
White American citizens pay less consideration to Sad peers, says a contemporary ogle
In a ogle of additional than 2,500 members published this day in Science Advances, Sheen S. Levine, adjunct study student in the sociology division at Columbia University and professor of management at University of Texas, Dallas; Charlotte Reypens, postdoctoral fellow at the University of Warwick; and David Stark, professor of sociology at Columbia University, scream that white American citizens pay less consideration to Sad peers.
In earlier study, Stark and Levine showed that an ethnically diverse group of traders became once extra more seemingly to calculate upright prices for shares, making the case that a various personnel is a wiser personnel.
Years after this study became once published, Levine observed that folks in the industry community “looked earnestly attracted to promoting diversity.” Nonetheless, in his conversations with Sad of us in the personnel, he realized that they “felt welcome at the door,” but their ideas and accomplishments had been veritably overlooked. To take a look at this lack of consideration, Levine and Stark developed a model to measure of us’s willingness to study from others.
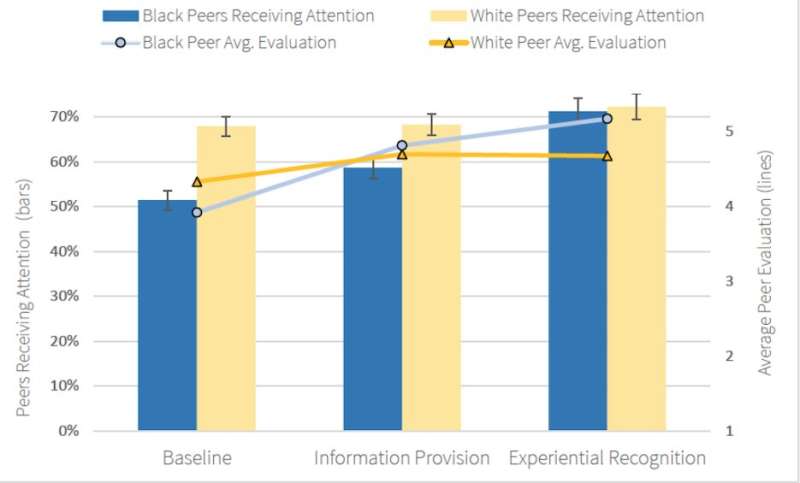
In the contemporary ogle, the researchers gave ogle members, a group of gender-balanced white American citizens, a puzzle with the offer of a bonus if they answered precisely. Every participant became once in a problem to ogle how their peers, both white or Sad, solved the same puzzle, and must peaceable net whether or no longer to study from them. The splendid technique to get the curious resolution became once to make utilize of input from the peers, permitting the researchers to take a look at whether or no longer members had been extra more seemingly to push aside files from one racial group.
Genuinely, the researchers chanced on that members had been 33 p.c extra more seemingly to hear to and study from white peers when when put next with Sad ones; besides they rated Sad peers as less expert than white peers.
“Leaders of organizations must peaceable hear to these findings in repeat to adore racial disparity in patterns of consideration,” Stark mentioned. “It be in all individuals’s hobby that we procure ways to unravel this ‘racial consideration deficit’.”
However the researchers also chanced on that the bias is more seemingly to be reversed.
When they gave ogle members critical aspects about their peers’ achievements—things like past awards and degrees—members rated the Sad peers curious as competent as the white ones, but had been peaceable reluctant to study from them. What made the biggest distinction in the puzzle project, though, became once giving members a risk to work side-by-side with peers. When members seen how competent their Sad peers had been, they adopted their lead in a 2nd round of the sport, the ogle chanced on. The bias disappeared.
“Range promotes enhanced levels of performance,” mentioned theoretical physicist Sylvester James Gates, Jr., president of the American Bodily Society, and a recipient of the National Medal of Science. “Nonetheless, diversity handiest works if there could be a full of life exchange of ideas. In the paper, Racial Consideration Deficit, Levine, Reypens, and Stark illustrate how this conversation is no longer occurring between white and Sad colleagues to the detriment of the convey of job atmosphere.”
“The authors of this paper absorb made a vital contribution to the social sciences by demonstrating behaviorally how and how noteworthy white of us ignore, fail to see, and underestimate Sad of us,” mentioned Michèle Lamont, professor of sociology and African and African American Be taught at Harvard University and frail president of the American Sociological Affiliation. “Their ogle of ‘recognition gaps’ explores contemporary paths in our conception of how inequality operates, which has every little thing to enact with how day after day judgements of price are omnipresent and construct racism so tense to strive against.”
Extra files:
Sheen S. Levine et al, Racial consideration deficit, Science Advances (2021). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg9508
Citation:
White American citizens pay less consideration to Sad peers, says a contemporary ogle (2021, September 17)
retrieved 18 September 2021
from https://phys.org/info/2021-09-white-american citizens-consideration-gloomy-peers.html
This doc is field to copyright. Other than any curious dealing for the reason of private ogle or study, no
phase could be reproduced without the written permission. The protest material is provided for files functions handiest.