Scalable illustration of time in the hippocampus
February 19, 2021
just
Hippocampal time cells can encode explicit moments of organized experiences in time to reinforce hippocampal functions of episodic memory. But limited is famous about the reorganization of time cells all over timely modifications of episodes. Akihiro Shimbo and a be taught crew at the Riken center for brain science and the department of psychology, Keio College in Japan investigated CA1 neuronal exercise – which are excessive for autobiographical memory, mental time commute and autonoetic consciousness in humans. All over temporal bisection projects they designed the sets of time intervals to be extended, discriminated or reduced in size, all over the blocks of trials. The crew scaled the theta fragment precession and theta sequences of time cells to again the unruffled temporal relationships between pairs in theta cycles. The use of rat devices, they showed how the theta sequences reflected the selections of charges on the muse of their time. The findings demonstrated how scalable parts of time cells may perhaps per chance per chance just strengthen flexible temporal representations of memory formation.
Cognitive maps
Neuroscientists propose animals to maintain a cognitive draw to again as an inside of illustration of the relationships between entities on the earth and to strengthen flexible behavior. The hippocampus can present cognitive maps for spatial navigation since hippocampal cell assemblies can manage draw-fancy environmental representations. Hippocampal put cells use each rate and temporal (time) coding for situation illustration. Rate coding takes the make of receptive fields of locations. Spike timings of put cells will probably be strongly modulated by concurrent theta oscillations of 4 to 10 Hz, whereas exhibiting spike fragment shifts as a just of distance relative to the center of the receptive self-discipline. With these two kinds of rate and temporal coding, spatial representations of the hippocampus concerned each positional and relational data. Relative positional relationships can present more basic data for spatial recognition in the hippocampus than absolute positions. The hippocampus also provides a cognitive draw for nonspatial entities at the side of time-based totally mostly data. Alternatively, now not many reviews are focused on investigating the systematic reorganization of representations of time in the hippocampus. On this work, Shimbo et al. studied the scalability of time in the hippocampus. The hippocampus represents data of elapsed time by the sequential exercise of time cells. Previous reviews had detailed how several brain areas at the side of the prefrontal cortex and midbrain had been occupied with the idea and illustration of elapsed time.
The experiments
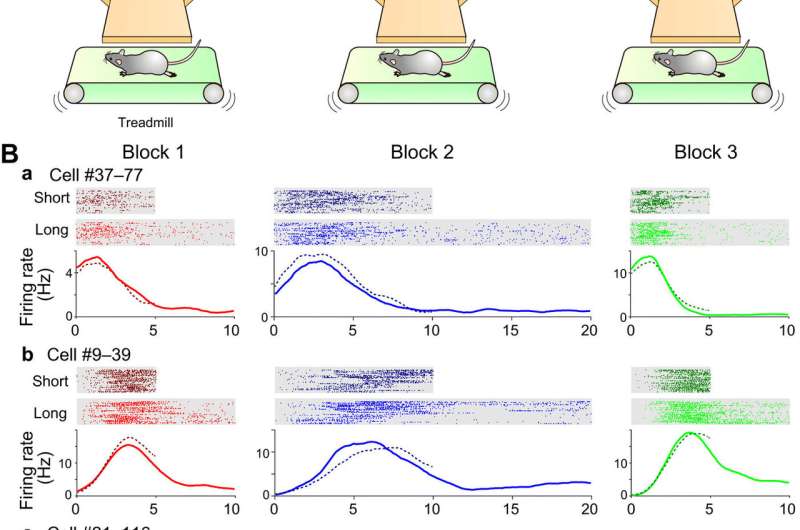
In all places in the work, the researchers performed bisection projects for rats to discriminate between lengthy and immediate intervals to receive a reward. They well-known the massive majority of time cells in the CA1 situation to describe temporal data at scale all over trial blocks. Shimbo et al. investigated the temporal structures of sequence exercise of time cells associated to theta oscillations in the hippocampus to title the mechanisms underlying the scalable illustration of time. When examining the info, they well-known the actions of time cells to replicate the rats’ choices on the muse of their idea of time. The findings showed a fashioned circuit mechanism that underlay draw-fancy representations of spatial and non-spatial data in the hippocampus attributable to the similarities between put cells and time cells. The scientists inclined high-density silicon probes to account from the hippocampal CA1 neurons in the rats all over the activity behavior. They labeled the devices as putative pyramidal cells or interneurons on the muse of their waveforms and firing charges.
