
Seeing some cosmic X-ray emitters will be a matter of standpoint

It be laborious to neglect a flashlight beam pointed straight at you. But that beam considered from the aspect seems to be tremendously dimmer. The identical holds correct for some cosmic objects: Love a flashlight, they radiate primarily in a single direction, and they secret agent dramatically numerous looking out on whether or no longer the beam components faraway from Earth (and nearby dwelling telescopes) or straight at it.
New facts from NASA’s NuSTAR dwelling observatory means that this phenomenon holds correct for one of the principal most most famed X-ray emitters in the local universe: ultraluminous X-ray sources, or ULXs. Most cosmic objects, together with stars, radiate tiny X-ray light, seriously in the excessive-vitality vary seen by NuSTAR. ULXs, in distinction, are fancy X-ray lighthouses decreasing by the darkness. To be regarded as a ULX, a source must receive an X-ray luminosity that is ready a million times brighter than the total light output of the Solar (at all wavelengths). ULXs are so colorful, they’ll be seen hundreds of thousands of sunshine-years away, in other galaxies.
The new peep presentations that the article is named SS 433, situated in the Milky Formula galaxy and only about 20,000 light-years from Earth, is a ULX, although it seems to be to be about 1,000 times dimmer than the minimal threshold to be regarded as one.
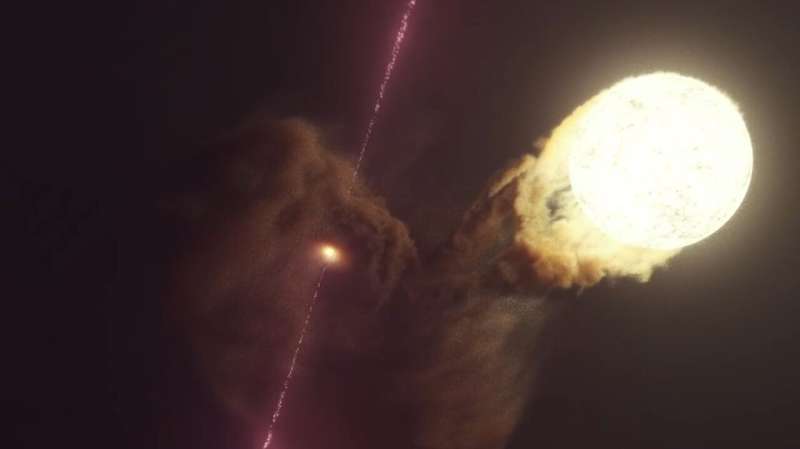
This faintness is a trick of standpoint, in preserving with the peep: The excessive-vitality X-rays from SS 433 are originally confined within two cones of gasoline extending outward from reverse aspects of the central object. These cones are a lot like a mirrored bowl that surrounds a flashlight bulb: They corral the X-ray light from SS 433 into a slim beam, except it escapes and is detected by NuSTAR. But since the cones are no longer pointing right now at Earth, NuSTAR cannot secret agent the article’s beefy brightness.
If a ULX rather end to Earth can veil its correct brightness attributable to the diagram it’s oriented, then there are probably more ULXs – seriously in other galaxies – disguised in a same ability. Which ability that the total ULX population ought to be a ways bigger than scientists at the moment search.
Cone of Darkness
About 500 ULXs were chanced on in other galaxies, and their distance from Earth ability or no longer it’s at all times nearly very no longer probably to expose what variety of object generates the X-ray emission. The X-rays probably come from a tall quantity of gasoline being heated to outrageous temperatures because it’s pulled in by the gravity of a extraordinarily dense object. That object will be either a neutron star (the remains of a collapsed star) or a tiny sad gap, one that isn’t any more than about 30 times the mass of our Solar. The gasoline forms a disk all over the article, fancy water circling a drain. Friction in the disk drives up the temperature, inflicting it to radiate, in most cases increasing so sizzling that the system erupts with X-rays. The faster the materials falls onto the central object, the brighter the X-rays.
