Susceptibility to severe COVID-19
The coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has resulted in unheard of adjustments in all draw of our lives and has positioned biomedical research at the forefront. One of the a spacious series of pressing questions surrounding severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections is identifying the determinants of the scientific spectrum, from people with asymptomatic illness to patients with severe COVID-19. As much as 40% of infections shall be asymptomatic, suggesting that a mountainous percentage of people shall be safe from illness (1). On the diversified close of the spectrum is severe illness, with an overall estimated fatality price near 1% (2). On pages 422 and 424 of this recount, Zhang et al. (3) and Bastard et al. (4), respectively, document analyses of >1600 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 from >15 nations to determine endogenous factors that resolve susceptibility to severe COVID-19.
Many research have confidence targeted on characterizing the heterogeneity of COVID-19 in the case of demographics, with certain proof of upper mortality in males and older people. The adaptive immune design, including each B and T cells, has now not too long ago been identified to play a considerable aim in providing preexisting immunity to SARS-CoV-2 (5–7). These research have confidence highlighted mechanisms that provide protection to in opposition to severe symptoms but have confidence now not published factors that predispose to mortality. Consequently, received immune responses to prior infections may perchance well also honest tale for a mountainous share of the variability in illness presentation, even supposing questions reside about additional determinants of illness, equivalent to preexisting comorbidities. Host genetic threat factors have confidence additionally emerged as a capacity motive at the encourage of scientific heterogeneity and additionally provide the likelihood of thought molecular pathways for tailored therapeutic intervention.
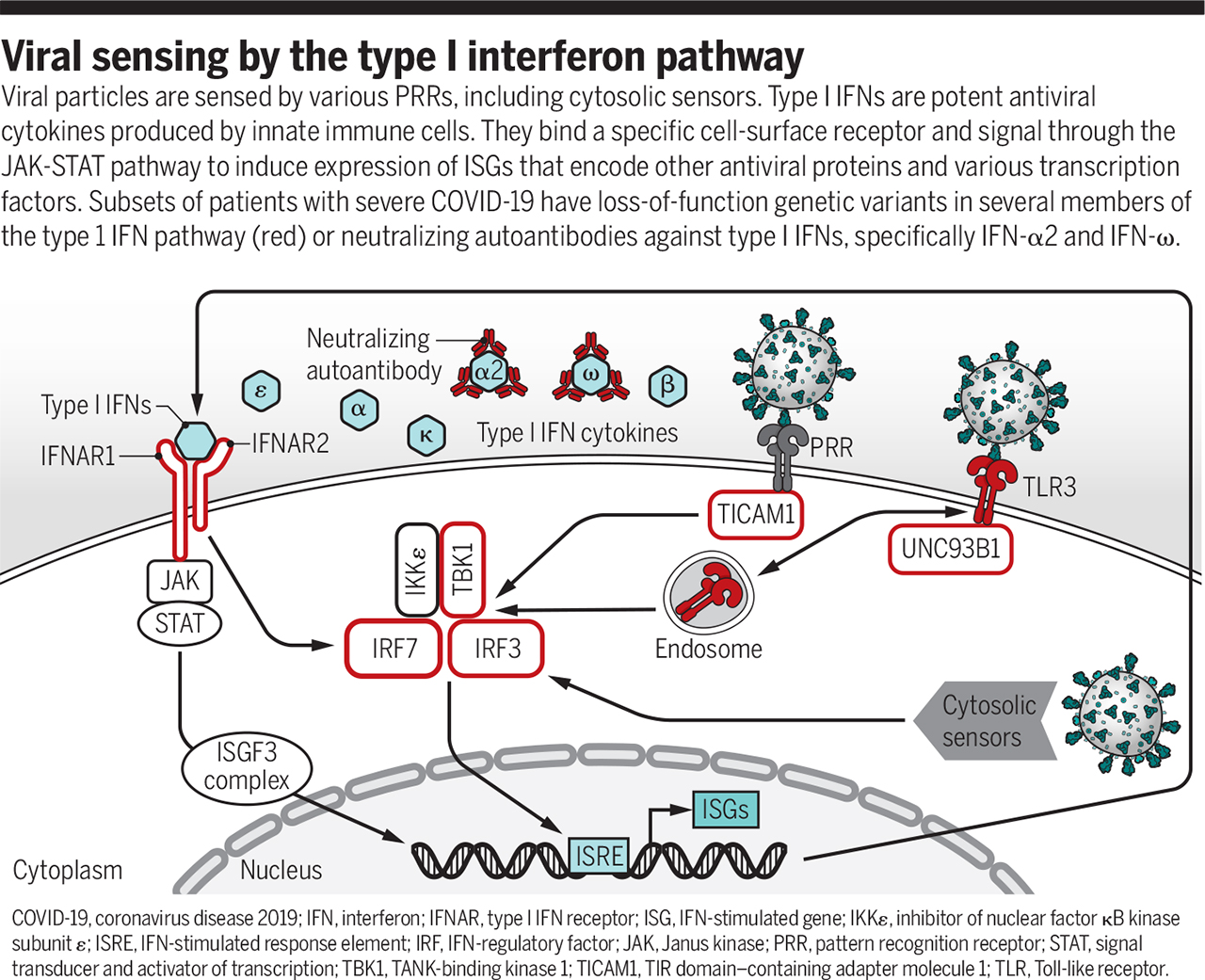
Minute-scale research have confidence implicated the kind I interferon (IFN) pathway as preserving in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 (8, 9). The model I IFN pathway plays a needed aim in mediating innate immune responses to viral infections. This family of cytokines is made out of 13 IFN-α subtypes, IFN-β, IFN-ω, IFN-κ, and IFN-ϵ, which all signal during the heterodimeric IFN I receptor, aloof of IFN-α/β receptor 1 (IFNAR1) and IFNAR2 (conception the resolve). In host cells, kind I IFNs are expressed at low amounts, poised to combat infections. Upon infection, they are impulsively produced by immune cells, equivalent to macrophages and dendritic cells, to limit the spread of pathogens. As neatly as, kind I IFNs induce the expression of plenty of hundred interferon stimulated genes that can additional limit pathogen replication through diverse mechanisms. Nonetheless, this in general preserving immune response can, when overactivated, consequence in autoimmune diseases. Conversely, loss-of-aim variants in genes encoding participants of the kind I IFN pathway consequence in severe immunodeficiencies characterised by existence-threatening viral infections. No longer too long ago, multiple research demonstrated that impaired kind 1 IFN responses shall be a trademark of severe COVID-19 (10–12), but why this pathway used to be suppressed remained unclear.