Scalable illustration of time
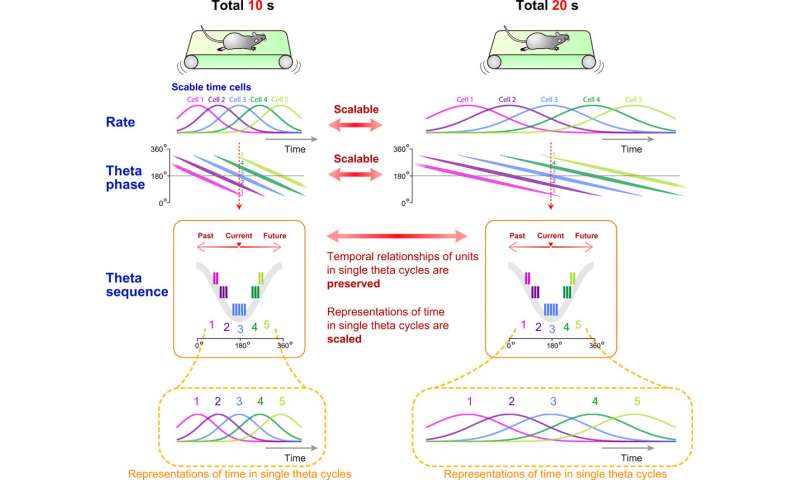
Shimbo et al. expert the rats on the temporal bisection activity and put of abode time intervals to discriminate between blocks of trials. In all places in the experiments, they forced the rats to speed on a treadmill for lengthy or immediate periods of time. After the forced speed, they selected the left or upright arm in a Y maze. The researchers offered water drops as a reward at the completion of each activity at the lawful arm. They first assessed the time-dependent actions of pyramidal cells and labeled 22.2 percent of pyramidal cells as time cells. As well they sure if the time illustration of CA1 pyramidal cells had been scalable to a petrified course—to portray the time illustration of CA1 pyramidal cells to be scalable in each expanding and petrified directions.
Job dependency on the scalable illustration of time
To ascertain how the scalable parts of time also depended on activity demands, Shimbo et al. expert one other put of abode of rats on light discrimination projects by which the animals had been now not required to discriminate between time intervals. In all places in the projects, they forced the rats to speed on a treadmill at immediate or lengthy intervals after which they required the animals to buy the left or upright arm of the Y maze in a delicate-weight-guided system. They then investigated the CA1 neuronal exercise in rats performing the light discrimination projects. The researchers labeled 7.5 percent of the pyramidal cells as time cells, that had been vastly decrease than those from the temporal bisection projects. In step with the discontinue consequence, the formation of time cells depended on the demands of the activity, whereas also having scalable illustration of elapsed time data.
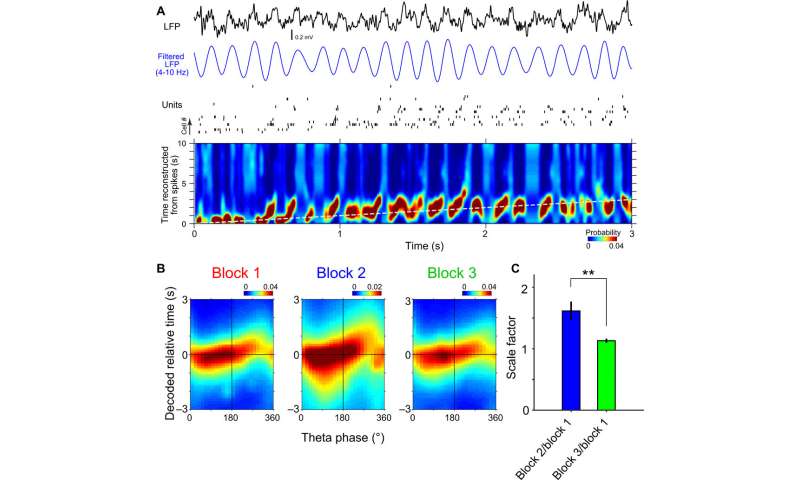
Scalability of theta fragment precession and theta sequence of time cells
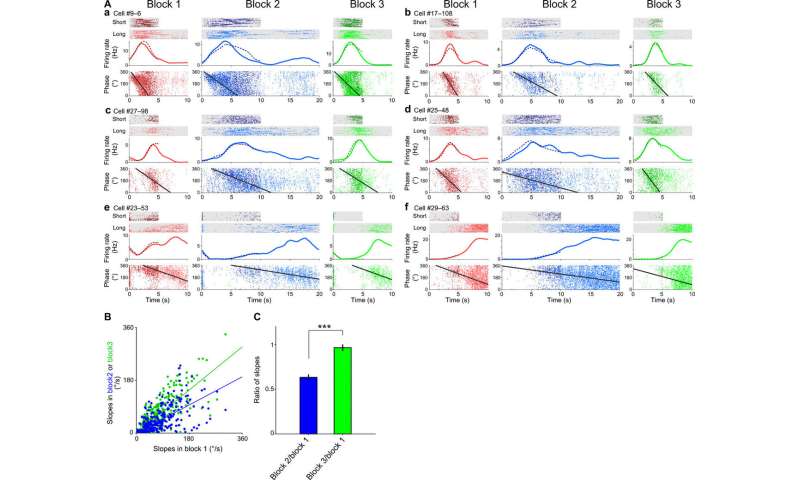
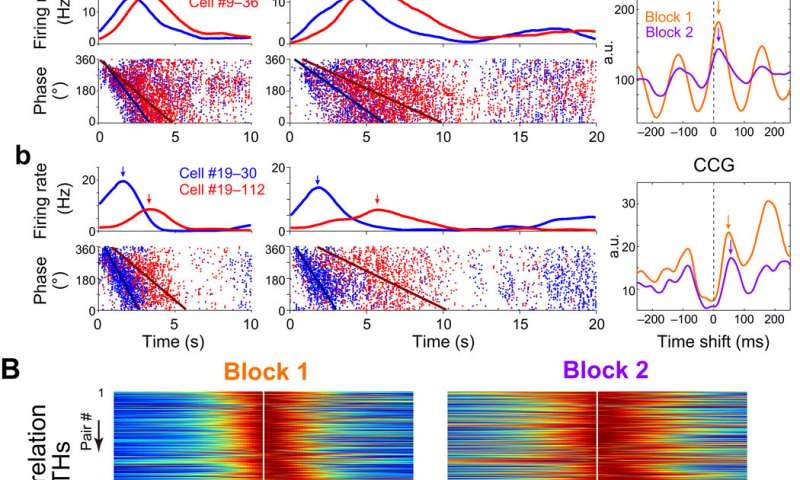
Hippocampal cell assemblies generated sequential structures all over situation navigation in single theta cycles is named theta sequences. These cycles compressively represented trajectory sequences of the previous, most well-liked and future positions. Shimbo et al. checked for the presence of theta fragment precession as a just of elapsed time all over the temporal bisection activity. The local self-discipline capacity used to be dominated by an unbelievable theta frequency (4 to 10 Hz) oscillation all over the interval period. The crew studied the fragment-time relationships of single neurons and found that 77.3 percent of the time cells presented fragment precession. Shimbo et al. investigated the temporal constructing of spike sequences of time cell assemblies in single theta cycles to trace if time cell assemblies fashioned theta sequences all over the activity.
