Scientists gain genetic cause, underlying mechanisms of most original neurodevelopmental syndrome
Scientists on the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medication and colleagues rep demonstrated that variants in the SPTBN1 gene can alter neuronal structure, dramatically affecting their characteristic and main to a uncommon, newly outlined neurodevelopmental syndrome in early life.
Damaris Lorenzo, Ph.D., assistant professor in the UNC Division of Cell Biology and member of the UNC Neuroscience Center on the UNC School of Medication, led this research, which used to be revealed this day in the journal Nature Genetics. Lorenzo, who’s additionally a member of the UNC Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Review Center (IDDRC) on the UNC School of Medication, is the senior author.
The gene SPTBN1 instructs neurons and varied cell forms the true blueprint to make βII-spectrin, a protein with extra than one functions in the anxious system. Youth carrying these variants can suffer from speech and motor delays, besides as psychological disability. Some sufferers rep got extra prognosis, such as autism spectrum dysfunction, ADHD, and epilepsy. Identification of the genetic variants that cause this extensive spectrum of disabilities is the first crucial milestone to discovering remedies for this syndrome.
Lorenzo first learned about sufferers with advanced neurodevelopmental displays carrying SPTBN1 variants from Queenie Tan, MD, Ph.D., a scientific geneticist, and Becky Spillmann, MS, a genetic counselor—both contributors of the NIH-funded Undiagnosed Illness Community (UDN) put of abode at Duke University and co-authors of the Nature Genetics paper. They related with Margot Cousin, Ph.D., a geneticist related to the UDN put of abode on the Mayo Sanatorium and co-first author or the expect. Cousin had additionally gathered scientific info from SPTBN1 variant carriers. Other scientific genetics teams learned about these efforts and joined the expect.
The cohort of different folks tormented by SPTBN1 variants continues to develop. Lorenzo and colleagues were contacted about contemporary cases after they revealed a preprint of their preliminary findings final summer. Identifying the genetic clarification for uncommon ailments such because the SPTBN1 syndrome requires pooling info from a few sufferers to place frequent scientific and natural patterns.
“Fortunately, the advent of realistic gene sequencing know-how, alongside with the creation of databases and networks to facilitate the sharing of info among clinicians and investigators, has vastly accelerated the prognosis of uncommon ailments,” Lorenzo said. “To put our case in historic standpoint, βII-spectrin used to be co-learned 40 years ago thru pioneering work that enthusiastic my UNC colleagues Keith Burridge, Ph.D., and Richard Cheney, Ph.D., besides as my postdoctoral mentor Vann Bennett, Ph.D., at Duke. Nevertheless, its affiliation with disease eluded us till now.”
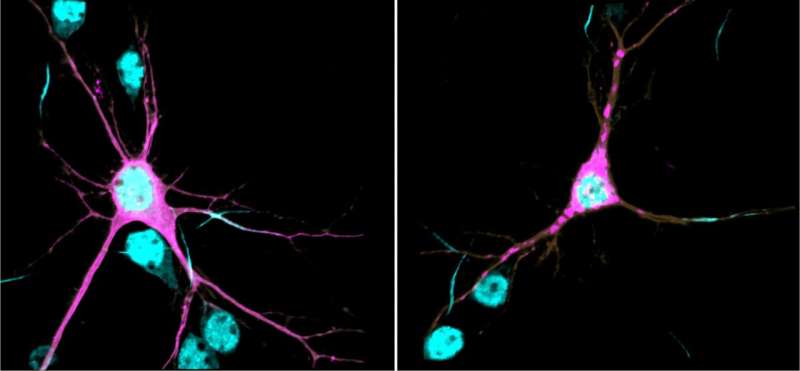
βII-spectrin is tightly related to the neuronal cytoskeleton—a posh community of filamentous proteins that spans the neuron and performs pivotal roles of their increase, form, and plasticity. βII-spectrin forms an prolonged scaffolding community that provides mechanical integrity to membranes and helps to orchestrate the true positioning of molecular complexes throughout the neuron. By blueprint of research revealed in PNAS in 2019, Lorenzo learned that βII-spectrin is crucial for traditional mind wiring in mice and for right transport of organelles and vesicles in axons—the lengthy extensions that elevate indicators from neurons to varied neurons. βII-spectrin is an major part of the direction of that enables traditional pattern, maintenance, and characteristic of neurons.
On this contemporary expect, Lorenzo’s research crew showed that, on the biochemical level, the genetic variants identified in sufferers are sufficient to cause protein aggregation, aberrant affiliation of βII-spectrin with the cytoskeleton, impair axonal organelle transport and increase, and switch the morphology of neurons. These deficiencies can permanently alter how neurons connect and be in contact with each and each varied, which is thought to make contributions to the etiology of neurodevelopmental disorders. The crew showed that reduction of βII-spectrin levels most productive in neurons disrupts structural connectivity between cortical areas in mutant mice, a deficit additionally noticed in mind MRIs of some sufferers.
In collaboration with Sheryl Moy, Ph.D., professor in the UNC Division of Psychiatry and director of the Mouse Behavioral Phenotyping (MBP) Core of the UNC IDDRC, the researchers learned that these mice rep developmental and behavioral deficits per displays noticed in humans.
“Now that we rep established the the true blueprint to place chance of pathogenicity to SPTBN1 variants and to search out out how they alter neurons, our instant function is to learn extra in regards to the affected molecular and mobile mechanisms and mind circuits, and settle into consideration programs for doubtless scientific interventions,” Lorenzo said.
To this stay, her crew will collaborate with Adriana Beltran, Ph.D., assistant professor in the UNC Division of Genetics and director of the UNC Human Pluripotent Cell Core, to exercise neurons differentiated from affected person-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. And the research crew will proceed to tap into molecular modeling predictions in collaboration with Brenda Temple, Ph.D., professor in the UNC Division of Biochemistry and Biophysics and director of the UNC Structural Bioinformatics Core, both co-authors on the Nature Genetics paper.
“As a normal science investigator, it be so relaxing to exercise info and instruments to provide answers to sufferers,” Lorenzo said. “I first witnessed this thrill of scientific discovery and collaborative work as a graduate pupil 15 years ago when our lab identified the genetic clarification for the first spectrinopathy affecting the anxious system, and it has been an excellent motivator since.”
That work used to be the invention of variants in a special spectrin gene because the clarification for spinocebellar ataxia kind 5 (SCA5), led by Laura Ranum, Ph.D., who on the time used to be on the University of Minnesota. In word up work, as part of that crew, Lorenzo contributed insights into the pathogenic mechanism of SCA5.
“With the exception of the instant relevance to affected sufferers, insights from our work on SPTNB1 syndrome will expose discoveries in varied advanced disorders with overlapping pathologies,” Lorenzo said. “It’s inspiring to be part of such crucial work with a crew of dedicated scientists and clinicians.”
More info:
Pathogenic SPTBN1 variants cause an autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental syndrome, Nature Genetics (2021). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-021-00886-z , www.nature.com/articles/s41588-021-00886-z
Citation:
Scientists gain genetic cause, underlying mechanisms of most original neurodevelopmental syndrome (2021, July 1)
retrieved 2 July 2021
from https://medicalxpress.com/info/2021-07-scientists-genetic-underlying-mechanisms-neurodevelopmental.html
This document is topic to copyright. Except for any wonderful dealing for the function of non-public expect or research, no
part may well be reproduced with out the written permission. The divulge material is provided for info purposes most productive.