Zhang et al. document a mountainous genetic sequencing effort to clarify host threat factors to SARS-CoV-2 infection, inspecting exome or genome sequences from 659 patients with severe COVID-19 for rare pathogenic variants that may perchance well be associated to existence-threatening illness. The authors targeted on the kind I IFN pathway and analyzed 13 candidate genes which have confidence previously been linked with susceptibility to diversified viral infections. Deleterious variants that can impair gene aim were identified in 3.5% (23/659) of cases. Defects in kind I IFN gene expression and protein ranges were recapitulated in affected person cells harboring these variants, demonstrating recurrent diminished reveal of this pathway in severe illness. SARS-CoV-2 viral loads were higher in patients’ immune cells than in cells from healthy donors (who were infection-detrimental and seronegative for SARS-CoV-2), demonstrating an incapacity to neatly certain the virus. Collectively, these recordsdata implicate the importance of kind I IFN signaling in defense in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 infection and counsel that inherited deleterious variants demonstrate a subset of severe COVID-19.
Bastard et al. identified neutralizing autoantibodies as one other capacity motive for severe COVID-19. Autoantibodies acknowledge and thereby may perchance well also honest inhibit host proteins; they are a trademark of many autoimmune diseases and are regarded as a contributor to autoimmune pathophysiology. Neutralizing autoantibodies in opposition to kind I IFNs, largely IFN-α2 and IFN-ω, were stumbled on in as much as 13.7% (135/987) of patients with existence-threatening COVID-19 and were proven to neutralize activation of the pathway in vitro. In opposition to this, these autoantibodies were now not expose in 663 patients with asymptomatic or aloof COVID-19 and were excellent stumbled on in 0.33% (4/1227) healthy people now not exposed to SARS-CoV-2. The presence of neutralizing autoantibodies correlated with low serum IFN-α concentrations. Autoantibodies in opposition to kind I IFNs were additionally detected in blood samples of some patients bought sooner than SARS-CoV-2 infection, indicating that their manufacturing used to be now not triggered by the virus in those patients. Particularly, inactivating autoantibodies were identified basically in males (94%) and may perchance honest be a motive for the higher male-explicit illness mortalities.
Viral sensing by the type I interferon pathway
Viral particles are sensed by various PRRs, including cytosolic sensors. Type I IFNs are potent antiviral cytokines produced by innate immune cells. They bind a specific cell-surface receptor and signal through the JAK-STAT pathway to induce expression of ISGs that encode other antiviral proteins and various transcription factors. Subsets of patients with severe COVID-19 have loss-of-function genetic variants in several members of the type 1 IFN pathway (red) or neutralizing autoantibodies against type I IFNs, specifically IFN-α2 and IFN-ω.
