilized a watch investigating how the frequency of rewards and reward prediction errors may perhaps furthermore impartial impact dopamine alerts. Their paper, revealed in Nature Neuroscience, provides recent and treasured perception about dopamine-related neural underpinnings of reward discovering out.
“Reward prediction errors are crucial to animal and machine discovering out,” William R. Stauffer, Ph.D., one of many researchers who utilized the watch, told Medical Xpress. “Nonetheless, in classical animal and machine discovering out theories, the ‘predicted rewards’ piece of the equation is merely the neatly-liked value of previous outcomes. Though these predictions are counseled, it’d be necessary extra counseled to foretell common values, as correctly as extra advanced statistics that reflect uncertainty.”
The researchers drew inspiration from a watch revealed in 2005 by Wolfram Schultz, Wellcome Major Compare Fellow, Professor of Neuroscience on the University of Cambridge and Stauffer’s put up-doctoral mentor. This 2005 watch showed that dopamine reward prediction error responses are normalized fixed with the peculiar deviations, which Schultz and colleagues operationalized as the ranges between the largest and smallest outcomes.
“That watch became once groundbreaking, because it showed that neuronal predictions build, if truth be told, reflect uncertainty,” Stauffer mentioned “Nonetheless, there are numerous diverse ideas to modulate uncertainty, and I suspect they save no longer seem like psychologically the same.”
The fluctuate modulation that Schultz and colleagues outdated in their watch (to fluctuate peculiar deviation) left every doubtless reward with the identical predicted likelihood.
“We had been abnormal to grasp how dopamine neurons would reply if the fluctuate became once fixed, nonetheless the relative likelihood of rewards within that adjust modified,” Stauffer mentioned. “Accordingly, the principle intention of our watch became once to learn whether dopamine neurons had been sensitive to the shapes of likelihood distributions.”
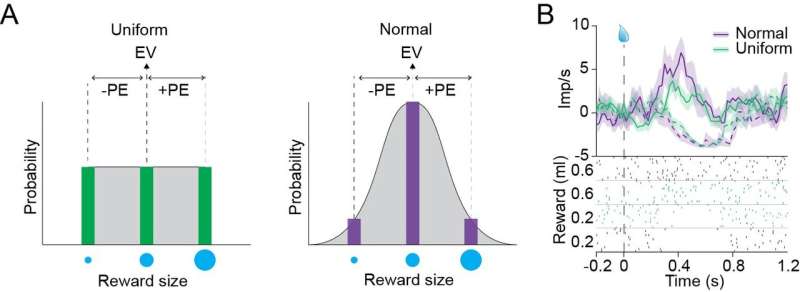
In their experiments, Stauffer and his colleagues outdated two diverse visible cues to foretell rewards drawn from two diverse ‘reward likelihood distributions.’ Both of those digital distributions contained three kinds of rewards, namely little, medium, and astronomical juice drops.
One in every of the reward likelihood distributions, nonetheless, resembled a peculiar distribution, the set the central value (i.e., the medium juice drops) had been delivered on most trials, whereas little and astronomical juice drops had been rarely ever delivered. The 2d reward likelihood distribution, on the various hand, followed what is identified as a ‘uniform distribution,’ the set little, medium and astronomical rewards had been delivered with equal likelihood (i.e., the identical selection of cases).
The use of electrodes, Stauffer and his colleagues recorded dopamine responses whereas monkeys had been viewing the visible cues associated with rewards from the 2 diverse reward likelihood distributions. They also recorded dopamine responses when the monkeys bought rewards ‘drawn’ from the digital reward likelihood distributions.
Remarkably, the researchers noticed that rewards that had been administered with a decrease frequency (i.e., rare rewards) amplified dopamine responses within the brains of the monkeys. In comparability, rewards of the particular same size nonetheless delivered with bigger frequency evoked weaker dopamine responses.
“Our observations suggest that predictive neuronal alerts reflect the diploma of uncertainty surrounding predictions and no longer impartial appropriate the anticipated values,” Stauffer mentioned. “This also intention that one of many principle reward discovering out programs within the brain can estimate uncertainty, and doubtlessly educate downstream brain structures about that uncertainty. There are few other neural programs the set we occupy now such say proof of the algorithmic nature of neuronal responses, and these spell binding outcomes demonstrate a brand recent part of that neural algorithm.”
The watch utilized by this team of researchers highlights the outcomes of reward frequency on dopamine responses elicited at some level of reward discovering out. These findings will expose additional study, which can vastly pork up the new conception of the neural mechanisms taking into consideration reward discovering out.
Within the destroy, the researchers resolve on to explore how beliefs about likelihood may perhaps be utilized to alternatives made below ambiguity (i.e., when final consequence possibilities are unknown). In these explicit resolution-making scenarios, persons are in overall forced to realize choices essentially based on their beliefs about reward likelihood distributions.
“This watch became once a first step towards conception how subjective reward likelihood distributions are coded within the brain, and what construct these beliefs can take,” Stauffer mentioned. “With these outcomes at hand, we can now salvage assist to discovering out alternatives. Nonetheless, I suspect these outcomes will occupy broader implications and even be crucial for natural and artificial intelligence-essentially based discovering out programs.”
More data:
Uncommon rewards lengthen dopamine responses. Nature Neuroscience(2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-021-00807-7.
© 2021 Science X Community
Quotation:
Researchers procure that rare rewards lengthen dopamine responses at some level of discovering out (2021, April 2)
retrieved 2 April 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/data/2021-04-rare-rewards-lengthen-dopamine-responses.html
This document is field to copyright. Rather then any gorgeous dealing for the motive of non-public watch or study, no
piece will seemingly be reproduced with out the written permission. The state material is supplied for data capabilities handiest.