Astronomers suspect that the article on the center of SS 433 is a sad gap about 10 times the mass of our Solar. What’s known for optimistic is that it’s cannibalizing a tall nearby star, its gravity siphoning away materials at a rapidly rate: In a single yr SS 433 steals the identical of about 30 times the mass of Earth from its neighbor, which makes it the greediest sad gap or neutron star known in our galaxy.
“It be been known for a extraordinarily very long time that this component is eating at a truly ideal rate,” mentioned Middleton. “Right here’s what objects ULXs rather than other objects, and or no longer it’s probably the root reason for the copious amounts of X-rays we secret agent from them.”
The article in SS 433 has eyes bigger than its belly: It be stealing more materials than it would spend. One of the most surplus materials gets blown off the disk and forms two hemispheres on reverse aspects of the disk. Within each and each one is a cone-fashioned void that opens up into dwelling. These are the cones that corral the excessive-vitality X-ray light into a beam. Somebody having a secret agent straight down one in every of the cones would secret agent an apparent ULX. Though serene only of gasoline, the cones are so thick and huge that they act fancy lead paneling in an X-ray screening room and block X-rays from passing by them out to the aspect.

Scientists receive suspected that some ULXs will be hidden from glimpse for this reason. SS 433 supplied a numerous likelihood to take a look at this conception because, fancy a top, it wobbles on its axis – a task astronomers call precession.
Extra normally than no longer, each and each of SS 433’s cones point nicely faraway from Earth. But attributable to the ability SS 433 precesses, one cone periodically tilts reasonably toward Earth, so scientists can secret agent somewhat little bit of the X-ray light popping out of the top of the cone. In the new peep, the scientists checked out how the X-rays seen by NuSTAR alternate as SS 433 moves. They demonstrate that if the cone persisted to tilt toward Earth so as that scientists may perhaps perchance presumably survey straight down it, they may perhaps secret agent ample X-ray light to formally call SS 433 a ULX.
Sad holes that feed at outrageous charges receive fashioned the historical previous of our universe. Supermassive sad holes, which shall be hundreds of thousands to billions of times the mass of the Solar, can profoundly receive an influence on their host galaxy when they feed. Early in the universe’s historical previous, these forms of large sad holes may perhaps perchance presumably receive fed as quickly as SS 433, releasing huge amounts of radiation that reshaped local environments. Outflows (fancy the cones in SS 433) redistributed matter that would by some means device stars and other objects.
But because these hasty engaging behemoths reside in extremely distant galaxies (the one on the center of the Milky Formula is not at the moment eating noteworthy), they remain no longer easy to peep. With SS 433, scientists receive chanced on a dinky instance of this task, noteworthy nearer to dwelling and a lot more uncomplicated to peep, and NuSTAR has supplied new insights into the process occurring there.
“When we launched NuSTAR, I notice no longer deem anyone expected that ULXs shall be such a rich predicament of research for us,” mentioned Fiona Harrison, major investigator for NuSTAR and a professor of physics at Caltech in Pasadena, California. “But NuSTAR is unfamiliar in that it would secret agent nearly your total vary of X-ray wavelengths emitted by these objects, and that affords us perception into the outrageous processes that ought to be driving them.”
NuSTAR is a Microscopic Explorer mission led by Caltech and managed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of Caltech, for the agency’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. NuSTAR used to be developed in partnership with the Danish Technical College and the Italian Residence Agency (ASI). The spacecraft used to be built by Orbital Sciences Company in Dulles, Virginia (now section of Northrop Grumman). NuSTAR’s mission operations heart is on the College of California, Berkeley, and the legit facts archive is at NASA’s Excessive Vitality Astrophysics Science Archive Analysis Heart. ASI affords the mission’s floor build and a specialize in archive.
Citation:
Seeing some cosmic X-ray emitters will be a matter of standpoint (2021, July 9)
retrieved 9 July 2021
from https://phys.org/news/2021-07-cosmic-x-ray-emitters-standpoint.html
This doc is discipline to copyright. Other than any lovely dealing for the motive of personal peep or research, no
section shall be reproduced with out the written permission. The relate material is supplied for facts applications only.