GRAPHIC: A. KITTERMAN/SCIENCE
” data-hide-link-title=”0″ data-icon-position=”” href=”https://science.sciencemag.org/content/sci/370/6515/404/F1.large.jpg?width=800&height=600&carousel=1″ rel=”gallery-fragment-images-80926722″ title=”Viral sensing by the type I interferon pathway Viral particles are sensed by various PRRs, including cytosolic sensors. Type I IFNs are potent antiviral cytokines produced by innate immune cells. They bind a specific cell-surface receptor and signal through the JAK-STAT pathway to induce expression of ISGs that encode other antiviral proteins and various transcription factors. Subsets of patients with severe COVID-19 have loss-of-function genetic variants in several members of the type 1 IFN pathway (red) or neutralizing autoantibodies against type I IFNs, specifically IFN-α2 and IFN-ω.”>
Viral particles are sensed by diverse PRRs, including cytosolic sensors. Kind I IFNs are potent antiviral cytokines produced by innate immune cells. They bind a explicit cell-ground receptor and signal during the JAK-STAT pathway to induce expression of ISGs that encode diversified antiviral proteins and diverse transcription factors. Subsets of patients with severe COVID-19 have confidence loss-of-aim genetic variants in plenty of participants of the kind 1 IFN pathway (red) or neutralizing autoantibodies in opposition to kind I IFNs, particularly IFN-α2 and IFN-ω.
GRAPHIC: A. KITTERMAN/SCIENCE
By inspecting patients with severe COVID-19, these two research present proof that kind I IFNs are preserving in opposition to COVID-19 and that limiting this response through both gene mutations or autoantibodies results in severe illness. Autoantibodies in opposition to diversified proinflammatory cytokines—including kind II IFN (IFN-γ), interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-17A, and IL-17F—were reported in healthy people, patients with autoimmune diseases, and diversified opportunistic infections, even supposing the aim of these autoantibodies is now not continuously understood (13). Finding out the mechanisms of received immunodeficiency, more than seemingly associated to intercourse and growing older, may perchance well also encourage lower infectious illness morbidity and mortality.
Kind I IFN concentrations are tightly regulated, with plenty of rare monogenic autoinflammatory and immunodeficiency concerns attributable to both too much or too itsy-bitsy interferon manufacturing, respectively. Healthy people may perchance well also honest have confidence impaired kind I IFN responses owing to inherited loss-of-aim variants in genes encoding draw of the kind I IFN signaling cascade but reside clinically soundless until they encounter particular viruses or diversified microbes (8). This could well also be the case in severe COVID-19 patients who effect now not have confidence any prior history of scientific immunodeficiency.
Collectively, this work has most considerable therapeutic implications. Inhaled IFN-β and systemic antiviral therapies are being studied for COVID-19 in scientific trials (14). The research of Zhang et al. and Bastard et al. provide a capacity avenue for identifying people that are at threat of making existence-threatening SARS-CoV-2 infection, basically older males, by a presymptomatic screening of their blood samples for kind I IFN autoantibodies. Identification of such patients may perchance well also honest even be most considerable to keep some distance flung from capacity therapeutic utilize of their convalescent plasma (which is able to enjoy the cytokine-neutralizing autoantibodies) in ongoing scientific trials. Furthermore, recombinant IFN-β remedy may perchance well also honest now not earnings patients with neutralizing autoantibodies, whereas it would also honest work neatly for patients who carry loss-of-aim variants in kind I IFN genes, diversified than IFNAR1 or IFNAR2. In patients with autoantibodies, remedy with IFN-β shall be well-known for this reason of neutralizing autoantibodies in opposition to this cytokine appear to be much less general (4, 14). Findings from these research have confidence paved the model for precision remedy and custom-made remedy suggestions for COVID-19.
What remains unknown are the contributions of genetic variation commence air of the kind I IFN pathway for defense in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Furthermore, even supposing Zhang et al. targeted on rare germline variation, the roles of general single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and received somatic mutations in immune cells, which ranking with age, must aloof be investigated. Extra comprehensive genetic research may perchance well also additionally encourage present insights into the seemingly contribution of deleterious variation in the severe SARS-CoV-2–associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in formative years (15). Though the research of Zhang et al. and Bastard et al. illuminate the importance of pathways guilty for clearing infections, it is additionally that you presumably can imagine that proinflammatory variants may perchance well also honest both lower or strengthen illness severity. Why some patients who carry pathogenic variants in innate immune genes, equivalent to IFN-associated genes, reside asymptomatic until their exposure to a explicit pathogen is seemingly explained by the presence of diversified genetic editing alleles or epigenetic factors. Honest genomic research can resolution these forms of questions; alternatively, they must aloof be expanded to higher and extra diverse populations (past largely European descent) to meaningfully tackle the susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 and diversified doubtlessly pandemic viral infections. Somehow, through collaborative efforts, biomedical research must aloof and may perchance honest encourage combat spread of the virus by identifying people at threat with fleet diagnostic checks and facilitating current targeted therapies.
Acknowledgments: We thank D. Kastner and E. Beck for priceless discussions.