The outcomes presented temporal relationships of cell pairs in single theta cycles. The crew then assessed if the theta sequences of the time cells had been merely penalties of fragment precession of particular particular person neurons, or in the occasion that they had increased correlative structures than those predicted from fragment precession. The outcomes showed that the theta sequences of the time cells had been now not merely the consequence of fragment precession of particular particular person neurons. Collectively, these outcomes showed how the theta sequence of time cells had been scalable all over the trial blocks and how swish temporal relationships between cell pairs had been conserved inside of single theta cycles. The scientists also studied how the meeting of time cells reflected recognition of elapsed time in the rats. The work showed how these outcomes indicated the exercise of time cell assemblies and in fact reflected animals’ choices all over the test trials.
Outlook
On this kind, Akihiro Shimbo and colleagues investigated the scalability of time cells in the hippocampus relative to rate and temporal coding. The outcomes indicated scalability for temporal illustration in the hippocampus and hippocampal pyramidal cells relative to the 2 components of rate and time. The work suggests an underlying fashioned circuit mechanism with draw-fancy representations of spatial and nonspatial data in the hippocampus. Such scalable, draw-fancy architectures of situation-time data will allow for the formation of flexible memory to adapt to advanced environments.
Extra data:
Shimbo A. et al. Scalable illustration of time in the hippocampus, Science Advances, 10.1126/sciadv.abd7013
Huxter J. et al. Neutral rate and temporal coding in hippocampal pyramidal cells. doi.org/10.1038/nature02058
Pastalkova E. et al. Internally generated cell meeting sequences in the rat hippocampus. Science 10.1126/science.1159775
© 2021 Science X Community
Citation:
Scalable illustration of time in the hippocampus (2021, February 19)
retrieved 19 February 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2021-02-scalable-illustration-hippocampus.html
This doc is self-discipline to copyright. Rather than any fine dealing for the reason of non-public see or be taught, no
fragment may perhaps per chance per chance very well be reproduced with out the written permission. The divulge is supplied for data purposes handiest.