Uncover, snappy-charging lithium battery handles 5 times the contemporary
Conscientiously introducing contemporary supplies into the construct of at the moment’s lithium-ion batteries has the aptitude to drastically enhance their efficiency, and scientists secure lovely took affirm upon a promising possibility in carbon nanotubes. By incorporating these supplies into the electrode of a lithium metal battery, the researchers secure produced a model that is not simplest safer, nonetheless has the aptitude to worth up in lovely a allotment of the time of common devices.
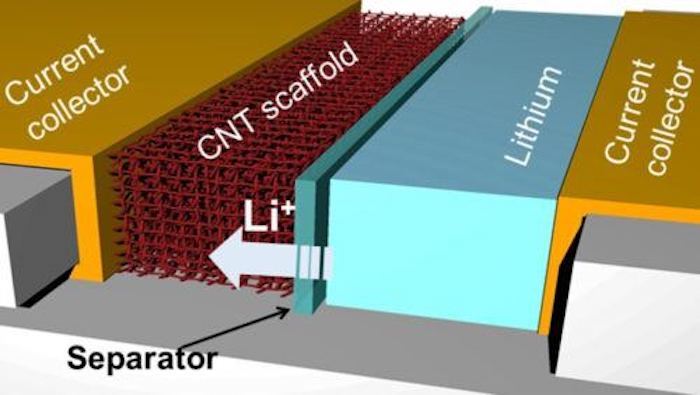
The analysis was as soon as conducted at Texas A&M University’s Faculty of Engineering and centers on a battery architecture with expansive skill. When a veteran lithium-ion battery fees and discharges, the lithium ions are ferried from side to side between the cathode and anode, the latter of which is on the final fabricated from a combine of graphite and copper.
But scientists watch a extensive alternative in the employ of pure lithium metal as a change, which affords very high vitality density and must get for batteries that worth powerful sooner and offer as powerful as 10 times the skill. One watch final Twelve months described a lithium anode as “severe to interrupt the vitality density bottleneck of contemporary li-ion chemistry.” Suffice to impart, there may perchance be basically huge ardour in making these items work.
Standing within the kind, nonetheless, are dangly tentacles called dendrites. These tree-like structures type up on the floor of the anode when lithium ions aren’t evenly deposited and as they grow, they’ll pierce key substances of the battery and reason it to rapid circuit and or snatch fire. If that doesn’t happen, they reason the battery to rapid lose its worth anyway.
So a extensive deal of research centers on the screech of dendrite formation, and the Texas A&M team believes it may perchance possibly presumably secure came upon a resolution in ultralight and extremely conductive carbon nanotubes. The construct mirrors that of every other experimental battery we regarded at in 2018 that uses a skinny carbon nanotube movie to successfully suffocate dendrites earlier than they properly obtain shape, nonetheless the researchers at the serve of the contemporary watch secure taken a pretty quite a lot of device.
For its anode, the team mild carbon nanotubes to type 3-dimensional porous scaffolds laced with molecules that reason the lithium ions to bind to its floor. It took some experimentation, nonetheless with the supreme focus of these binding molecules, the team came upon it had produced a battery anode that refrained from the buildup of dendrites on its floor.
Juran Noh
“But as soon as we had lovely the supreme amount of these binding molecules, we may perchance presumably ‘unzip’ the carbon nanotube scaffolds at lovely definite locations, allowing lithium ions to reach by and bind on to the total floor of the scaffolds as a alternative of secure on the outer floor of the anode and originate dendrites,” says watch creator Juran Noh.
One more end result of this even and safe distribution of the lithium ions was as soon as an elevated ability of the battery to fabricate bigger currents. So powerful so, the team reports that the anode can deal with currents 5 times that of common batteries. This raises the possibility of a battery that is not simplest safer and with bigger vitality density, nonetheless one who can also be charged in presumably a allotment of the time.
“Building lithium metal anodes which may perchance be safe and secure prolonged lifetimes has been a scientific bother for many a protracted time,” Noh acknowledged. “The anodes we secure developed overcome these hurdles and are a basically crucial, preliminary step towards industrial functions of lithium metal batteries.”
The analysis was as soon as printed within the journal Nano Letters.
Source: Texas A&M